Would It Be A Bad Thing To Wipe Out A Species … If It’s A Mosquito?

Would It Be A Bad Thing to Wipe Out A Species … If It’s A Mosquito?
Mosquitoes have a nasty reputation.
The species Aedes aegypti, for example, is currently responsible for spreading the Zika virus through the Americas and also infects humans with dengue fever, chikungunya and yellow fever.
This raises the question: Should there be an effort to get rid of Aedes aegypti for good?
“There’s been lots of debate in the last 10 years whether we should eradicate mosquitoes, or at least the 100 species or so that serve as disease vectors for humans,” says David Magnus, director of Stanford University’s Center for Biomedical Ethics. “If you look at the science, the majority [of scientists] think we could probably eliminate mosquitoes without too much harm on the environment.”
Read the full story here.
Illustration: Matthew Twombly
More Posts from Study-astronomy-biology-ref and Others
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

For the first time in almost a decade, we’re going back to Jupiter. Our Juno spacecraft arrives at the king of planets on the fourth of July. From a unique polar orbit, Juno will repeatedly dive between the planet and its intense belts of charged particle radiation. Juno’s primary goal is to improve our understanding of Jupiter’s formation and evolution, which will help us understand the history of our own solar system and provide new insight into how other planetary systems form.
In anticipation, here are a few things you need to know about the Juno mission and the mysterious world it will explore:
1. This is the Big One

The most massive planet in our solar system, with dozens of moons and an enormous magnetic field, Jupiter rules over a kind of miniature solar system.
2. Origin Story

Why study Jupiter in the first place? How does the planet fit into the solar system as a whole? What is it hiding? How will Juno unlock its secrets? A series of brief videos tells the stories of Jupiter and Juno. Watch them HERE.
3. Eyes on Juno
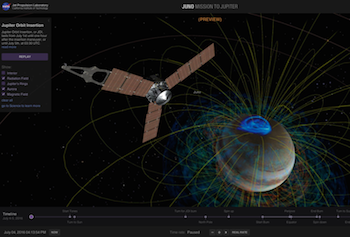
If you really want a hands-on understanding of Juno’s flight through the Jupiter system, there’s no better tool than the “Eyes on Juno” online simulation. It uses data from the mission to let you realistically see and interact with the spacecraft and its trajectory—in 3D and across both time and space.
4. You’re on JunoCam!

Did you know that you don’t have to work for NASA to contribute to the Juno mission? Amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts everywhere are invited to help with JunoCam, the mission’s color camera. You can upload your own images of Jupiter, comment on others’ images, and vote on which pictures JunoCam will take when it reaches the Jovian system.
5. Ride Along
It’s easy to follow events from the Juno mission as they unfold. Here are several ways to follow along online:
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

The circulatory system: dissection of the stomach and intestines, with the arteries and veins indicated in red and blue. Coloured lithograph by Joseph Maclise, 1841/1844.



The solar eclipse that occurred in Chile on July 2, 2019 photographed by Dan Marker-Moore. Great job!
Via Colossal


The Veil Nebula - Sharpless 103
Located 1,500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust known as the Veil Nebula. The Veil Nebula is the visible portion of a massive supernova that erupted around 7,000 years ago to form what is now known as the Cygnus Loop. The Veil Nebula has a diameter of 100 light-years which appears to be 6 times the diameter of the full moon in the night sky. Due to the scale of the Veil, astronomers often segment the nebula into western (Caldwell 34), eastern (Caldwell 33) and northern portions. This particular images shows the western portion of the nebula with NGC 6960 (the Witches Broom), NGC 6979 (Pickering’s Triangle), and other significant cataloged objects.
Credit: NASA/Digital Sky Survey

The Lagoon Nebula - M8 in Infrared
The Lagoon Nebula (also known as Messier 8/M8 or NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud and emission nebula located in the constellation Sagittarius approximately 5,000 light-year from earth. The nebula contains a number of Bok globules, which can be seen as dark, collapsing clouds of gaseous material. This Particular image shows a star forming central region in infrared and was captured by the VISTA telescope at ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile.
Credit: ESO/VISTA

THE TRAPPIST-1 DISCOVERY
NASA’s announcement today was awe-inspiring. We’ve compiled the essential info you want to know about this incredible discovery.
OVERVIEW: 7 PLANETS, 3 HABITABLE
Astronomers have found at least seven Earth-sized planets orbiting the same star 40 light-years away, according to a study published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
The seven exoplanets were all found in tight formation around an ultracool dwarf star called TRAPPIST-1. Estimates of their mass also indicate that they are rocky planets, rather than being gaseous like Jupiter. Three planets are in the habitable zone of the star, known as TRAPPIST-1e, f and g, and may even have oceans on the surface.
“I think we’ve made a crucial step towards finding if there is life out there,” said Amaury Triaud, one of the study authors and an astronomer at the University of Cambridge. “I don’t think any time before we had the right planets to discover and find out if there was (life). Here, if life managed to thrive and releases gases similar to what we have on Earth, we will know.”
ONLY 40 LIGHT YEARS AWAY
The system is just 40 light-years away. On a cosmic scale, that’s right next door. Of course, practically speaking, it would still take us hundreds of millions of years to get there with today’s technology – but again, it is notable in that the find speaks volumes about the potential for life-as-we-know-it beyond Earth.
The Hubble Space Telescope is already being used to search for atmospheres around the planets, and Emmanuël Jehin, a scientist who also worked on the research, asserts that future telescopes could allow us to truly see into the heart of this system: “With the upcoming generation of telescopes, such as ESO’s European Extremely Large Telescope and the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, we will soon be able to search for water and perhaps even evidence of life on these worlds.”
ALIEN SKIES
In contrast to our sun, the TRAPPIST-1 star – classified as an ultra-cool dwarf – is so cool that liquid water could survive on planets orbiting very close to it, closer than is possible on planets in our solar system. All seven of the TRAPPIST-1 planetary orbits are closer to their host star than Mercury is to our sun. The planets also are very close to each other. If a person was standing on one of the planet’s surface, they could gaze up and potentially see geological features or clouds of neighboring worlds, which would sometimes appear larger than the moon in Earth’s sky.
The planets may also be tidally locked to their star, which means the same side of the planet is always facing the star, therefore each side is either perpetual day or night. This could mean they have weather patterns totally unlike those on Earth, such as strong winds blowing from the day side to the night side, and extreme temperature changes.

The gender divide in science is cultural rather than anything to do with women’s brains and some countries do much better than others, she says.
In astrophysics southern European countries like France, Spain and Italy do much better than northern European countries like Germany and The Netherlands, for instance.
“In all those countries the proportion of women is going up but the pattern has stayed the same, which is interesting,” she says.
“The progress is slow, things are changing gradually.”
Her advice to women in science? “Don’t be daunted, hang in there, work hard, of course, be courageous.”
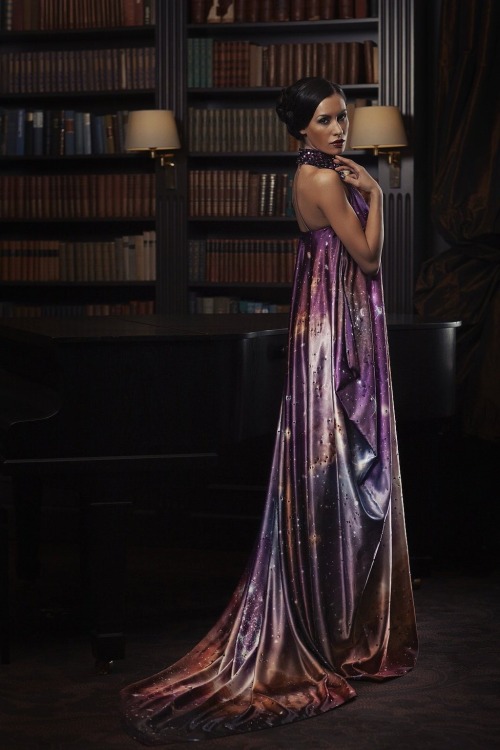
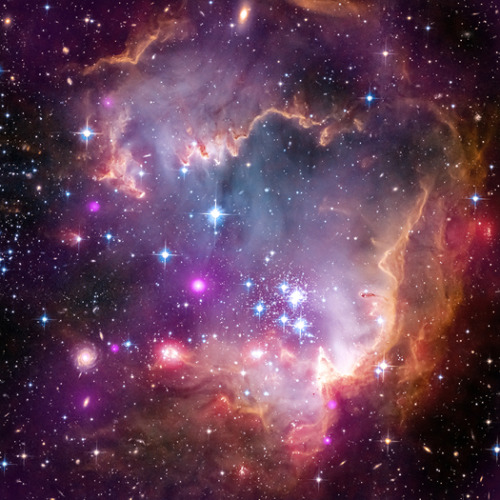
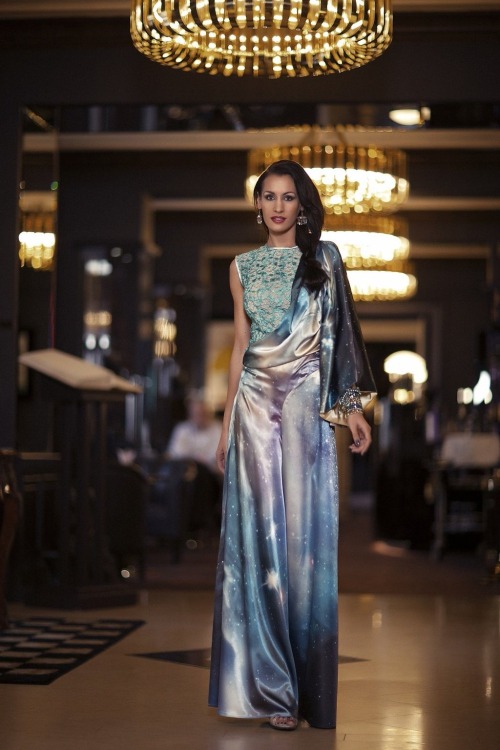
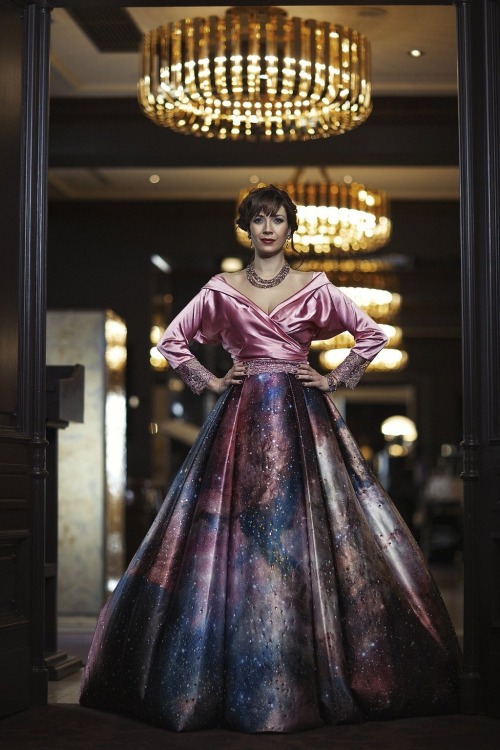
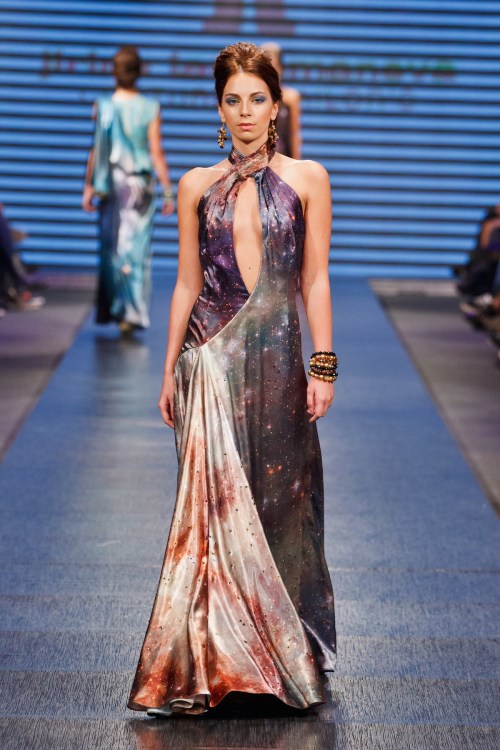
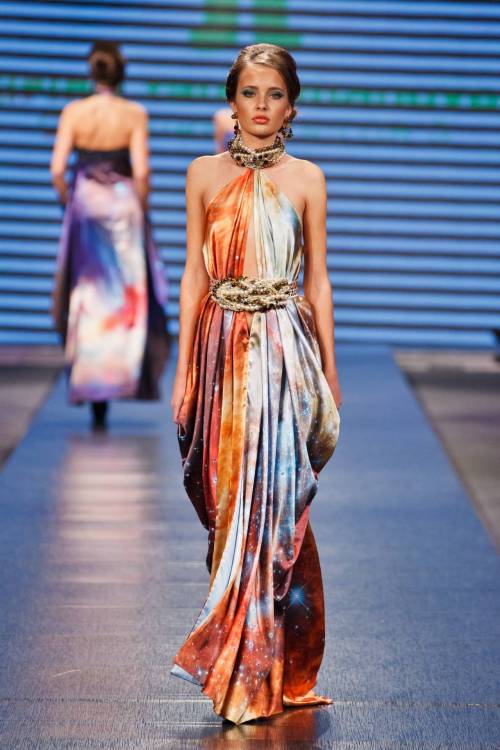
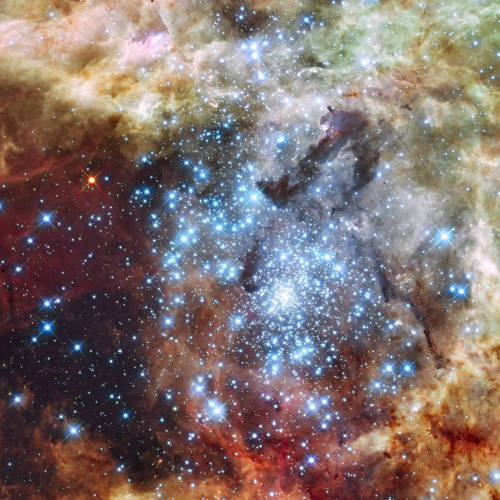
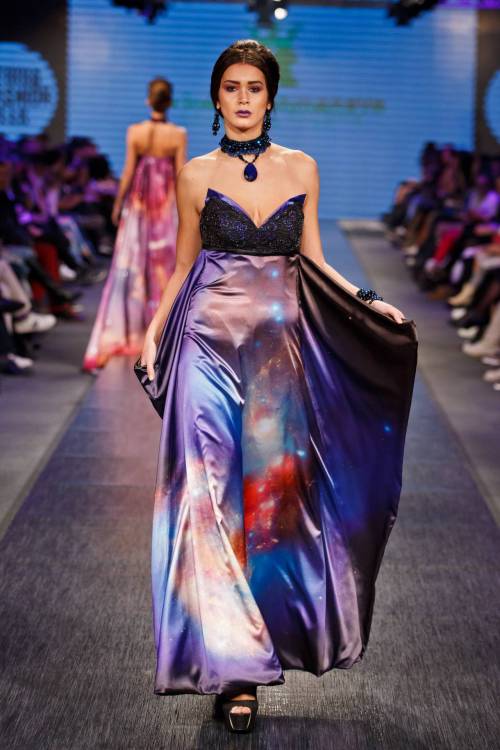
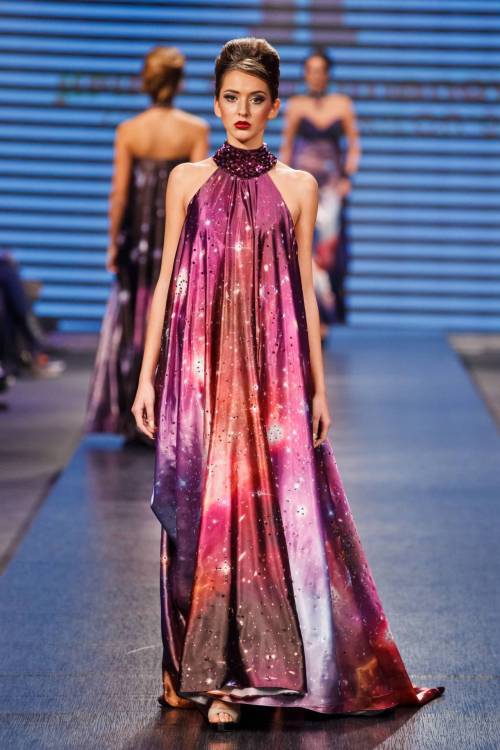
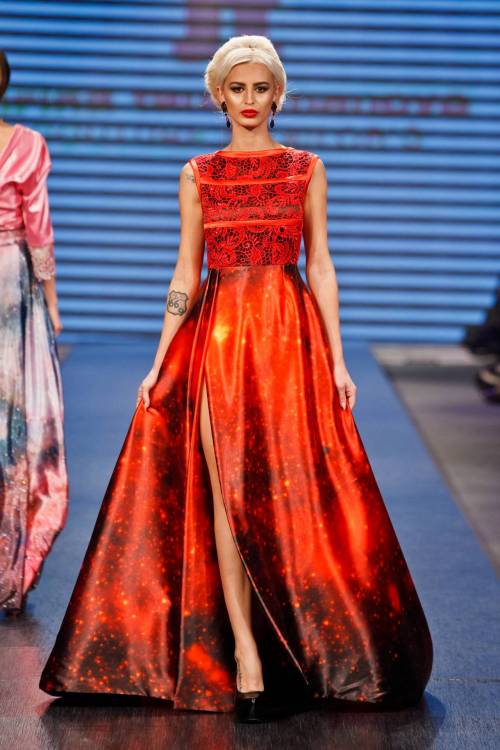










The astro-fashion-loving Internet collectively gasped when ESA’s Hubble twitter account posted three gorgeous gowns, by Czech designer Jirina Tauchmanova with only credit “Photo: Vasek”, which google thinks is a Canadian tennis player. For four long days I couldn’t find anymore images, until, today! Which is why I’m sharing a belated #FashionFriday and #StarrySunday combo.
These gown were shown at Serbia Fashion Week back in December 2015 as Jirina Tauchmanova‘s Spring/Summer 2016 collection – I hope that means they will be available for purchase soon!
I think I recognize at least two of the images, NGC 602 & 30 Doradus, but I’m going to have to see these in person to be sure, yes, definitely, and probably try them on, too.
–Emily
-
 bigpaperforhaters-blog reblogged this · 7 months ago
bigpaperforhaters-blog reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 bigpaperforhaters-blog liked this · 7 months ago
bigpaperforhaters-blog liked this · 7 months ago -
 capt-star-beard liked this · 6 years ago
capt-star-beard liked this · 6 years ago -
 denguepatrolskpopok-blog liked this · 6 years ago
denguepatrolskpopok-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 devilxv liked this · 7 years ago
devilxv liked this · 7 years ago -
 comtedemoney liked this · 7 years ago
comtedemoney liked this · 7 years ago -
 juanelas reblogged this · 8 years ago
juanelas reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pejw liked this · 8 years ago
pejw liked this · 8 years ago -
 pyrotec729 reblogged this · 8 years ago
pyrotec729 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 typosum liked this · 8 years ago
typosum liked this · 8 years ago -
 pyrotec729 reblogged this · 8 years ago
pyrotec729 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 touchthepenguin reblogged this · 8 years ago
touchthepenguin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 rinbylin reblogged this · 8 years ago
rinbylin reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 yellowgrowngreen reblogged this · 8 years ago
yellowgrowngreen reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 thelegmoon liked this · 8 years ago
thelegmoon liked this · 8 years ago -
 paklamokganern-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
paklamokganern-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 takineko reblogged this · 8 years ago
takineko reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 takineko liked this · 8 years ago
takineko liked this · 8 years ago -
 malicious-angelx reblogged this · 8 years ago
malicious-angelx reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 malicious-angelx liked this · 8 years ago
malicious-angelx liked this · 8 years ago -
 this-should-do liked this · 8 years ago
this-should-do liked this · 8 years ago -
 trapemall reblogged this · 8 years ago
trapemall reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 asphaltgray reblogged this · 8 years ago
asphaltgray reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 createdmammon reblogged this · 8 years ago
createdmammon reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 createdmammon liked this · 8 years ago
createdmammon liked this · 8 years ago -
 tachyon-at-rest reblogged this · 8 years ago
tachyon-at-rest reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 tachyon-at-rest liked this · 8 years ago
tachyon-at-rest liked this · 8 years ago -
 wordswilling liked this · 8 years ago
wordswilling liked this · 8 years ago -
 melemonly liked this · 8 years ago
melemonly liked this · 8 years ago

This is a studyblr for everyone have some passion for science, especially astronomy and biology
129 posts


