Carina Nebula Rosette Nebula Heart Nebula Fairy Pillar Nebula Orion Nebula Eagle Nebula Flame Vista Nebula








Carina Nebula Rosette Nebula Heart Nebula Fairy Pillar Nebula Orion Nebula Eagle Nebula Flame Vista Nebula Crab Nebula
More Posts from Study-astronomy-biology-ref and Others
yknow black dwarfs,,, do they actually exist and do they actually live longer than the universe,,
Yes. When stars of a certain mass run out of fuel, they expel their outer layers ( a planetary nebula)
What’s left, in the center is a white dwarf. The core of the original star. Can you see it in the center of this planetary nebula? (NGC 7662)

That white dwarf glows only because of heat, it is not actually making any new light. So, that white dwarf will cool down and leave a dark chunk of mass behind









On October 8 a privileged few could see auroras in abnormally low latitudes, as the spectacular pictures above taken in Wales and Northern England.
Via TON: Northern Lights Put On Spectacular Show As Aurora Borealis Lit Skies Over Wales And Yorkshire.
Festo’s Bionic Flying Fox, as an example of Bio-mimicry.
German automation company Festo has created a Flying Fox (Fruit Bat) made of a 580g foam body with a carbon fibre skeleton and a membrane like material for the wings.
This robot imitates the exact body and wing movements of an actual bad in order for it to fly. This idea of bio-mimicry is one that is paving the way for a host of natural moving, nature inspired machines.

Would It Be A Bad Thing to Wipe Out A Species … If It’s A Mosquito?
Mosquitoes have a nasty reputation.
The species Aedes aegypti, for example, is currently responsible for spreading the Zika virus through the Americas and also infects humans with dengue fever, chikungunya and yellow fever.
This raises the question: Should there be an effort to get rid of Aedes aegypti for good?
“There’s been lots of debate in the last 10 years whether we should eradicate mosquitoes, or at least the 100 species or so that serve as disease vectors for humans,” says David Magnus, director of Stanford University’s Center for Biomedical Ethics. “If you look at the science, the majority [of scientists] think we could probably eliminate mosquitoes without too much harm on the environment.”
Read the full story here.
Illustration: Matthew Twombly




“NEW GALAXY DISCOVERED ORBITING THE MILKY WAY” You would think that scientists would have already discovered most of the galaxies around the Milky Way, but that does not seem to be the case. Astronomers have recently detected a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way called the Crater 2 dwarf. This galaxy was discovered through measuring its ‘half-light diameter’. Since galaxies don’t have actual definitive edges, astronomers measure galaxies by looking at the brightest part of the galaxy where half of the total amount of light from the it is emitted - half-light diameter. This galaxy has a half-light diameter of 7000 light years, which would look twice as big as the full moon if we could see it with the naked eye. Gabriel Torrealba and his colleagues at the University of Cambridge, the team that discovered this galaxy, was only able to find it by using a computer that looked for over-densities of stars in data (hinting at the possibilities of galaxies or something else) from images taken by a telescope in Chile. The galaxy has eluded the detection of the scientific community for so long only because its stars are spread out so thinly, giving it a ghost-like appearance. In addition, this dwarf galaxy is near four other new-found objects: the Crater globular star cluster as well as three dwarf galaxies in Leo - a group of objects that is now falling towards the Milky Way. Interestingly, this galaxy is quite new due to it retaining a round shape suggesting that it had never encountered a giant galaxy, otherwise gravity would have bent the dwarf out of shape.
Read more about this fascinating story on: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2084438-never-before-seen-galaxy-spotted-orbiting-the-milky-way/


Gliese 832c: is a Potentially Habitable Super-Earth Discovered only 16 Light-Years from Earth
A team of astronomers led by Dr Robert Wittenmyer of the University of New South Wales have discovered the super-Earth. The newly discovered exoplanet, labeled Gliese 832c, has an orbital period of 35.68 days, a mass 5.4 times that of Earth’s and receives about the same average energy as Earth does from the Sun. Gliese 832c might have Earth-like temperatures, giving it a similar terrestrial atmosphere. If the planet has a similar atmosphere to Earth it may be possible for life to survive, although seasonal shifts would be extrem.
Gliese 832c was discovered from its gravitational pull on its star, which causes the star to wobble slightly.

How a blobfish looks with and without extreme water pressure. Blobfish live in water pressures 60-120 times greater than sea level.






Could dark energy be caused by frozen neutrinos?
“Since its discovery in 1998, the accelerated expansion has lacked a compelling, simple explanation that didn’t hypothesize a completely new set of forces, properties or interactions. If you wanted a scalar field — a quintessence model — it had to be finely tuned. But in a very clever paper just submitted yesterday by Fergus Simpson, Raul Jimenez, Carlos Pena-Garay, and Licia Verde, they note that if a generic scalar field couples to the neutrinos we have in our Universe, that fine-tuning goes away, and that scalar field will automatically begin behaving as a cosmological constant: as energy inherent to space itself.”
The accelerated expansion of our Universe was one of the biggest surprise discoveries of all-time, and something that still lacks a good physical explanation. While many models of dark energy exist, it remains a completely phenomenological study: everything appears consistent with a cosmological constant, but nothing appears to be a good motivator for why the Universe should have one. Until now, that is! In a new paper by Fergus Simpson, Raul Jimenez, Carlos Pena-Garay and Licia Verde, they note that any generic scalar field that couples to the neutrino sector would dynamically and stably give rise to a type of dark energy that’s indistinguishable from what we’ve observed. The huge advance is that this scenario doesn’t require any fine-tuning, thanks to this dark energy arising from neutrinos “freezing,” or becoming non-relativistic. In addition, there are experimental signatures to look for to confirm it, too, in the form of neutrinoless double-beta decay!
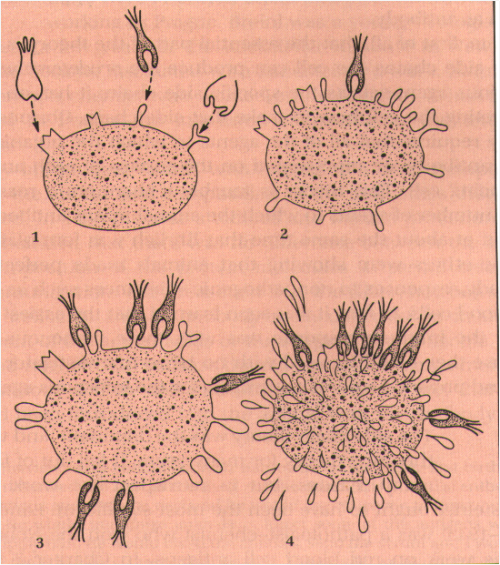
Antibodies are the secreted form of B-lymphocyte receptors and are a part of adaptive immunity, but how are these proteins formed?
Above is a diagram illustrating Paul Ehlrich’s Side Chain Theory of Antibody Formation. Ehlrich proposed that immunoglobulin molecules, a fundamental component of adaptive immunity, served as membrane bound proteins that bound to particular threats, similarly to the former “key in lock” view of enzymes in catalyzing biological reactions. Ehrlich also suggested that the action of binding a pathogenic molecule to the receptor would generate a signal to stimulate the production of more receptors of the same specificity. These “side chains” that were added on would then break off from the cell surface and become what we call antibodies.
We now know, however, that soluble immunoglobulin receptors are specially manufactured to be secreted as antibody, rather than just “breaking off” of the lymphocyte, even though they have the same specificity as their membrane-bound counterparts.
-
 celeberoticafanfic liked this · 1 year ago
celeberoticafanfic liked this · 1 year ago -
 watouhealthgag liked this · 1 year ago
watouhealthgag liked this · 1 year ago -
 ewwwspider reblogged this · 3 years ago
ewwwspider reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 sarahsabir reblogged this · 3 years ago
sarahsabir reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thewanderingslowpoke reblogged this · 3 years ago
thewanderingslowpoke reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thewanderingslowpoke liked this · 3 years ago
thewanderingslowpoke liked this · 3 years ago -
 charlie-mac-posts liked this · 3 years ago
charlie-mac-posts liked this · 3 years ago -
 diavolaangelica liked this · 3 years ago
diavolaangelica liked this · 3 years ago -
 diavolaangelica reblogged this · 3 years ago
diavolaangelica reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 venetus-pallium liked this · 3 years ago
venetus-pallium liked this · 3 years ago -
 jollyrogers777 reblogged this · 3 years ago
jollyrogers777 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nebulajam reblogged this · 3 years ago
nebulajam reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 lauraatulsa reblogged this · 4 years ago
lauraatulsa reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 lauraatulsa liked this · 4 years ago
lauraatulsa liked this · 4 years ago -
 wildernestt reblogged this · 4 years ago
wildernestt reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wildernestt liked this · 4 years ago
wildernestt liked this · 4 years ago -
 bookofnotomorrow liked this · 4 years ago
bookofnotomorrow liked this · 4 years ago -
 throughcnidarianeyes reblogged this · 4 years ago
throughcnidarianeyes reblogged this · 4 years ago

This is a studyblr for everyone have some passion for science, especially astronomy and biology
129 posts






