NASA Is Building The Next Mars Rover In Mixed Reality and It’s Absolutely Jaw-dropping!
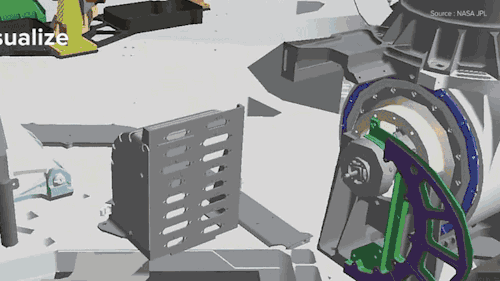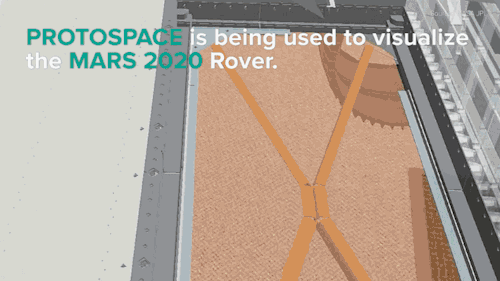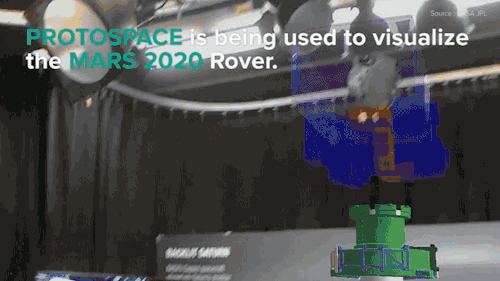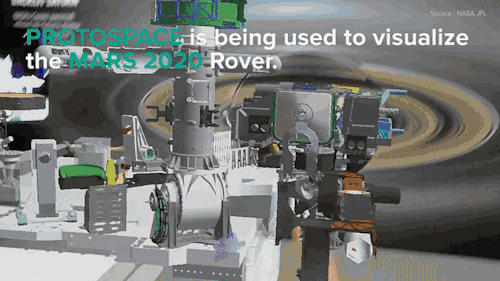
NASA is building the next Mars rover in mixed reality and It’s absolutely jaw-dropping!
More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others
this website pisses me off, everyones always like “space is so cool!” not its not, space is bullshit and i hate everything about it, i genuinely just saw the phrase “a black hole with a mass two billion times the mass of the sun” im so pissed off, shut the fuck up, dont patronise me scientists you know i dont know what the fuck that means, my sad little brain cant comprehend the mass of one sun let alone two fucking billion, i cant even count past 10 without getting confused and youre out here talking about the mass of two billion fucking suns, shut the hell up. and dont even get me started about black holes or the expansion of the universe because thats another two seperate rants entierly. oh and apparently theres a planet made of ice except the ice is also on fire??? yeah sure fucking thing, scientists. and this is just the shit i know about. i purposely dont research space because it pisses me off so much, god knows what other fucking bullshit exists out there that ive yet to read a fucking wikipedia article about. i dont think space is real, literally everything about space is so fucking fake, this is just some elaborate fucking practicle joke. two billion times the mass of the sun, fuck you
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn about the science of photonics to create space communications, get updates on Juno, mining data from Voyager for new discoveries and more.

1. Carried on a Beam of Light
One of our major priorities is to make space communications more efficient. While our communications systems have matured over the decades, they still use the same radio-frequency system developed in the earliest days of the agency. After more than 50 years, we’re investing in new ways to increase data rates while also finding more efficient communications systems. Photonics–generating, detecting and manipulating particles of light–may provide the solution.
+ See how it works

2. It’s No Joke: Two New Moons for the Seventh Planet
Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by Uranus 30 years ago, but researchers are still making discoveries using the data it gathered. A new study led by University of Idaho researchers suggests there could be two tiny, previously undiscovered moonlets orbiting near two of the planet’s rings.
+ Find out how they were discovered

3. Vortex of Mystery
As southern winter solstice approaches in the Saturn system, our Cassini spacecraft has revealed dramatic seasonal changes in the atmospheric temperature and composition of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. Winter is taking a grip on Titan’s southern hemisphere, and a strong, whirling vortex has intensified in the upper atmosphere over the south pole.
+See more

4. The Spiders of Mars
Ten thousand volunteers viewing images of Martian south polar regions have helped identify targets for closer inspection, yielding new insights about seasonal slabs of frozen carbon dioxide and erosional features known as “spiders.” From the comfort of home, the volunteers have been exploring the surface of Mars by reviewing images from the Context Camera on our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and identifying certain types of seasonal terrains near Mars’ south pole.
+ Learn more and see how you can join in

7. Better Safe than Sorry
Juno entered safe mode last week and early indications are a software performance monitor induced a reboot of the spacecraft’s onboard computer. In this case, the safe mode turned off instruments and a few non-critical spacecraft components, and it confirmed the spacecraft was pointed toward the sun to ensure the solar arrays received power.The spacecraft acted as expected during the transition into safe mode, restarted successfully and is healthy. High-rate data has been restored, and the spacecraft is conducting flight software diagnostics. Meanwhile, the Juno science team continues to analyze returns from the first close Jupiter flyby on Aug. 27. Revelations so far include that Jupiter’s magnetic fields and aurora are bigger and more powerful than thought. Scientists have also had their first glimpse below the planet’s swirling cloud deck. The next close flyby is scheduled on Dec. 11, with all science instruments on.
+ Get the details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
ooooo how awesome!

Prototype of Space Station’s Advanced Plant Habitat via NASA http://ift.tt/2fremIw
Spacewalk Friday: Installing a New "Parking Spot" on Station
This Friday, Aug. 19, two U.S. astronauts will install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.

Commercial crew flights from Florida’s Space Coast to the International Space Station will restore America’s human spaceflight launch capability and increase the time U.S. crews can dedicate to scientific research.

The adapter being installed (imaged below) was launched on a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft and arrived on orbit July 20. NASA astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will perform the spacewalk to install the equipment this Friday, Aug. 19. This will be the fourth spacewalk in Williams’ career and the first for Rubins.

Four previous spacewalks…like the one below…helped set the stage for installation of this docking adapter. During those previous spacewalks, other crew members laid hundreds of feet of power and data cables outside the space station.

On Wednesday, the robotics team using the Canadarm2 and its attached “Dextre” manipulator, will reach into the SpaceX Dragon trunk and pull out the docking adapter and position it for Friday’s spacewalk activities.

The morning of the spacewalk, while the astronauts are getting suited up, the robotic arm will position the docking adaptor near the port so that it will be ready for installation.

The two astronauts will venture outside the space station to install the first International Docking Adapter (IDA). This new adapter port will provide a parking space for U.S. Commercial Crew vehicles.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Friday, Aug. 19; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
OMG congrats! How exciting! I can't wait to see your photos! I've tried with my SLR and uh it has NOT gone well lol.
I did it.
After a year of talking I finally bit the bullet and got a DSLR camera (Nikon D5300) for astrophotography. Will be using it at the observatory (16″ Cassegrain) as well as during hikes for sweeping vistas under the Milky Way. Very excited to explore astrophotography as a hobby and can’t wait to start uploading pictures
Getting to Mars: 4 Things We’re Doing Now
We’re working hard to send humans to Mars in the 2030s. Here are just a few of the things we’re doing now that are helping us prepare for the journey:
1. Research on the International Space Station

The International Space Station is the only microgravity platform for the long-term testing of new life support and crew health systems, advanced habitat modules and other technologies needed to decrease reliance on Earth.

When future explorers travel to the Red Planet, they will need to be able to grow plants for food, atmosphere recycling and physiological benefits. The Veggie experiment on space station is validating this technology right now! Astronauts have grown lettuce and Zinnia flowers in space so far.

The space station is also a perfect place to study the impacts of microgravity on the human body. One of the biggest hurdles of getting to Mars in ensuring that humans are “go” for a long-duration mission. Making sure that crew members will maintain their health and full capabilities for the duration of a Mars mission and after their return to Earth is extremely important.

Scientists have solid data about how bodies respond to living in microgravity for six months, but significant data beyond that timeframe had not been collected…until now! Former astronaut Scott Kelly recently completed his Year in Space mission, where he spent a year aboard the space station to learn the impacts of microgravity on the human body.
A mission to Mars will likely last about three years, about half the time coming and going to Mars and about half the time on the Red Planet. We need to understand how human systems like vision and bone health are affected and what countermeasures can be taken to reduce or mitigate risks to crew members.
2. Utilizing Rovers & Tech to Gather Data

Through our robotic missions, we have already been on and around Mars for 40 years! Before we send humans to the Red Planet, it’s important that we have a thorough understanding of the Martian environment. Our landers and rovers are paving the way for human exploration. For example, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has helped us map the surface of Mars, which will be critical in selecting a future human landing site on the planet.

Our Mars 2020 rover will look for signs of past life, collect samples for possible future return to Earth and demonstrate technology for future human exploration of the Red Planet. These include testing a method for producing oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, identifying other resources (such as subsurface water), improving landing techniques and characterizing weather, dust and other potential environmental conditions that could affect future astronauts living and working on Mars.

We’re also developing a first-ever robotic mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid, collect a multi-ton boulder from its surface and redirect it into a stable orbit around the moon. Once it’s there, astronauts will explore it and return with samples in the 2020s. This Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM) is part of our plan to advance new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
3. Building the Ride
Okay, so we’ve talked about how we’re preparing for a journey to Mars…but what about the ride? Our Space Launch System, or SLS, is an advanced launch vehicle that will help us explore beyond Earth’s orbit into deep space. SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket and will launch astronauts in our Orion spacecraft on missions to an asteroid and eventually to Mars.

In the rocket’s initial configuration it will be able to take 154,000 pounds of payload to space, which is equivalent to 12 fully grown elephants! It will be taller than the Statue of Liberty and it’s liftoff weight will be comparable to 8 fully-loaded 747 jets. At liftoff, it will have 8.8 million pounds of thrust, which is more than 31 times the total thrust of a 747 jet. One more fun fact for you…it will produce horsepower equivalent to 160,000 Corvette engines!

Sitting atop the SLS rocket will be our Orion spacecraft. Orion will be the safest most advanced spacecraft ever built, and will be flexible and capable enough to carry humans to a variety of destinations. Orion will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
4. Making it Sustainable
When humans get to Mars, where will they live? Where will they work? These are questions we’ve already thought about and are working toward solving. Six partners were recently selected to develop ground prototypes and/or conduct concept studies for deep space habitats.

These NextSTEP habitats will focus on creating prototypes of deep space habitats where humans can live and work independently for months or years at a time, without cargo supply deliveries from Earth.

Another way that we are studying habitats for space is on the space station. In June, the first human-rated expandable module deployed in space was used. The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is a technology demonstration to investigate the potential challenges and benefits of expandable habitats for deep space exploration and commercial low-Earth orbit applications.
Our journey to Mars requires preparation and research in many areas. The powerful new Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft will travel into deep space, building on our decades of robotic Mars explorations, lessons learned on the International Space Station and groundbreaking new technologies.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
There’s even more to Mars.

1. Batten Down the Hatches
Good news for future astronauts: scientists are closer to being able to predict when global dust storms will strike the Red Planet. The winds there don’t carry nearly the same force that was shown in the movie “The Martian,” but the dust lofted by storms can still wreak havoc on people and machines, as well as reduce available solar energy. Recent studies indicate a big storm may be brewing during the next few months.
+ Get the full forecast

2. Where No Rover Has Gone Before
Our Opportunity Mars rover will drive down an ancient gully that may have been carved by liquid water. Several spacecraft at Mars have observed such channels from a distance, but this will be the first up-close exploration. Opportunity will also, for the first time, enter the interior of Endeavour Crater, where it has worked for the last five years. All this is part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004. Opportunity landed on Mars in January of that year, on a mission planned to last 90 Martian days (92.4 Earth days). More than 12 Earth years later, it’s still rolling.
+ Follow along + See other recent pictures from Endeavour Crater

3. An Uphill Climb
Opportunity isn’t the only NASA Mars rover getting a mission extension. On the other side of the planet, the Curiosity rover is driving and collecting samples amid some of the most scenic landscapes ever visited on Mars. Curiosity’s two-year mission extension also began Oct. 1. It’s driving toward uphill destinations, including a ridge capped with material rich in the iron-oxide mineral hematite, about a mile-and-a-half (two-and-a-half kilometers) ahead. Beyond that, there’s an exposure of clay-rich bedrock. These are key exploration sites on lower Mount Sharp, which is a layered, Mount-Rainier-size mound where Curiosity is investigating evidence of ancient, water-rich environments that contrast with the harsh, dry conditions on the surface of Mars today.
+ Learn more

4. Keep a Sharp Lookout
Meanwhile, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter continues its watch on the Red Planet from above. The mission team has just released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
+ Take a look

5. 20/20 Vision for the 2020 Rover
In the year 2020, Opportunity and Curiosity will be joined by a new mobile laboratory on Mars. In the past week, we tested new “eyes” for that mission. The Mars 2020 rover’s Lander Vision System helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. The system can direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area.
+ Get details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


MERRY CHRISTMAS AND HAPPY HOLIDAYS FROM ME AND THE BOYS!

Ice is no match for CSU-developed coating
Anyone who’s ever chipped ice off a windshield or nervously watched a plane get de-iced, take note: Colorado State University researchers have invented an ice-repellent coating that out-performs today’s best de-icing products.
Researchers led by Arun Kota, assistant professor of mechanical engineering and biomedical engineering, have created an environmentally friendly, inexpensive, long-lasting coating that could keep everything from cars and ships to planes and power lines ice-free.
Their innovation, described in the Journal of Materials Chemistry, is a gel-based, soft coating made out of PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane), a silicone polymer gel with already widespread industrial use. Their experiments were supported by careful analysis of ice adhesion mechanics.
The performance measure of de-icing coatings is called ice adhesion strength - the shear stress necessary to remove ice from a surface - and is measured in kilopascals (kPa). Kota’s group demonstrated ice adhesion strength for their coating of about 5 kPa. By contrast, soft coatings available on the market have ice adhesion strength of about 40 kPa (lower is better). Other types of de-icing coatings made of rigid materials like Teflon typically perform at around 100 kPa.
Read more.
-
 maevetheeuropan reblogged this · 8 years ago
maevetheeuropan reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 claraxbarton liked this · 8 years ago
claraxbarton liked this · 8 years ago -
 maevemauvaise reblogged this · 8 years ago
maevemauvaise reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 maevemauvaise liked this · 8 years ago
maevemauvaise liked this · 8 years ago -
 briandavidphillips reblogged this · 8 years ago
briandavidphillips reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 doodlebug1292-blog liked this · 8 years ago
doodlebug1292-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 rjbailey reblogged this · 8 years ago
rjbailey reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rifter1973 reblogged this · 8 years ago
rifter1973 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rifter1973 liked this · 8 years ago
rifter1973 liked this · 8 years ago -
 rjbailey liked this · 8 years ago
rjbailey liked this · 8 years ago -
 cell-phone-hippie liked this · 8 years ago
cell-phone-hippie liked this · 8 years ago -
 d1athome liked this · 8 years ago
d1athome liked this · 8 years ago -
 mianjunaid30-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
mianjunaid30-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 deathtofrance liked this · 8 years ago
deathtofrance liked this · 8 years ago -
 techfoxus-blog liked this · 8 years ago
techfoxus-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 kimpimmel reblogged this · 8 years ago
kimpimmel reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nikolasfuturist reblogged this · 8 years ago
nikolasfuturist reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ericjr30-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
ericjr30-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 ericjr30-blog liked this · 8 years ago
ericjr30-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sallydoodle liked this · 8 years ago
sallydoodle liked this · 8 years ago -
 bootyp0pjohnson reblogged this · 8 years ago
bootyp0pjohnson reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 itechuoutguy-blog liked this · 8 years ago
itechuoutguy-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 the-auto-pilot-riot reblogged this · 8 years ago
the-auto-pilot-riot reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 a-mac-user reblogged this · 8 years ago
a-mac-user reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 engadget reblogged this · 8 years ago
engadget reblogged this · 8 years ago
