That’s It. That’s The Best Tweet. We Can All Go Home Now.

That’s it. That’s the best tweet. We can all go home now.
More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others

A 25-year-old student has just come up with a way to fight drug-resistant superbugs without antibiotics.
The new approach has so far only been tested in the lab and on mice, but it could offer a potential solution to antibiotic resistance, which is now getting so bad that the United Nations recently declared it a “fundamental threat” to global health.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria already kill around 700,000 people each year, but a recent study suggests that number could rise to around 10 million by 2050.
In addition to common hospital superbug, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), scientists are now also concerned that gonorrhoea is about tobecome resistant to all remaining drugs.
But Shu Lam, a 25-year-old PhD student at the University of Melbourne in Australia, has developed a star-shaped polymer that can kill six different superbug strains without antibiotics, simply by ripping apart their cell walls.
“We’ve discovered that [the polymers] actually target the bacteria and kill it in multiple ways,” Lam told Nicola Smith from The Telegraph. “One method is by physically disrupting or breaking apart the cell wall of the bacteria. This creates a lot of stress on the bacteria and causes it to start killing itself.”
The research has been published in Nature Microbiology, and according to Smith, it’s already being hailed by scientists in the field as “a breakthrough that could change the face of modern medicine”.
Before we get too carried away, it’s still very early days. So far, Lam has only tested her star-shaped polymers on six strains of drug-resistant bacteria in the lab, and on one superbug in live mice.
But in all experiments, they’ve been able to kill their targeted bacteria - and generation after generation don’t seem to develop resistance to the polymers.
Continue Reading.
NASA Technology in Your Life
How does NASA technology benefit life on Earth? It probably has an impact in more ways than you think! Since 1976, our Spinoff program has profiled nearly 2,000 space technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services. In celebration of Spinoff’s 40th year of publication, we’ve assembled a collection of spinoffs that have had the greatest impact on Earth.
Take a look and see how many you utilize on a regular basis:
Digital Image Sensors

Whether you take pictures and videos with a DSLR camera or a cell phone, or even capture action on the go with a device like a GoPro Hero, you’re using NASA technology. The CMOS active pixel sensor in most digital image- capturing devices was invented when we needed to miniaturize cameras for interplanetary missions. This technology is also widely used in medical imaging and dental X-ray devices.
Enriched Baby Formula

While developing life support for Mars missions, NASA-funded researchers discovered a natural source for an omega-3 fatty acid previously found primarily in breast milk that plays a key role in infant development. The ingredient has since been added to more than 90% of infant formula on the market and is helping babies worldwide develop healthy brains, eyes and hearts.
NASTRAN Software

NASTRAN is a software developed by our engineers that performs structural analysis in the 1960s. Still popular today, it’s been used to help design everything from airplanes and cars to nuclear reactors and even Disney’s Space Mountain roller coaster.
Food Safety Standards

Looking to ensure the absolute safety of prepackaged foods for spaceflight, we partnered with the Pillsbury Company to create a new, systematic approach to quality control. Now known as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), the method has become an industry standard that benefits consumers worldwide by keeping food free from a wide range of potential chemical, physical and biological hazards.
Neutral Body Posture Specifications

What form does the human body naturally assume when all physical influences, including the pull of gravity, stop affecting it? We conducted research to find out using Skylab, America’s first space station, and later published specifications for what it called neutral body posture. The study has informed seat designs in everything from airplanes and office chairs to several models of Nissan automobiles.
Advanced Water Filtration

We recently discovered unexpected sources of water on the moon and Mars, but even so, space remains a desert for human explorers, and every drop must be recycled and reused. A nano filter devised to purify water in orbit is currently at work on Earth, in devices that supply water to remote villages as well as in a water bottle that lets hikers and adventurers stay hydrated using streams and lakes.
Swimsuit Designs

Wind-tunnel testing at our Langley Research Center played a key role in the development of Speedo’s LZR Racer swimsuit, proving which materials and seams best reduced drag as a swimmer cuts through the water. The swimsuit made a splash during its Olympic debut in 2008, as nearly every medal winner and world-record breaker wore the suit.
Air Purifier

When plants grow, they release a gas called ethylene that accelerates decay, hastening the wilting of flowers and the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Air circulation on Earth keeps the fumes from building up, but in the hermetically sealed environment of a spacecraft, ethylene poses a real challenge to the would-be space farmers. We funded the development of an ethylene scrubber for the International Space Station that has subsequently proved capable of purifying air on Earth from all kinds of pathogens and particulates. Grocery stores use it to keep produce fresh longer. It’s also been marketed for home use and has even been embraced by winemakers, who employ the scrubber to keep aging wine in barrels free from mold, mildew and musty odors.
Scratch-Resistant, UV-Reflective Lenses

Some of the earliest research into effective scratch-resistant coatings for prescription and sunglass lenses drew from work done at Ames Research Center on coatings for astronaut helmet visors and plastic membranes used in water purification systems. In the 1980s, we developed sunlight-filtering lenses to provide eye protection and enhance colors, and these lenses have found their way into sunglasses, ski goggles and safety masks for welders.
Dustbuster

An Apollo-era partnership with Black & Decker to build battery-operated tools for moon exploration and sample collection led to the development of a line of consumer, medical and industrial hand-held cordless tools. This includes the popular Dustbuster cordless vacuum.
To see even more of our spinoff technologies, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/offices/oct/40-years-of-nasa-spinoff
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
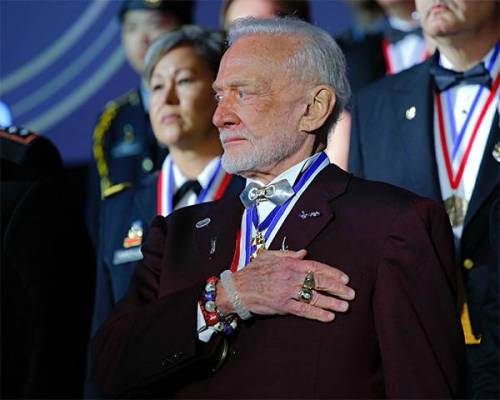





2002: Buzz Aldrin punches conspiracy theorist, Bart Sibrel in the face for calling him a coward, a liar, and a thief for faking the moon landing.








The Solar System!

bonus Pluto!
Living and Working Aboard Station
Join us on Facebook Live for a conversation with astronaut Kate Rubins and the director of the National Institutes for Health on Tuesday, October 18 at 11:15 a.m. ET.
Astronaut Kate Rubins has conducted out of this world research aboard Earth’s only orbiting laboratory. During her time aboard the International Space Station, she became the first person to sequence DNA in space. On Tuesday, she’ll be live on Facebook with National Institute of Health director Francis Collins, who led the effort to map the human genome. You can submit questions for Kate using the hashtag #SpaceChat on Twitter, or during the live event. Here’s a primer on the science this PhD astronaut has been conducting to help inspire your questions:

Kate has a background in genomics (a branch of molecular genetics that deals with the study of genomes,specifically the identification and sequencing of their constituent genes and the application of this knowledge in medicine, pharmacy,agriculture, and other fields). When she began her tenure on the station, zero base pairs of DNA had been sequenced in space. Within just a few weeks, she and the Biomolecule Sequencer team had sequenced their one billionth base of DNA aboard the orbital platform.
“I [have a] genomics background, [so] I get really excited about that kind of stuff,” Rubins said in a downlink shortly after reaching the one billion base pairs sequenced goal.
Learn more about this achievement:
+First DNA Sequencing in Space a Game Changer
+Science in Short: One Billion Base Pairs Sequenced
Why is DNA Sequencing in Space a Big Deal?
A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
+Why Sequencing DNA in Space is a Big Deal
https://youtu.be/1N0qm8HcFRI
Miss the Reddit AMA on the subject? Here’s a transcript:
+NASA AMA: We just sequenced DNA in space for the first time. Ask us anything!
NASA and Its Partnerships

We’re not doing this alone. Just like the DNA sequencing was a collaborative project with industry, so is the Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces investigation. In this experiment aboard the station, astronauts will study how certain materials used in the pharmaceutical industry dissolve in water while in microgravity. Results from this investigation could help improve the design of tablets that dissolve in the body to deliver drugs, thereby improving drug design for medicines used in space and on Earth. Learn more about what we and our partners are doing:
+Eli Lilly Hard to Wet Surfaces – been happening the last week and a half or so
Researchers to Test How Solids Dissolve in Space to Design Better Tablets and Pills on Earth
With our colleagues at the Stanford University School of Medicine, we’re also investigating the effects of spaceflight on stem cell-derived heart cells, specifically how heart muscle tissue, contracts, grows and changes in microgravity and how those changes vary between subjects. Understanding how heart muscle cells change in space improves efforts for studying disease, screening drugs and conducting cell replacement therapy for future space missions. Learn more:
+Heart Cells
+Weekly Recap From the Expedition Lead Scientist for Aug. 18, 2016
It’s Not Just Medicine

Kate and her crew mates have also worked on the combustion experiments.
Kate has also worked on the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), an experimental expandable capsule that docks with the station. As we work on our Journey to Mars, future space habitats are a necessity. BEAM, designed for Mars or other destinations, is a lightweight and relatively simple to construct solution. Kate has recently examined BEAM, currently attached to the station, to take measurements and install sensors.

Kate recently performed a harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment, by removing seed cassettes and stowing them in cold stowage.

The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions. Read more about the experiment:
+Plant RNA Harvest
NASA Astronaut Kate Rubins is participating in several investigations examining changes in her body as a result of living in space. Some of these changes are similar to issues experienced by our elderly on Earth; for example, bone loss (osteoporosis), cardiovascular deconditioning, immune dysfunction, and muscle atrophy. Understanding these changes and how to prevent them in astronauts off the Earth may help improve health for all of us on the Earth. In additional, the crew aboard station is also working on more generalized studies of aging.
+ Study of the effects of aging on C. elegans, a model organism for a range of biological studies.

From astrophysicist Katie Mack. I’m 100% behind her.
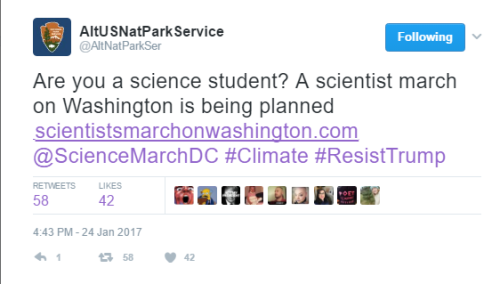
GUYS https://twitter.com/AltNatParkSer/status/824054953404669953 http://www.scientistsmarchonwashington.com/ THE NATIONAL PARK SERVICE IS IN OPEN REBELLION
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
There’s even more to Mars.

1. Batten Down the Hatches
Good news for future astronauts: scientists are closer to being able to predict when global dust storms will strike the Red Planet. The winds there don’t carry nearly the same force that was shown in the movie “The Martian,” but the dust lofted by storms can still wreak havoc on people and machines, as well as reduce available solar energy. Recent studies indicate a big storm may be brewing during the next few months.
+ Get the full forecast

2. Where No Rover Has Gone Before
Our Opportunity Mars rover will drive down an ancient gully that may have been carved by liquid water. Several spacecraft at Mars have observed such channels from a distance, but this will be the first up-close exploration. Opportunity will also, for the first time, enter the interior of Endeavour Crater, where it has worked for the last five years. All this is part of a two-year extended mission that began Oct. 1, the latest in a series of extensions going back to the end of Opportunity’s prime mission in April 2004. Opportunity landed on Mars in January of that year, on a mission planned to last 90 Martian days (92.4 Earth days). More than 12 Earth years later, it’s still rolling.
+ Follow along + See other recent pictures from Endeavour Crater

3. An Uphill Climb
Opportunity isn’t the only NASA Mars rover getting a mission extension. On the other side of the planet, the Curiosity rover is driving and collecting samples amid some of the most scenic landscapes ever visited on Mars. Curiosity’s two-year mission extension also began Oct. 1. It’s driving toward uphill destinations, including a ridge capped with material rich in the iron-oxide mineral hematite, about a mile-and-a-half (two-and-a-half kilometers) ahead. Beyond that, there’s an exposure of clay-rich bedrock. These are key exploration sites on lower Mount Sharp, which is a layered, Mount-Rainier-size mound where Curiosity is investigating evidence of ancient, water-rich environments that contrast with the harsh, dry conditions on the surface of Mars today.
+ Learn more

4. Keep a Sharp Lookout
Meanwhile, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter continues its watch on the Red Planet from above. The mission team has just released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
+ Take a look

5. 20/20 Vision for the 2020 Rover
In the year 2020, Opportunity and Curiosity will be joined by a new mobile laboratory on Mars. In the past week, we tested new “eyes” for that mission. The Mars 2020 rover’s Lander Vision System helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. The system can direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area.
+ Get details
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 puppybotz liked this · 3 months ago
puppybotz liked this · 3 months ago -
 certified-bi reblogged this · 4 months ago
certified-bi reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 anotherwordortwo reblogged this · 4 months ago
anotherwordortwo reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 daiquirishortcake reblogged this · 4 months ago
daiquirishortcake reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 daiquirishortcake liked this · 4 months ago
daiquirishortcake liked this · 4 months ago -
 wernher-von-brawny reblogged this · 4 months ago
wernher-von-brawny reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 yocoolguy liked this · 4 months ago
yocoolguy liked this · 4 months ago -
 goldenmaplearts12 liked this · 4 months ago
goldenmaplearts12 liked this · 4 months ago -
 spiderlegsmusic liked this · 4 months ago
spiderlegsmusic liked this · 4 months ago -
 itsrrrrrrrr reblogged this · 4 months ago
itsrrrrrrrr reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 bibliothekar liked this · 4 months ago
bibliothekar liked this · 4 months ago -
 scooter58 liked this · 4 months ago
scooter58 liked this · 4 months ago -
 scottguy reblogged this · 4 months ago
scottguy reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 bainer liked this · 4 months ago
bainer liked this · 4 months ago -
 parts-of-me-unravelling liked this · 4 months ago
parts-of-me-unravelling liked this · 4 months ago -
 sqrlgrrl2 liked this · 4 months ago
sqrlgrrl2 liked this · 4 months ago -
 dumbasspostsstuff liked this · 4 months ago
dumbasspostsstuff liked this · 4 months ago -
 ceevee5 reblogged this · 4 months ago
ceevee5 reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 hastingsmylove liked this · 5 months ago
hastingsmylove liked this · 5 months ago -
 igorderbucklige liked this · 5 months ago
igorderbucklige liked this · 5 months ago -
 spectra-bear liked this · 6 months ago
spectra-bear liked this · 6 months ago -
 theradiojunkie liked this · 6 months ago
theradiojunkie liked this · 6 months ago -
 thetruthof reblogged this · 6 months ago
thetruthof reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 thetruthof liked this · 6 months ago
thetruthof liked this · 6 months ago -
 radicool-kids liked this · 6 months ago
radicool-kids liked this · 6 months ago -
 kjdadj liked this · 6 months ago
kjdadj liked this · 6 months ago -
 actuallynobutwhynot reblogged this · 6 months ago
actuallynobutwhynot reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 actuallynobutwhynot liked this · 6 months ago
actuallynobutwhynot liked this · 6 months ago -
 sizhune reblogged this · 7 months ago
sizhune reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 catkurohazama liked this · 8 months ago
catkurohazama liked this · 8 months ago -
 roofermadness reblogged this · 8 months ago
roofermadness reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 hnyibee liked this · 9 months ago
hnyibee liked this · 9 months ago -
 cobaltstarling reblogged this · 9 months ago
cobaltstarling reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 fl0ppy-fries liked this · 9 months ago
fl0ppy-fries liked this · 9 months ago -
 hookahpop reblogged this · 9 months ago
hookahpop reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 xx-sharpfawngz-xx liked this · 9 months ago
xx-sharpfawngz-xx liked this · 9 months ago -
 theboredstagehand liked this · 9 months ago
theboredstagehand liked this · 9 months ago -
 sounddrive reblogged this · 9 months ago
sounddrive reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 ohmelodycave liked this · 9 months ago
ohmelodycave liked this · 9 months ago -
 sounddrive liked this · 10 months ago
sounddrive liked this · 10 months ago -
 vintagedaisywitch liked this · 1 year ago
vintagedaisywitch liked this · 1 year ago -
 edgy-gremlin liked this · 1 year ago
edgy-gremlin liked this · 1 year ago -
 saphicspacesociety17 reblogged this · 1 year ago
saphicspacesociety17 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yourpalarii liked this · 1 year ago
yourpalarii liked this · 1 year ago -
 oblivionates liked this · 1 year ago
oblivionates liked this · 1 year ago -
 redheadredliiips liked this · 1 year ago
redheadredliiips liked this · 1 year ago -
 may-or-whatever reblogged this · 1 year ago
may-or-whatever reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 may-or-whatever liked this · 1 year ago
may-or-whatever liked this · 1 year ago -
 athena-theowl liked this · 1 year ago
athena-theowl liked this · 1 year ago

