Three NASA Telescopes Look At An Angry Young Star Together
Three NASA Telescopes Look at an Angry Young Star Together
Science is a shared endeavor. We learn more when we work together. Today, July 18, we’re using three different space telescopes to observe the same star/planet system!

As our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) enters its third year of observations, it's taking a new look at a familiar system this month. And today it won't be alone. Astronomers are looking at AU Microscopii, a young fiery nearby star – about 22 million years old – with the TESS, NICER and Swift observatories.

TESS will be looking for more transits – the passage of a planet across a star – of a recently-discovered exoplanet lurking in the dust of AU Microscopii (called AU Mic for short). Astronomers think there may be other worlds in this active system, as well!

Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) telescope on the International Space Station will also focus on AU Mic today. While NICER is designed to study neutron stars, the collapsed remains of massive stars that exploded as supernovae, it can study other X-ray sources, too. Scientists hope to observe stellar flares by looking at the star with its high-precision X-ray instrument.

Scientists aren't sure where the X-rays are coming from on AU Mic — it could be from a stellar corona or magnetic hot spots. If it's from hot spots, NICER might not see the planet transit, unless it happens to pass over one of those spots, then it could see a big dip!

A different team of astronomers will use our Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory to peer at AU Mic in X-ray and UV to monitor for high-energy flares while TESS simultaneously observes the transiting planet in the visible spectrum. Stellar flares like those of AU Mic can bathe planets in radiation.
Studying high-energy flares from AU Mic with Swift will help us understand the flare-rate over time, which will help with models of the planet’s atmosphere and the system’s space weather. There's even a (very) small chance for Swift to see a hint of the planet's transit!

The flares that a star produces can have a direct impact on orbiting planets' atmospheres. The high-energy photons and particles associated with flares can alter the chemical makeup of a planet's atmosphere and erode it away over time.
Another time TESS teamed up with a different spacecraft, it discovered a hidden exoplanet, a planet beyond our solar system called AU Mic b, with the now-retired Spitzer Space Telescope. That notable discovery inspired our latest poster! It’s free to download in English and Spanish.

Spitzer’s infrared instrument was ideal for peering at dusty systems! Astronomers are still using data from Spitzer to make discoveries. In fact, the James Webb Space Telescope will carry on similar study and observe AU Mic after it launches next year.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
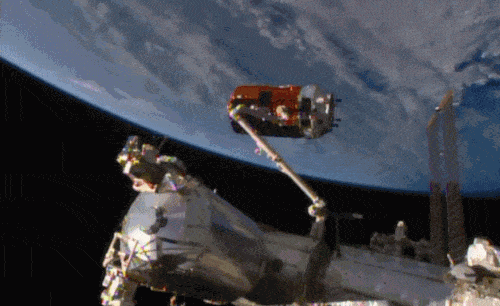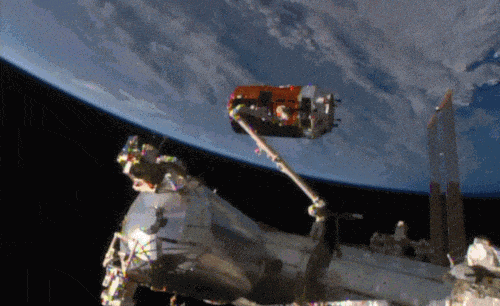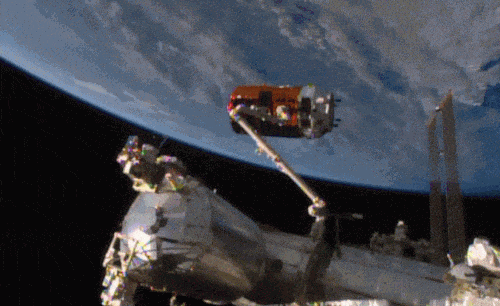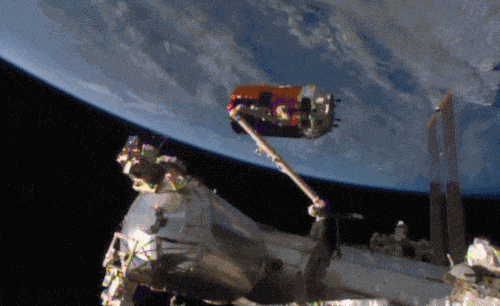
Aboard the International Space Station this morning, Astronaut Kimiya Yui of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) successfully captured JAXA's Kounotori 5 H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV-5) at 6:28 a.m. EDT.
Yui commanded the station's robotic arm, Canadarm2, to reach out and grapple the HTV-5, while NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren provided assistance and Scott Kelly monitored HTV-5 systems. The HTV-5 launched aboard an H-IIB rocket at 7:50 a.m. Wednesday, Aug. 19, from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. Since then, the spacecraft has performed a series of engine burns to fine-tune its course for arrival at the station.
The HTV-5 is delivering more than 8,000 pounds of equipment, supplies and experiments in a pressurized cargo compartment. The unpressurized compartment will deliver the 1,400-pound CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) investigation, an astrophysics mission that will search for signatures of dark matter and provide the highest energy direct measurements of the cosmic ray electron spectrum.
Below is a breathtaking image shared by Astronaut Scott Kelly of the HTV-5 and Canadarm2, which reached out and grappled the cargo spacecraft.


Thanks everyone for your fantastic questions! Sorry I couldn’t answer all of them. I hope you have fun on Monday, Aug. 21st and share your photos and experiences with us! https://www.flickr.com/groups/nasa-eclipse2017/
Safe viewing and talk to you later! https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/safety
Stars Make Firework Supplies!
The next time you see fireworks, take a moment to celebrate the cosmic pyrotechnics that made them possible. From the oxygen and potassium that help fireworks burn to the aluminum that makes sparklers sparkle, most of the elements in the universe wouldn’t be here without stars.
From the time the universe was only a few minutes old until it was about 400 million years old, the cosmos was made of just hydrogen, helium and a teensy bit of lithium. It took some stellar activity to produce the rest of the elements!

Stars are element factories
Even after more than 13 billion years, the hydrogen and helium that formed soon after the big bang still make up over 90 percent of the atoms in the cosmos. Most of the other elements come from stars.

Stars began popping into the universe about 400 million years after the big bang. That sounds like a long time, but it’s only about 3% of the universe’s current age!
Our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will study the universe’s early days to help us learn more about how we went from a hot, soupy sea of atoms to the bigger cosmic structures we see today. We know hydrogen and helium atoms gravitated together to form stars, where atoms could fuse together to make new elements, but we're not sure when it began happening. Roman will help us find out.

The central parts of atoms, called nuclei, are super antisocial – it takes a lot of heat and pressure to force them close together. Strong gravity in the fiery cores of the first stars provided just the right conditions for hydrogen and helium atoms to combine to form more elements and generate energy. The same process continues today in stars like our Sun and provides some special firework supplies.
Carbon makes fireworks explode, helps launch them into the sky, and is even an ingredient in the “black snakes” that seem to grow out of tiny pellets. Fireworks glow pink with help from the element lithium. Both of these elements are created by average, Sun-like stars as they cycle from normal stars to red giants to white dwarfs.
Eventually stars release their elements into the cosmos, where they can be recycled into later generations of stars and planets. Sometimes they encounter cosmic rays, which are nuclei that have been boosted to high speed by the most energetic events in the universe. When cosmic rays collide with atoms, the impact can break them apart, forming simpler elements. That’s how we get boron, which can make fireworks green, and beryllium, which can make them silver or white!

Since massive stars have even stronger gravity in their cores, they can fuse more elements – all the way up to iron. (The process stops there because instead of producing energy, fusing iron is so hard to do that it uses up energy.)
That means the sodium that makes fireworks yellow, the aluminum that produces silver sparks (like in sparklers), and even the oxygen that helps fireworks ignite were all first made in stars, too! A lot of these more complex elements that we take for granted are actually pretty rare throughout the cosmos, adding up to less than 10 percent of the atoms in the universe combined!
Fusion in stars only got us through iron on the periodic table, so where do the rest of our elements come from? It’s what happens next in massive stars that produces some of the even more exotic elements.

Dying stars make elements too!
Once a star many times the Sun’s mass burns through its fuel, gravity is no longer held in check, and its core collapses under its own weight. There, atoms are crushed extremely close together – and they don’t like that! Eventually it reaches a breaking point and the star explodes as a brilliant supernova. Talk about fireworks! These exploding stars make elements like copper, which makes fireworks blue, and zinc, which creates a smoky effect.
Something similar can happen when a white dwarf star – the small, dense core left behind after a Sun-like star runs out of fuel – steals material from a neighboring star. These white dwarfs can explode as supernovae too, spewing elements like the calcium that makes fireworks orange into the cosmos.

When stars collide
White dwarfs aren’t the only “dead” stars that can shower their surroundings with new elements. Stars that are too massive to leave behind white dwarfs but not massive enough to create black holes end up as neutron stars.
If two of these extremely dense stellar skeletons collide, they can produce all kinds of elements, including the barium that makes fireworks bright green and the antimony that creates a glitter effect. Reading this on a phone or computer? You can thank crashing dead stars for some of the metals that make up your device, too!

As for most of the remaining elements we know of, we've only seen them in labs on Earth so far.
Sounds like we’ve got it all figured out, right? But there are still lots of open questions. Our Roman Space Telescope will help us learn more about how elements were created and distributed throughout galaxies. That’s important because the right materials had to come together to form the air we breathe, our bodies, the planet we live on, and yes – even fireworks!
So when you’re watching fireworks, think about their cosmic origins!
Learn more about the Roman Space Telescope at: https://roman.gsfc.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Glacier Turns into a ‘Snow Swamp’
In just four days this summer, miles of snow melted from Lowell Glacier in Canada. Mauri Pelto, a glaciologist at Nichols College, called the area of water-saturated snow a “snow swamp.”

These false-color images show the rapid snow melt in Kluane National Park in the Yukon Territory. The first image was taken on July 22, 2018, by the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2; the next image was acquired on July 26, 2018, by the Landsat 8 satellite.
Ice is shown as light blue, while meltwater is dark blue. On July 26, the slush covered more than 25 square miles (40 square km).
During those four days, daily temperatures 40 miles (60 km) northeast of the glacier reached 84 degrees Fahrenheit (29 degrees Celsius) — much higher than normal for the region in July.
Read more: https://go.nasa.gov/2Q9JSeO
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Flying to New Heights With the Magnetospheric Multiscale Mission
A mission studying Earth’s magnetic field by flying four identical spacecraft is headed into new territory.

The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, has been studying the magnetic field on the side of Earth facing the sun, the day side – but now we’re focusing on something else. On February 9, MMS started the three-month-long process of shifting to a new orbit.

One key thing MMS studies is magnetic reconnection – a process that occurs when magnetic fields collide and re-align explosively into new positions. The new orbit will allow MMS to study reconnection on the night side of the Earth, farther from the sun.

Magnetic reconnection on the night side of Earth is thought to be responsible for causing the northern and southern lights.

To study the interesting regions of Earth’s magnetic field on the night side, the four MMS spacecraft are being boosted into an orbit that takes them farther from Earth than ever before. Once it reaches its final orbit, MMS will shatter its previous Guinness World Record for highest altitude fix of a GPS.
To save on fuel, the orbit is slowly adjusted over many weeks. The boost to take each spacecraft to its final orbit will happen during the first week of April.

On April 19, each spacecraft will be boosted again to raise its closest approach to Earth, called perigee. Without this step, the spacecraft would be way too close for comfort -- and would actually reenter Earth’s atmosphere next winter!

The four MMS spacecraft usually fly really close together – only four miles between them – in a special pyramid formation called a tetrahedral, which allows us to examine the magnetic environment in three dimensions.

But during orbit adjustments, the pyramid shape is broken up to make sure the spacecraft have plenty of room to maneuver. Once MMS reaches its new orbit in May, the spacecraft will be realigned into their tetrahedral formation and ready to do more 3D magnetic science.

Learn more about MMS and find out what it’s like to fly a spacecraft.

For Earth Day, we’re inviting you to take a moment to celebrate our wonderful water world, Earth. As far as we know, our Blue Marble is the only place in the universe with life, and that life depends on water. Snap a photo of yourself outside and tag it #GlobalSelfie – bonus points if your selfie features your favorite body of water! http://go.nasa.gov/3xFt0H0
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Meet Fermi: Our Eyes on the Gamma-Ray Sky
Black holes, cosmic rays, neutron stars and even new kinds of physics — for 10 years, data from our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have helped unravel some of the biggest mysteries of the cosmos. And Fermi is far from finished!

On June 11, 2008, at Cape Canaveral in Florida, the countdown started for Fermi, which was called the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST) at the time.
The telescope was renamed after launch to honor Enrico Fermi, an Italian-American pioneer in high-energy physics who also helped develop the first nuclear reactor.
Fermi has had many other things named after him, like Fermi’s Paradox, the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, the Enrico Fermi Nuclear Generating Station, the Enrico Fermi Institute, and the synthetic element fermium.

Photo courtesy of Argonne National Laboratory
The Fermi telescope measures some of the highest energy bursts of light in the universe; watching the sky to help scientists answer all sorts of questions about some of the most powerful objects in the universe.
Its main instrument is the Large Area Telescope (LAT), which can view 20% of the sky at a time and makes a new image of the whole gamma-ray sky every three hours. Fermi’s other instrument is the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor. It sees even more of the sky at lower energies and is designed to detect brief flashes of gamma-rays from the cosmos and Earth.

This sky map below is from 2013 and shows all of the high energy gamma rays observed by the LAT during Fermi’s first five years in space. The bright glowing band along the map’s center is our own Milky Way galaxy!

So what are gamma rays?
Well, they’re a form of light. But light with so much energy and with such short wavelengths that we can’t see them with the naked eye. Gamma rays require a ton of energy to produce — from things like subatomic particles (such as protons) smashing into each other.
Here on Earth, you can get them in nuclear reactors and lightning strikes. Here’s a glimpse of the Seattle skyline if you could pop on a pair of gamma-ray goggles. That purple streak? That’s still the Milky Way, which is consistently the brightest source of gamma rays in our sky.

In space, you find that kind of energy in places like black holes and neutron stars. The raindrop-looking animation below shows a big flare of gamma rays that Fermi spotted coming from something called a blazar, which is a kind of quasar, which is different from a pulsar... actually, let’s back this up a little bit.

One of the sources of gamma rays that Fermi spots are pulsars. Pulsars are a kind of neutron star, which is a kind of star that used to be a lot bigger, but collapsed into something that’s smaller and a lot denser. Pulsars send out beams of gamma rays. But the thing about pulsars is that they rotate.
So Fermi only sees a beam of gamma rays from a pulsar when it’s pointed towards Earth. Kind of like how you only periodically see the beam from a lighthouse. These flashes of light are very regular. You could almost set your watch by them!

Quasars are supermassive black holes surrounded by disks of gas. As the gas falls into the black hole, it releases massive amount of energy, including — you guessed it — gamma rays. Blazars are quasars that send out beams of gamma rays and other forms of light — right in our direction.
When Fermi sees them, it’s basically looking straight down this tunnel of light, almost all the way back to the black hole. This means we can learn about the kinds of conditions in that environment when the rays were emitted. Fermi has found about 5,500 individual sources of gamma rays, and the bulk of them have been blazars, which is pretty nifty.

But gamma rays also have many other sources. We’ve seen them coming from supernovas where stars die and from star factories where stars are born. They’re created in lightning storms here on Earth, and our own Sun can toss them out in solar flares.
Gamma rays were in the news last year because of something Fermi spotted at almost the same time as the National Science Foundation (NSF)’s Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) and European Gravitational Observatory’s Virgo on August 17, 2017. Fermi, LIGO, Virgo, and numerous other observatories spotted the merger of two neutron stars. It was the first time that gravitational waves and light were confirmed to come from the same source.

Fermi has been looking at the sky for almost 10 years now, and it’s helped scientists advance our understanding of the universe in many ways. And the longer it looks, the more we’ll learn. Discover more about how we’ll be celebrating Fermi’s achievements all year.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Will Perseverance be near any other Rovers?

🌊🌊🌊 This natural-color image captured May 17 near the coast of Guinea-Bissau in West Africa shows estuaries branching out like a network of roots from a plant. Crossfading to a data visualization helps reveals water clarity due to dissolved organic matter in Guinea-Bissau.
With their long tendrils, the rivers meander through the country’s lowland plains to join the Atlantic Ocean. On the way, they carry water, nutrients, but also sediments out from the land. These estuaries play an important role in agriculture for this small country that is mostly made up of flat terrain. While the coastal valleys can flood often during the rainiest part of the year in the summer, the rain makes the valleys good locations for farming, especially rice cultivation. Using satellite data, researchers continue to observe the country's change in terrain and as a result, they're documenting a regrowth of previously eroded coastal areas.
Learn more
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How had your background in the US Air Force as a flight test engineer prepare you for the challenges and demands of being an astronaut?
-
 stariceling reblogged this · 1 year ago
stariceling reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 decorbuziers-memorial liked this · 1 year ago
decorbuziers-memorial liked this · 1 year ago -
 khomsan-10110 liked this · 1 year ago
khomsan-10110 liked this · 1 year ago -
 pinkstor3 liked this · 1 year ago
pinkstor3 liked this · 1 year ago -
 crashalido liked this · 3 years ago
crashalido liked this · 3 years ago -
 inasociety liked this · 3 years ago
inasociety liked this · 3 years ago -
 anomaloustarstuff reblogged this · 3 years ago
anomaloustarstuff reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 persianpolaris liked this · 4 years ago
persianpolaris liked this · 4 years ago -
 skeletonb0n3s liked this · 4 years ago
skeletonb0n3s liked this · 4 years ago -
 missmannersposts reblogged this · 4 years ago
missmannersposts reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thehkr liked this · 4 years ago
thehkr liked this · 4 years ago -
 foxfootunderscore liked this · 4 years ago
foxfootunderscore liked this · 4 years ago -
 ororuba reblogged this · 4 years ago
ororuba reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 ororuba liked this · 4 years ago
ororuba liked this · 4 years ago -
 prismetric-technologies liked this · 4 years ago
prismetric-technologies liked this · 4 years ago -
 aikookinomaii-blog liked this · 4 years ago
aikookinomaii-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 adam-mickiewicz-is-overrated liked this · 4 years ago
adam-mickiewicz-is-overrated liked this · 4 years ago -
 urippadeze liked this · 4 years ago
urippadeze liked this · 4 years ago -
 lijretta liked this · 4 years ago
lijretta liked this · 4 years ago -
 robinwaaaaa liked this · 4 years ago
robinwaaaaa liked this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago -
 swampcastle reblogged this · 4 years ago
swampcastle reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 naturaleccentricity liked this · 4 years ago
naturaleccentricity liked this · 4 years ago -
 btcheslovemexxx liked this · 4 years ago
btcheslovemexxx liked this · 4 years ago -
 sheephead6 liked this · 4 years ago
sheephead6 liked this · 4 years ago -
 space-up-my-sleeve reblogged this · 4 years ago
space-up-my-sleeve reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 sparkles12 liked this · 4 years ago
sparkles12 liked this · 4 years ago -
 shoruku liked this · 4 years ago
shoruku liked this · 4 years ago -
 mgunawan2020-blog liked this · 4 years ago
mgunawan2020-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 lenthebabe liked this · 4 years ago
lenthebabe liked this · 4 years ago -
 saltythexfilesindianjonescop liked this · 4 years ago
saltythexfilesindianjonescop liked this · 4 years ago -
 hitchcockphoto liked this · 4 years ago
hitchcockphoto liked this · 4 years ago -
 pineconeishere liked this · 4 years ago
pineconeishere liked this · 4 years ago -
 jopomopo liked this · 4 years ago
jopomopo liked this · 4 years ago -
 ori-the-axolotl liked this · 4 years ago
ori-the-axolotl liked this · 4 years ago -
 mindsincr-s liked this · 4 years ago
mindsincr-s liked this · 4 years ago -
 dragons-barb liked this · 4 years ago
dragons-barb liked this · 4 years ago -
 confortavelmente-entorpecido liked this · 4 years ago
confortavelmente-entorpecido liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts