10 Amazing Space Discoveries By The World’s Largest Flying Observatory
10 Amazing Space Discoveries by the World’s Largest Flying Observatory

On the night of May 26, 2010, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, the world’s largest flying observatory, first peered into the cosmos. Its mission: to study celestial objects and astronomical phenomena with infrared light. Many objects in space emit almost all their energy at infrared wavelengths. Often, they are invisible when observed in ordinary, visible light. Over the last decade, the aircraft’s 106-inch telescope has been used to study black holes, planets, galaxies, star-forming nebulas and more! The observations have led to major breakthroughs in astronomy, revolutionizing our understanding of the solar system and beyond. To celebrate its 10 years of exploration, here’s a look at the top 10 discoveries made by our telescope on a plane:
The Universe’s First Type of Molecule

Scientists believe that around 100,000 years after the big bang, helium and hydrogen combined to make a molecule called helium hydride. Its recent discovery confirms a key part of our basic understanding of the early universe.
A New View of the Milky Way

More than a pretty picture, this panorama of cosmic scale reveals details that can help explain how massive stars are born and what’s feeding our Milky Way galaxy’s supermassive black hole.
When Planets Collide

A double-star system that is more than 300 light-years away likely had an extreme collision between two of its rocky planets. A similar event in our own solar system may have formed our Moon.
How A Black Hole Feasts

Fear not, the dark, my friend. And let the feast begin! Magnetic fields in the Cygnus A galaxy are trapping material where it is close enough to be devoured by a hungry black hole.
Somewhere Like Home

The planetary system around Epsilon Eridani, a star located about 10 light-years away, has an architecture remarkably similar to our solar system. What’s more, its central star is a younger, fainter version of our Sun.
A Quiet Place

Black holes in many galaxies are actively consuming material, but our Milky Way galaxy’s central black hole is relatively quiet. Observations show magnetic fields may be directing material around, not into, the belly of the beast.
The Great Escape

Ever wonder how material leaves a galaxy? The wind flowing from the center of the Cigar Galaxy is so strong it’s pulling a magnetic field — and the mass of 50 to 60 million Suns — with it.
Exploding Star, New Worlds

What happens when a star goes boom? It turns out that supernova explosions can produce a substantial amount of material from which planets like Earth can form.
Stellar Sibling Rivalry

They say siblings need time and space to grow, but here’s one that really needs some room. A newborn star in the Orion Nebula is clearing a bubble of space around it, preventing any new luminous family members from forming nearby.
Clues to Life’s Building Blocks

Radiation from stars is making organic molecules in nebula NGC 7023, also known as the Iris Nebula, larger and more complex. The growth of these molecules is one of the steps that could lead to the emergence of life under the right circumstances.
SOFIA is a modified Boeing 747SP aircraft that allows astronomers to study the solar system and beyond in ways that are not possible with ground-based telescopes. Find out more about the mission at www.nasa.gov/SOFIA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Primordialbitch and Others
Your fave is problematic: Neutron Stars
Neutron stars are probably one of the weirdest type of objects to exist in the universe… but first let me explain what a neutron star is
when a star with the mass of 8-20 times of the sun dies (and by dies I mean fucking explodes), the core collapses to form a neutron star
they are incredibly dense, spin rapidly and have very strong magnetic fields
sounds all fun and games, right? sounds normal? well listen up
So, we know that electrons usually refuse to be squeezed together. but in a death event of a big star, the pressure is so extreme that protons and electrons get violently SMASHED together and form neutrons.
sounds like someone needs to take an anti-agression class if you ask me
Now, what once was a star more massive than the Sun, is condensed to a tiny ball (usually about 10-20km!) of neutrons, with all of the mass in this tiny ball.
To visualize, imagine the mass of the Sun (300 000X the mass of the Earth), in a little 20km sphere, the size of a small city.
To visualize the density of a neutron star, think of the classic model of the atom. if an atom was a sports field 100m across, it would be mostly empty. almost all of the atom’s mass sits in the core, in this example, the core is the size of a marble.
but in a neutron star, this doesn’t apply anymore. in a neutron star, the entire stadium would be filled to the brim with neutrons. ALL. OF. IT.
a single cubic centimetre of Neutronium has the mass of 400 million tons. that’s the total mass of every single car and truck in the US.
the typical gravity of a neutron star is about 100 million times of that of the Earth. clingy as shit
so far, we have detected over 1000 of these weird fucks in our galaxy alone. yikes
some Neutron stars are vampires. They can be in a binary star system where a normal star orbits them and they feed of that material
summary: extremely weird and violent space ball of rage, tiny, filled to the top with anger, sometimes a vampire
TRAILER: “TIME MASTERS (LES MAÎTRES DU TEMPS)” (1982)
This animated science fiction feature film was directed by René Laloux and Tibor Hernádi but most notably - designed by the artist Mœbius. It is based on Stefan Wul’s 1958 science fiction novel L'Orphelin de Perdide (The Orphan of Perdide).
It’s about a boy, Piel, who is stranded on the desert planet Perdide, where giant killer hornets live. He awaits rescue by the space pilot Jaffar, the exiled prince Matton, his sister Belle and Jaffar’s old friend Silbad - who are all trying to reach Perdide and save Piel before it is too late.
If you’ve seen this film, you’ve probably seen the English language dubs by the BBC in 1987 or 1991 called Time Masters.
This is a super rare film that you can find on DVD, but usually used, and pretty expensive.
New type of star system? Mysterious radio signal puzzles astronomers
by Laura Nicole Driessen

Meerkat telescope. Sotiris Sanidas, Author provided
After observing a part of the sky near the Southern Constellation of Ara for about two months using MeerKAT, a radio telescope based in the Karoo desert in South Africa, our team of scientists noticed something strange. The radio emission of an object brightened by a factor of three over roughly three weeks.
Intrigued, we continued watching the object and followed this up with observations from other telescopes. We discovered that the unusual flare came from a binary star system – two stars orbiting each other – in our own galaxy. The finding, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, has, however, turned out to be very difficult to explain.
Keep reading
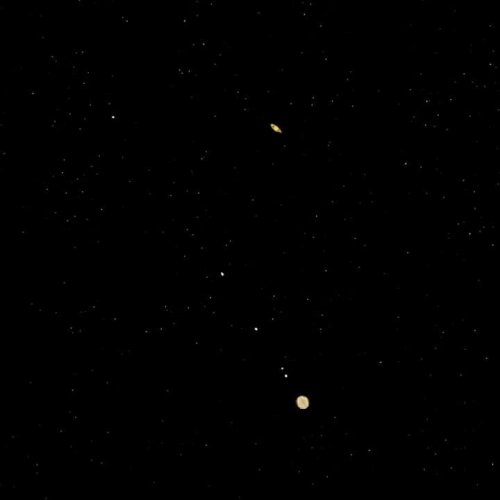
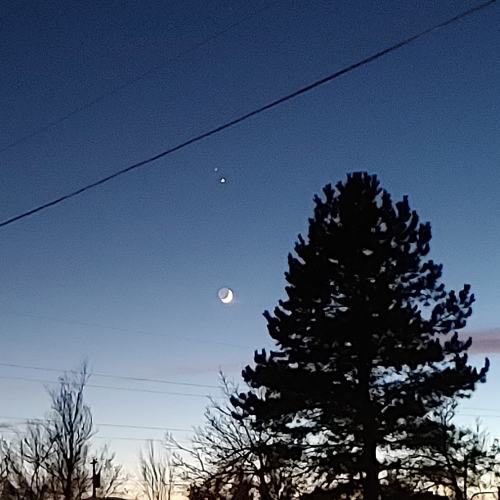
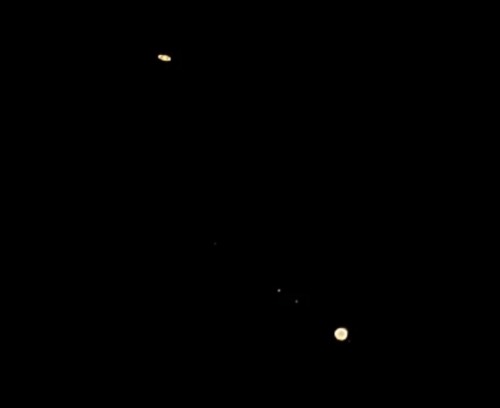






The Great Conjunction: Jupiter and Saturn 🌌.
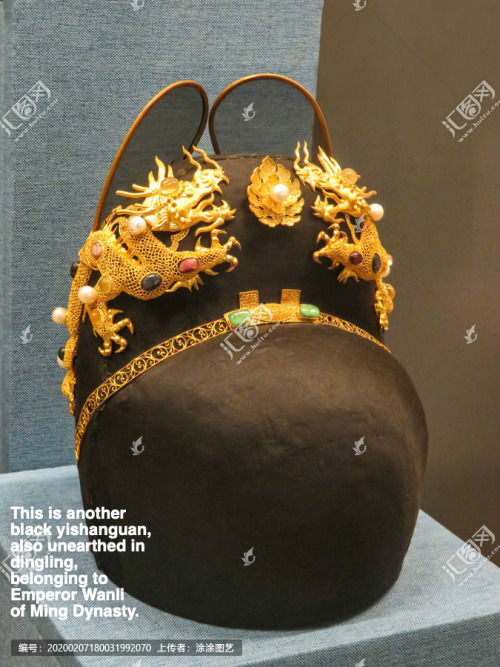
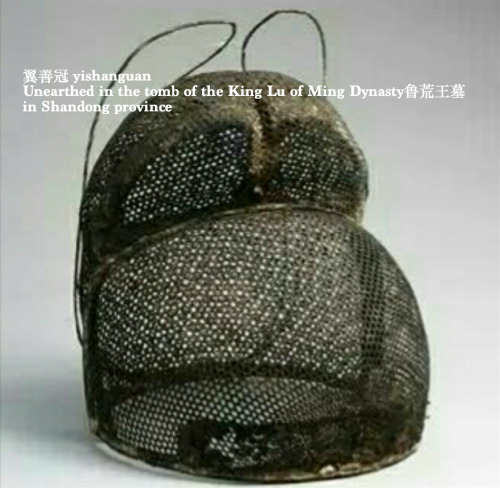
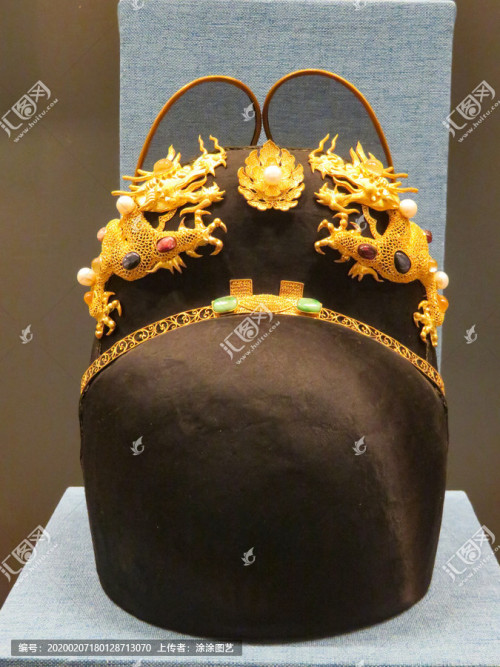
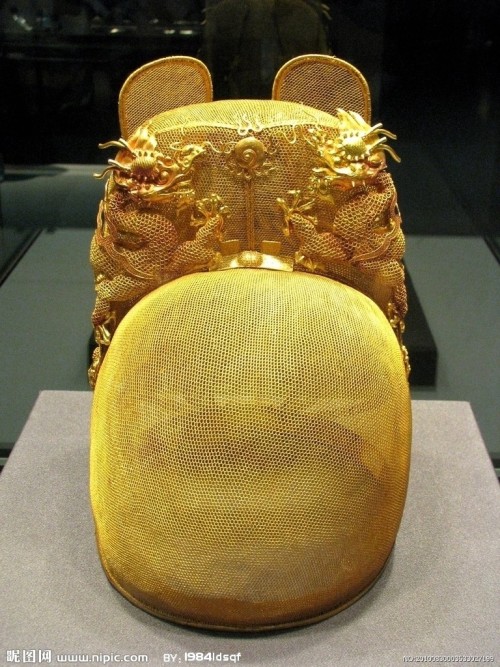
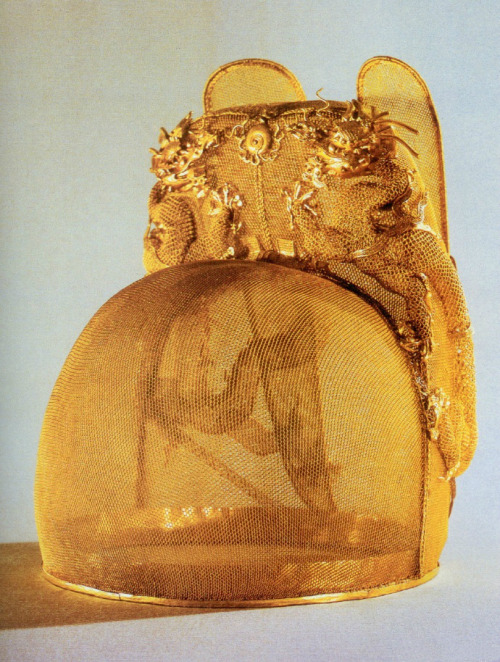
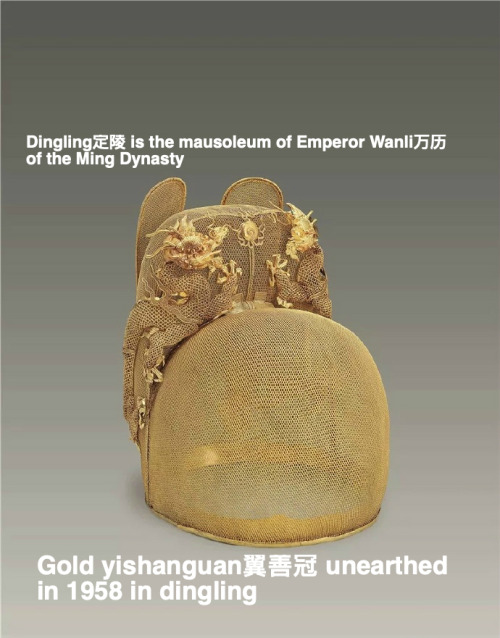









翼善冠yi-shan-guan, a type of hat in Chinese hanfu for ancient emperors and kings.
The term first appeared in Tang Dynasty and invented by Emperor Taizong of Tang. Quotes according to the official records of Tang, Song and Ming Dynasty. “唐贞观中,太宗采古制为翼善冠,自服之。朔望视朝,以常服及帛练裙襦通着之。若服袴褶,又与平巾帻通用。见宋王溥《唐会要.舆服上》﹑《旧唐书.舆服志》。明永乐三年,定皇帝常服冠以乌纱覆之,折角向上,亦名翼善冠。见《明史.舆服志二》。”
The yishanguan also has a corresponding hat of very similar shape in the official class and the commoner class, called wushamao乌纱帽, and in fact the yishanguan can be considered a variant of wushamao.
Actually yishanguan does have another name, called wu-sha-zhe-shang-jin乌纱折上巾, which means a hat made of black gauze with folded wings upward, and that’s what distinguishes it from an ordinary wushamao.
As for the origin of wushamao, it is futou幞头 in the Tang Dynasty. Futou in the Tang Dynasty originates from fujin幅巾 in the Han Dynasty. In the Han Dynasty, people wrapped their heads in a whole pair of soft cloth, so it was called fujin幅巾(It literally means a whole piece of cloth).

Some wushamao without wings, worn by officials, are similar in shape to the Yishanguan worn by the emperor. In Chinese historical dramas and costume dramas, jin-yi-wei锦衣卫, the imperial guards of secret service agent in the emperor’s court often wore this kind of wushamao without wings. And most wushamao have flush, long oval wings. There is a type of wushamao with particularly slender wings that is inherited from the Song Dynasty and is considered more formal.
The pictures below are ancient wushamao from the museums’ collection, as well as portraits of Ming Dynasty officials.


Because jinyiwei锦衣卫 resembles ancient agents, it is very popular among Chinese artists, who often draw characters wearing jinyiwei-style hanfu.

Then again, the following pictures are of Ming emperors wearing yishanguan. These pictures are accurate for reference.



Animated version drawn by 燕王WF

There are some ancient paintings from the Song and Ming dynasties, on which people are wearing various kinds of wushamao.






The above is the brief introduction about yishanguan and wushamao, after that I will also introduce more other types of hanfu hats.
So you know those mutant strains of radiotrophic fungus they discovered in Chernobyl? The ones that feed on gamma radiation? Those fungi, the radiation-eating fungi? From Chernobyl? They brought some on board the International Space Station and took some measurements. Here is the paper, titled:
A Self-Replicating Radiation-Shield for Human Deep-Space Exploration: Radiotrophic Fungi can Attenuate Ionizing Radiation aboard the International Space Station
Space is full of high-energy radiation, and radiation shielding is a big engineering challenge for Martian habitats and deep-space missions. What they figured out is that an 8-inch thick layer of mutant Chernobyl radiation-eating fungus in the walls of the spacecraft or habitat would serve as a self-replicating, self-sustaining radiation shield for long-haul missions.
This sounds like such a good and normal idea! Let’s do it!
seeing the photos from Webb up against photos from Hubble just makes me… I don’t even know like, wow! Look at that!











Black Hole Image Makes History; NASA Telescopes Coordinated Observations
A black hole and its shadow have been captured in an image for the first time, a historic feat by an international network of radio telescopes called the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). EHT is an international collaboration whose support in the U.S. includes the National Science Foundation.
A black hole is an extremely dense object from which no light can escape. Anything that comes within a black hole’s “event horizon,” its point of no return, will be consumed, never to re-emerge, because of the black hole’s unimaginably strong gravity. By its very nature, a black hole cannot be seen, but the hot disk of material that encircles it shines bright. Against a bright backdrop, such as this disk, a black hole appears to cast a shadow.
The stunning new image shows the shadow of the supermassive black hole in the center of Messier 87 (M87), an elliptical galaxy some 55 million light-years from Earth. This black hole is 6.5 billion times the mass of the Sun. Catching its shadow involved eight ground-based radio telescopes around the globe, operating together as if they were one telescope the size of our entire planet.
“This is an amazing accomplishment by the EHT team,” said Paul Hertz, director of the astrophysics division at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Years ago, we thought we would have to build a very large space telescope to image a black hole. By getting radio telescopes around the world to work in concert like one instrument, the EHT team achieved this, decades ahead of time.”
To complement the EHT findings, several NASA spacecraft were part of a large effort, coordinated by the EHT’s Multiwavelength Working Group, to observe the black hole using different wavelengths of light. As part of this effort, NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) and Neil Gehrels SwiftObservatory space telescope missions, all attuned to different varieties of X-ray light, turned their gaze to the M87 black hole around the same time as the Event Horizon Telescope in April 2017. If EHT observed changes in the structure of the black hole’s environment, data from these missions and other telescopes could be used to help figure out what was going on.
While NASA observations did not directly trace out the historic image, astronomers used data from NASA’s Chandra and NuSTAR satellites to measure the X-ray brightness of M87’s jet. Scientists used this information to compare their models of the jet and disk around the black hole with the EHT observations. Other insights may come as researchers continue to pore over these data.
There are many remaining questions about black holes that the coordinated NASA observations may help answer. Mysteries linger about why particles get such a huge energy boost around black holes, forming dramatic jets that surge away from the poles of black holes at nearly the speed of light. When material falls into the black hole, where does the energy go?
“X-rays help us connect what’s happening to the particles near the event horizon with what we can measure with our telescopes,” said Joey Neilsen, an astronomer at Villanova University in Pennsylvania, who led the Chandra and NuSTAR analysis on behalf of the EHT’s Multiwavelength Working Group.
NASA space telescopes have previously studied a jet extending more than 1,000 light-years away from the center of M87. The jet is made of particles traveling near the speed of light, shooting out at high energies from close to the event horizon. The EHT was designed in part to study the origin of this jet and others like it. A blob of matter in the jet called HST-1, discovered by Hubble astronomers in 1999, has undergone a mysterious cycle of brightening and dimming.
Chandra, NuSTAR and Swift, as well as NASA’s Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) experiment on the International Space Station, also looked at the black hole at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy, called Sagittarius A*, in coordination with EHT.
Getting so many different telescopes on the ground and in space to all look toward the same celestial object is a huge undertaking in and of itself, scientists emphasize.
“Scheduling all of these coordinated observations was a really hard problem for both the EHT and the Chandra and NuSTAR mission planners,” Neilsen said. “They did really incredible work to get us the data that we have, and we’re exceedingly grateful.”
Neilsen and colleagues who were part of the coordinated observations will be working on dissecting the entire spectrum of light coming from the M87 black hole, all the way from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma rays. With so much data from EHT and other telescopes, scientists may have years of discoveries ahead.
Original article:
http://nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/news/black-hole-image-makes-history
Time And Space
Pls tell me interesting facts about stars
Interesting facts about stars:
Heavy stars blow up and make heavier elements like gold. So, every bit of gold you’ve ever seen, worn, or touched came from the dying explosion of a star. Other elements made in supernovae include anything on the periodic table heavier than iron
Heavy stars blow up when they start fusing iron. Meaning, the iron in your frying pan, car, and your blood killed a star at least 3 times the mass of the sun.
Some massive stars that die end up compressing all their mass into a star about 6 miles across, or about the size of a city. This is called a neutron star.
To put this in perspective, these stars start out 3 times as big as our sun and all of their mass is crushed into something the size of a city. The space between atoms is squished away, and the protons and electrons combine to form neutrons.
Neutron stars are literally as dense as atomic nuclei
Most stars come in pairs
The most common stellar type is a red dwarf, which is a small, red, dim, cool star.
Honestly, that’s just the first few that come to mind, space is really crazy.
planetarium presenters trying to explain to a busload of 4th graders how incomprehensibly vast space is
-
 cookiehat liked this · 8 months ago
cookiehat liked this · 8 months ago -
 gsunny6 liked this · 2 years ago
gsunny6 liked this · 2 years ago -
 raggedybatman liked this · 2 years ago
raggedybatman liked this · 2 years ago -
 handmeyours liked this · 3 years ago
handmeyours liked this · 3 years ago -
 galaxyharrow reblogged this · 3 years ago
galaxyharrow reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 fairyqueen996 reblogged this · 3 years ago
fairyqueen996 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 kvaleksy liked this · 3 years ago
kvaleksy liked this · 3 years ago -
 raven6211 liked this · 3 years ago
raven6211 liked this · 3 years ago -
 adricofalzarius liked this · 3 years ago
adricofalzarius liked this · 3 years ago -
 sweetandsadsblog liked this · 3 years ago
sweetandsadsblog liked this · 3 years ago -
 mischief02 liked this · 3 years ago
mischief02 liked this · 3 years ago -
 adm-starblitzsteel-4305 reblogged this · 4 years ago
adm-starblitzsteel-4305 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 quraninyou liked this · 4 years ago
quraninyou liked this · 4 years ago -
 infinityunitblogblogger reblogged this · 4 years ago
infinityunitblogblogger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 unlikelyanonymous liked this · 4 years ago
unlikelyanonymous liked this · 4 years ago -
 rage-r liked this · 4 years ago
rage-r liked this · 4 years ago -
 lock-0n liked this · 4 years ago
lock-0n liked this · 4 years ago -
 thelittleoxymoron liked this · 4 years ago
thelittleoxymoron liked this · 4 years ago -
 micaaaa-h liked this · 4 years ago
micaaaa-h liked this · 4 years ago -
 theserpentandthesword reblogged this · 4 years ago
theserpentandthesword reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 hurluberlu31 liked this · 4 years ago
hurluberlu31 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sleepeatdestroyrepeat reblogged this · 4 years ago
sleepeatdestroyrepeat reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 neon-burning liked this · 4 years ago
neon-burning liked this · 4 years ago -
 eldrichlibrarian reblogged this · 4 years ago
eldrichlibrarian reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thomasswift85 reblogged this · 4 years ago
thomasswift85 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 foramadmaninabox reblogged this · 4 years ago
foramadmaninabox reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 fenwyld liked this · 4 years ago
fenwyld liked this · 4 years ago -
 starwalkerofthedepths reblogged this · 4 years ago
starwalkerofthedepths reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 heofthebalance reblogged this · 4 years ago
heofthebalance reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 angel-0ver-you reblogged this · 4 years ago
angel-0ver-you reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 angel-0ver-you liked this · 4 years ago
angel-0ver-you liked this · 4 years ago -
 barefootedd liked this · 4 years ago
barefootedd liked this · 4 years ago -
 alittlewitchyplace reblogged this · 4 years ago
alittlewitchyplace reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cashmoneyravestars liked this · 4 years ago
cashmoneyravestars liked this · 4 years ago -
 stellarmuffin liked this · 4 years ago
stellarmuffin liked this · 4 years ago -
 katdnsm liked this · 4 years ago
katdnsm liked this · 4 years ago
