Excited About The #CountdownToMars? We've Got You Covered.

Excited about the #CountdownToMars? We've got you covered.
We've created a virtual Mars photo booth, 3D rover experience and more for you to put your own creative touch on wishing Perseverance well for her launch to the Red Planet! Check it out, HERE.
Don’t forget to mark the July 30 launch date on your calendars!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

It’s the time of year for summer break, swimming, and oh, yes storms. June 1 marks the beginning of hurricane season on the Atlantic coast, but we’re not alone. Our neighboring planets have seen their fair share of volatile weather, too (like the Cassini spacecraft’s view of the unique six-sided jet stream at Saturn’s north pole known as “the hexagon”).
This week, we present 10 of the solar system’s greatest storms.

1. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
With tumultuous winds peaking at 400 mph, the Great Red Spot has been swirling wildly over Jupiter’s skies for at least 150 years and possibly much longer. People saw a big spot on Jupiter as early as the 1600s when they started stargazing through telescopes, though it’s unclear whether they were looking at a different storm. Today, scientists know the Great Red Spot has been there for a while, but what causes its swirl of reddish hues remains to be discovered. More >

2. Jupiter’s Little Red Spot
Despite its unofficial name, the Little Red Spot is about as wide as Earth. The storm reached its current size when three smaller spots collided and merged in the year 2000. More >

3. Saturn’s Hexagon
The planet’s rings might get most of the glory, but another shape’s been competing for attention: the hexagon. This jet stream is home to a massive hurricane tightly centered on the north pole, with an eye about 50 times larger than the average hurricane eye on Earth. Numerous small vortices spin clockwise while the hexagon and hurricane spin counterclockwise. The biggest of these vortices, seen near the lower right corner of the hexagon and appearing whitish, spans about 2,200 miles, approximately twice the size of the largest hurricane on Earth. More>
4. Monster Storm on Saturn
A tempest erupted in 2010, extending approximately 9,000 miles north-south large enough to eventually eat its own tail before petering out. The storm raged for 200 days, making it the longest-lasting, planet-encircling storm ever seen on Saturn. More >

5. Mars’ Dust Storm
Better cover your eyes. Dust storms are a frequent guest on the Red Planet, but one dust storm in 2001 larger by far than any seen on Earth raised a cloud of dust that engulfed the entire planet for three months. As the Sun warmed the airborne dust, the upper atmospheric temperature rose by about 80 degrees Fahrenheit. More >

6. Neptune’s Great Dark Spot
Several large, dark spots on Neptune are similar to Jupiter’s hurricane-like storms. The largest spot, named the “Great Dark Spot” by its discoverers, contains a storm big enough for Earth to fit neatly inside. And, it looks to be an anticyclone similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. More >

7. Sun Twister
Not to be confused with Earth’s tornadoes, a stalk-like prominence rose up above the Sun, then split into about four strands that twisted themselves into a knot and dispersed over a two-hour period. This close-up shows the effect is one of airy gracefulness. More >

8. Titan’s Arrow-shaped Storm
The storm blew across the equatorial region of Titan, creating large effects in the form of dark and likely “wet” from liquid hydrocarbons areas on the surface of the moon. The part of the storm visible here measures 750 miles in length east-to-west. The wings of the storm that trail off to the northwest and southwest from the easternmost point of the storm are each 930 miles long. More >

9. Geomagnetic Storms
On March 9, 1989, a huge cloud of solar material exploded from the sun, twisting toward Earth. When this cloud of magnetized solar material called a coronal mass ejection reached our planet, it set off a chain of events in near-Earth space that ultimately knocked out an entire power grid area to the Canadian province Quebec for nine hours. More >
10. Super Typhoon Tip
Back on Earth, Typhoon Tip of 1979 remains the biggest storm to ever hit our planet, making landfall in Japan. The tropical cyclone saw sustained winds peak at 190 mph and the diameter of circulation spanned approximately 1,380 miles. Fortunately, we now have plans to better predict future storms on Earth. NASA recently launched a new fleet of hurricane-tracking satellites, known as the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS), which will use the same GPS technology you and I use in our cars to measure wind speed and ultimately improve how to track and forecast hurricanes. More >
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Neutron Stars Are Even Weirder Than We Thought
Let’s face it, it’s hard for rapidly-spinning, crushed cores of dead stars NOT to be weird. But we’re only beginning to understand how truly bizarre these objects — called neutron stars — are.

Neutron stars are the collapsed remains of massive stars that exploded as supernovae. In each explosion, the outer layers of the star are ejected into their surroundings. At the same time, the core collapses, smooshing more than the mass of our Sun into a sphere about as big as the island of Manhattan.

Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) telescope on the International Space Station is working to discover the nature of neutron stars by studying a specific type, called pulsars. Some recent results from NICER are showing that we might have to update how we think about pulsars!
Here are some things we think we know about neutron stars:
Pulsars are rapidly spinning neutron stars ✔︎
Pulsars get their name because they emit beams of light that we see as flashes. Those beams sweep in and out of our view as the star rotates, like the rays from a lighthouse.

Pulsars can spin ludicrously fast. The fastest known pulsar spins 43,000 times every minute. That’s as fast as blender blades! Our Sun is a bit of a slowpoke compared to that — it takes about a month to spin around once.
The beams come from the poles of their strong magnetic fields ✔︎
Pulsars also have magnetic fields, like the Earth and Sun. But like everything else with pulsars, theirs are super-strength. The magnetic field on a typical pulsar is billions to trillions of times stronger than Earth’s!

Near the magnetic poles, the pulsar’s powerful magnetic field rips charged particles from its surface. Some of these particles follow the magnetic field. They then return to strike the pulsar, heating the surface and causing some of the sweeping beams we see.
The beams come from two hot spots… ❌❓✔︎ 🤷🏽
Think of the Earth’s magnetic field — there are two poles, the North Pole and the South Pole. That’s standard for a magnetic field.

On a pulsar, the spinning magnetic field attracts charged particles to the two poles. That means there should be two hot spots, one at the pulsar’s north magnetic pole and the other at its south magnetic pole.
This is where things start to get weird. Two groups mapped a pulsar, known as J0030, using NICER data. One group found that there were two hot spots, as we might have expected. The other group, though, found that their model worked a little better with three (3!) hot spots. Not two.
… that are circular … ❌❓✔︎ 🤷🏽
The particles that cause the hot spots follow the magnetic field lines to the surface. This means they are concentrated at each of the magnetic poles. We expect the magnetic field to appear nearly the same in any direction when viewed from one of the poles. Such symmetry would produce circular hot spots.

In mapping J0030, one group found that one of the hot spots was circular, as expected. But the second spot may be a crescent. The second team found its three spots worked best as ovals.
… and lie directly across from each other on the pulsar ❌❓✔︎ 🤷🏽
Think back to Earth’s magnetic field again. The two poles are on opposite sides of the Earth from each other. When astronomers first modeled pulsar magnetic fields, they made them similar to Earth’s. That is, the magnetic poles would lie at opposite sides of the pulsar.

Since the hot spots happen where the magnetic poles cross the surface of the pulsar, we would expect the beams of light to come from opposite sides of the pulsar.

But, when those groups mapped J0030, they found another surprising characteristic of the spots. All of the hot spots appear in the southern half of the pulsar, whether there were two or three of them.

This also means that the pulsar’s magnetic field is more complicated than our initial models!
J0030 is the first pulsar where we’ve mapped details of the heated regions on its surface. Will others have similarly bizarre-looking hotspots? Will they bring even more surprises? We’ll have to stay tuned to NICER find out!
And check out the video below for more about how this measurement was done.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Discover NASA Technology in Your Life
Have you ever wondered how space exploration impacts you? “Spinoffs” are products and services developed from NASA technology or improved through NASA partnerships. These innovations—first created to help explore space and study Earth—are responsible for billions of dollars in both revenue and saved costs, tens of thousands of jobs created, and for changing the world around us.
Our NASA Home & City interactive web platform allows you to explore some of the spinoff technologies you can find in your everyday life, demonstrating the wider benefits of America’s investments in its space program.

Here are the seven most unexpected items you can find in your homes and cities which were “spun off” from technologies to enable the study and exploration of space.
1. Wireless Headsets
“That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” On July 20, 1969, millions were glued to their television sets when NASA astronaut Neil Armstrong offered these famous words via live broadcast, upon becoming the first man to ever step foot on the Moon. This historic transmission was delivered from Armstrong’s headset to the headsets of Mission Control personnel at NASA, and then on to the world.
Improved by the technology that carried Neil Armstrong’s words, more compact and comfortable headsets were developed for airline pilots in the 1960s and '70s. Today those advancements continue to evolve in all forms of communications and telephone equipment. Mobile headsets provide greater efficiency and flexibility for everyone from professionals to video gamers.

2. Water Quality Monitoring
On the International Space Station very little goes to waste. This includes water, which is recovered from every possible source, cleaned and recycled.
Following our development of a simplified bacteria test for water quality on the space station, one engineer created a foundation to distribute test kits suitable for use in rural communities around the world. Water contamination is still a major problem in many places, and the test helps local communities and governments obtain and share water quality data using a smartphone app.
3. Skin Cream
We know that on Earth, gravity is a constant. For astronauts in orbit, however, it’s a different story—and according to a scientist at NASA's Johnson Space Center, studying what happens to bodies in microgravity “can lead to significant new discoveries in human biology for the benefit of humankind.”
As our researchers experimented with replicating microgravity conditions in the lab, they invented a bioreactor that could help simulate conditions that human cells experience in a space-like environment. This allowed them to perform tissue-growth experiments on the ground and in space, and eventually, to consider the question of how to protect human cells from the toxic effects of long-duration space missions.
Now, thanks to this NASA-patented bioreactor, one company uses agents from human cells that produce collagen to enrich its skin cream products. Lab tests have shown the rejuvenating cream to increase skin moisture content by 76 percent and reduce darkness and wrinkles by more than 50 percent.

4. Acoustic Guitars
From its start, NASA has innovated in all branches of aeronautics, which has led to numerous advances in helicopters, including ways to limit vibrations as they fly and advanced composites to build tougher, safer vehicles.
An industrious helicopter manufacturer that built up its expertise with NASA contracts later used the same special vibration analysis equipment to enhance the sound of acoustic guitars. The company also built the body out of a fiberglass composite used for rotor blades. The resulting instruments are stronger and less expensive to produce than those of traditional rosewood and produce a rich, full sound.

5. Tiny [Mobile] Homes
While the International Space Station is the largest spacecraft ever flown—it's about the size of a football field—living and working space for astronauts is still at a premium. NASA created a studio called the Habitability Design Center to experiment with the interior design of spacecraft to maximize usable space and make scientific research as efficient and effective as possible.
An architect who helped NASA design the interior of the International Space Station launched a company specializing in compact trailers for camping and exploration. Suitable for a full hookup campsite or going completely off-grid, the company's flagship trailer can accommodate two adults and two children for sleeping and can be customized with a range of features including a shower, refrigerator, toilet, and more. And it all fits into a unit light enough to be towed by a four-cylinder car.

6. Blue Light Blocking Ski Goggles
Skiers and snowboarders face extremely bright sunlight, especially when it's reflected off the white snow. That can make it hard to see, and not just because of glare. The blue in sunlight makes it more difficult to discern colors at the edge of the visible light spectrum, like reds. A NASA-designed filter used in snow goggles helps block up to 95 percent of blue light, making it easier for people on the slopes to see the terrain clearly.

7. Implants for the Hearing Impaired
Hearing aids, which make sound louder, can only do so much for those who were born or have become deaf. Cochlear implants work in a completely different way, converting sound into digital signals that can be processed by the brain. And the technology traces back in part to a NASA space shuttle engineer who used skills in electronics instrumentation and his own experiences with hearing loss to develop an early version of the life-changing device.

These are just a few examples of thousands of NASA Spinoff and dual-purpose technologies benefiting the world around us.
Trace space back to you and visit NASA Home and City today!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
SpaceX Dragon: What’s Onboard?
SpaceX is scheduled to launch its Dragon spacecraft into orbit on April 8, which will be the company’s eighth mission under our Commercial Resupply Services contract. This flight will deliver science and supplies to the International Space Station.

The experiments headed to the orbiting laboratory will help us test the use of an expandable space habitat in microgravity, assess the impact of antibodies on muscle wasting in a microgravity environment, use microgravity to seek insight into the interactions of particle flows at the nanoscale level and use protein crystal growth in microgravity to help in the design of new drugs to fight disease. Here’s an in-depth look at each of them:
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM)

Space is in limited supply on the International Space Station, but with BEAM, the amount of crew space could be expanded! BEAM is an experimental expandable capsule that attaches to the space station. After installation, it will expand to roughly 13-feet long and 10.5 feet in diameter, which would provide a large volume where a crew member could enter. During the two-year test mission, astronauts will enter the module for a few hours three-to-four times a year to retrieve sensor data and conduct assessments of the module’s condition.
Why? Expandable habitats greatly decrease the amount of transport volume at launch for future space missions. They not only take up less room on a rocket, but also provide greatly enhanced space for living and working once they are set up.
The Rodent Research-3-Eli Lilly

The Rodent Research-3-Eli Lilly investigation will use mice as a model for human health to study whether certain drugs might prevent muscle or bone loss while in microgravity.
Why? Crew members experience significant decreases in their bone density and muscle mass during spaceflight if they do not get enough exercise during long-duration missions. The results could expand scientist’s understanding of muscle atrophy and bone loss in space, by testing an antibody that has been known to prevent muscle wasting in mice on Earth.
Microbial Observatory-1
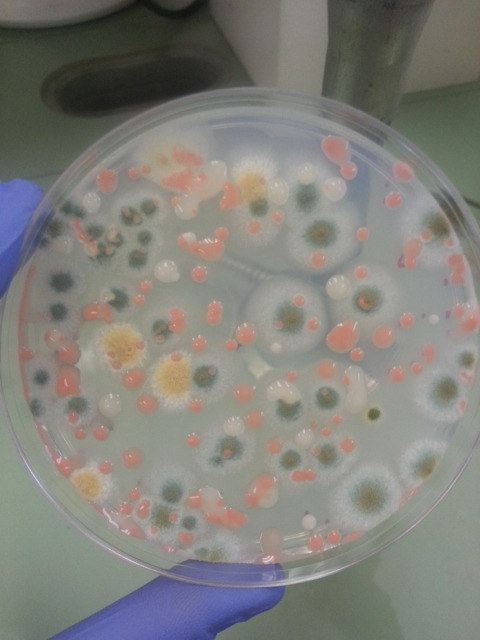
The Microbial Observatory-1 experiment will track and monitor changes to microbial flora over time on the space station.
Why? Obtaining data on these microbial flora could help us understand how such microbes could affect crew health during future long-duration missions.
Micro-10

The Micro-10 investigation will study how the stress of microgravity triggers changes in growth, gene expression, physical responses and metabolism of a fungus called Aspergillus nidulans.
Why? This experiment will study fungi in space for the purpose of potentially developing new medicine for use both in space and on Earth. The stressfull environment of space causes changes to all forms of life, from bacteria and fungi, to animals and people.
Genes in Space-1

Genes in Space-1 is a student-designed experiment that will test whether the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) — which is a fast and relatively inexpensive technique that can amplify or “photocopy” small segments of DNA — could be used to study DNA alterations that crew experience during spaceflight.
Why? In space, the human immune system’s function is altered. Findings from this experiment could help combat some of the DNA changes that crew onboard space station experience while on orbit.
Microchannel Diffusion

Nano science and nanotechnology are the study and application of exceptionally small things and can be used across the fields of medicine, biology, computer science and many others. The way fluid moves is very different on this small scale, so scientists want to know how microparticles might interact. The Microchannel Diffusion investigation simulates these interactions by studying them at a larger scale, the microscopic level. This is only possible on the orbiting laboratory, where Earth’s gravity is not strong enough to interact with the molecules in a sample, so they behave more like they would at the nanoscale.
Why? Nanofluidic sensors could measure the air in the space station, or used to deliver drugs to specific places in the body, among other potential uses. Knowledge learned from this investigation may have implications for drug delivery, particle filtration and future technological applications for space exploration.
The CASIS Protein Crystal Growth 4 (CASIS PCG 4)

CASIS PCG 4 is made up of two investigations that both leverage the microgravity environment in the growth of protein crystals and focus on structure-based drug design (SBDD). Growing crystals in microgravity avoids some of the obstacles they face on Earth, such as sedimentation.
Why? SBDD is an integral component in the drug discovery and development process. It relies on three-dimensional, structural information provided by the protein crystallography to inform the design of more potent, effective and selective drugs.
Watch the Launch!

The Dragon capsule will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Launch coverage begins at 3:15 p.m. EDT, with launch scheduled for 4:43 p.m. Watch live online on NASA Television: nasa.gov/nasatv
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
🔎 Lava Lake Discovery
🌋 Raikoke Volcano Eruption
🔥 Uptick in Amazon Fire Activity
2019 brought many memorable events on Planet Earth, and NASA satellites and astronauts captured a lot of the action! From new discoveries to tracking natural events and capturing amazing scenery, here are a few highlights from around the globe.
Read more about the images in this video, here.
Download Software Used to Get Rovers to the Red Planet
Watching our Perseverance rover safely land on the surface of Mars is the kind of historic feat that gets our adventure-loving hearts racing.

Launching and landing rovers on Mars requires overcoming challenges like defying gravity on two planets, surviving the extreme heat of atmospheric entry, and avoiding rocky obstacles. This takes more than just rocket science – it takes incredible software too.
Did you know that some of the same tried and tested software that helped ensure a safe arrival for Perseverance (and its predecessor, Curiosity) can be downloaded – by you...for free...right now?

Our 2021-22 Software Catalog is full of codes made for space that can be used by entrepreneurs, teachers, gamers, or just about anyone. Whether you are curious about the Martian atmosphere, want to visualize the inside of a volcano, or have an application we’ve never even considered, our software may be able to help. Check out our full site, updated regularly with the latest codes available for download.
Here are a few examples of what you could do with our software!
1. Simulate the Martian atmosphere to prepare spacecrafts for landing

To prepare for exactly what a spacecraft will face on landing day, no matter the location scientists choose, we created software that simulates the Martian atmosphere. The code, Mars (GRAM), is now available to anyone.
We also have a version that simulates Earth's atmosphere, allowing users (especially those in the world of drone design) a way to replicate and design for, potentially dangerous conditions without ever stepping away from the computer.
2. Explore the Red Planet virtually from home with help from the Curiosity rover team
Originally developed for scientists and engineers working on the Curiosity rover mission, OnSight allowed the team a virtual way to walk on and look around Mars. Using an immersive display, such as a virtual reality headset, scientists could see the Red Planet the way a rover would.
This software can also be used to provide virtual experiences of places here on Earth, such as caves and lava fields.
3. Dodge disasters with a risk management tool made for space missions

When preparing for complex space missions, like the upcoming Mars Sample Return mission, it’s crucial to examine how different elements, independently and collectively, impact the probability of success.
But risk management has become an important tool for businesses of all disciplines, from engineering to accounting – and the Space Mission Architecture and Risk Analysis Tool (SMART) could help.
Sound interesting? The NASA software catalog has these and more than 800 additional codes ready for download.
You can also follow our Technology Transfer program on Twitter to learn more about software and technology that can be put to use on Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
A room with Earth views! 🌎 Earlier this week, astronaut Ricky Arnold captured this spectacular view of our home planet while he was orbiting at a speed of 17,500 miles per hour. If you’re wondering where in the world this video was taken, it starts as the International Space Station is above San Francisco and moving southward through the Americas.
Each day, the station completes 16 orbits of our home planet as the six humans living and working aboard our orbiting laboratory conduct important science and research. Their work will not only benefit life here on Earth, but will help us venture deeper into space than ever before.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Get Space-Crafty with Earth Science!
It’s time to get space-crafty! (Get it?) We’re getting ready to launch Landsat 9 into space this fall, and we want to know, how does Landsat inspire you?
For nearly 50 years, Landsat satellites have been collecting important data and taking beautiful images of Earth, as a partnership between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Scientists and policy makers alike use this data to understand climate change, deforestation, the growth of cities, and so much more.

In celebration of the Landsat 9 launch in September, we are calling all crafters to create space-crafts inspired by your favorite Landsat image! From watercolor paintings to needlework to frosted cakes, let your creativity flow and show us how you see Landsat images.
Post a picture of your craft on Instagram, Twitter or Facebook with the hashtag #LandsatCraft. We will spotlight some on social media!
For a little inspiration, here are some #LandsatCraft examples from some of the people who work with Landsat:

“Looking through the Visible Earth Landsat gallery for inspiration, I saw the Landsat Image Mosaic of Antarctica (LIMA) and knew immediately what I had to do -- recreate it in a mosaic of my own. LIMA is a composite of more than 1,000 cloud-free Landsat 7 images of Antarctica, and when it was released in 2007 it was our first high resolution, true-color look at the icy continent.” – Kate Ramsayer, NASA Landsat Communications Coordinator

“I love embroidering satellite imagery and NASA data. For Landsat, I wanted something with lots of straight lines -- much easier to stitch! -- and crop fields like these fit the bill. It’s amazing how clearly we can see the influence of human activities in satellite imagery like this. It’s a constant reminder of the effect we have on our home planet.” – Katy Mersmann, Earth Science Social Media Lead

“We didn’t have the discipline or the organizational skills to do any of the really, really fancy images, like Lena Delta, so we chose Garden City, Kansas in 1972. We added a model of Landsat 1, too.” – Ryan Fitzgibbons, Earth Science Producer, and Charles Fitzgibbons, Age 8

"I was inspired by this Landsat image which demonstrates how we can use satellite imagery to remotely monitor cover crop performance, a sustainable farming practice that promotes soil health. Since I began working with NASA Harvest, NASA's Food Security and Agriculture Program, I've come to understand the critical importance of conservation agriculture and resilient farmlands in support of a food secure future for all, especially in the face of a changing climate." – Mary Mitkish, NASA Harvest Communications Lead

“I chose particular ingredients that represent the Landsat qualities that we celebrate:
The base spirit is gin because Landsat data is clean and precise. Vermouth represents our foreign collaborators. Using both lemon and lime juices signifies the diverse uses of the data. The ginger is for the land we study. The apple, well, because it’s American. The club soda makes it a long drink, for the long data record.” – Matthew Radcliff, NASA Landsat Producer

“Last year for the 50th Earth Day, I created this poster, inspired by our views of river deltas -- many captured by Landsat satellites -- which are particularly beautiful and evocative of water coursing through our land like a circulation system of nature. In 2000, Landsat 7 took one of my favorite images of the Lena Delta, which is the basis for this art.” – Jenny Mottar, Art Director for NASA Science
Are you feeling inspired to create yet? We’re so excited to see your #LandsatCraft projects! Follow NASA Earth on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram to see if your art is shared!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
10 Space & Football Facts You Probably Didn’t Know
There are more connections between space and football than you may have originally thought. Here are a few examples of how...
1. The International Space Station and a football field are basically the same size

Yes, that’s right! The International Space Station measures 357 feet end-to-end. That’s almost equivalent to the length of a football field including the end zones (360 feet).
2. It would take over 4,000 footballs to fill the Orion spacecraft

Our Orion spacecraft is being designed to carry astronauts to deep space destinations, like Mars! It will launch atop the most powerful rocket ever built, the Space Launch System rocket. If you were to fill the Orion spacecraft with footballs instead of crew members, you would fit a total of 4,625!
3. Our new Space Launch System rocket is taller than a football field is long

We’re building the most powerful rocket ever, the Space Launch System. At its full height it will stand 384 feet – 24 feet taller than a football field is long.
4. The crew living on space station will see the day begin and end…twice…during the Super Bowl

An average NFL game lasts more than three hours. Traveling at 17,500 mph, the crew on the space station will see two sunrises and two sunsets in that time…they see 16 sunrises and sunsets each day!
5. Playing football on Mars would be…lighter

On Mars, a football would weigh less than half a pound, while a 200-pund football player would weigh just about 75 pounds.
6. It would take over 3,000 hours for a football to reach the Moon

Talk about going long…if you threw a football to the Moon at 60 mph, the average speed of an NFL pass, it would take 3,982 hours, or 166 days, to get there. The quickest trip to the Moon was the New Horizons probe, which zipped pass the Moon in just 8 hours 35 minutes on its way to Pluto
7. The longest field goal kick in history would’ve been WAY easier to make on Mars

The longest field goal kick in NFL history is 64 yards. On Mars, at 1/3 the gravity of Earth, that same field goal, ignoring air resistance, could have been made from almost two football fields away (192 yards).
8. A quarterback would be able to throw even further on Mars

Aerodynamic drag doesn’t happen on Mars. With a very thin atmosphere and low gravity to drag the ball down, a quarterback could throw the football three times as far as he could on Earth. A receiver would have to be much further down the field to catch the throw
9. Football players and astronauts both need to exercise every day

Football players must be quick and powerful, honing the physical skills necessary for their unique positions. In space, maintaining physical fitness is a top priority, since astronauts will lose bone and muscle mass if they do not keep up their strength and conditioning.
10. Clear team communication is important on the football field AND in space

During football games, calling plays and relaying information from coaches on the sidelines or in the booth to players on the field is essential. Coaches communicate directly with quarterbacks and a defensive player between plays via radio frequencies. They must have a secure and reliable system that keeps their competitors from listening in and also keeps loud fan excitement from drowning out what can be heard. Likewise, reliable communication with astronauts in space and robotic spacecraft exploring far into the solar system is key to our mission success.
A radio and satellite communications network allows space station crew members to talk to the ground-based team at control centers, and for those centers to send commands to the orbital complex.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What led you to this job? (what’s your degree in/what are your passions)
-
 ardsami liked this · 1 year ago
ardsami liked this · 1 year ago -
 infinityunitblogblogger reblogged this · 4 years ago
infinityunitblogblogger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 itsyourtimemanagement liked this · 4 years ago
itsyourtimemanagement liked this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago -
 bitsofsciencelife reblogged this · 4 years ago
bitsofsciencelife reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wolpertinger001 reblogged this · 4 years ago
wolpertinger001 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 swpeternguyen liked this · 4 years ago
swpeternguyen liked this · 4 years ago -
 bayledesign liked this · 4 years ago
bayledesign liked this · 4 years ago -
 jaredh621 liked this · 4 years ago
jaredh621 liked this · 4 years ago -
 bitsofsciencelife reblogged this · 4 years ago
bitsofsciencelife reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 blogaletselenanme liked this · 4 years ago
blogaletselenanme liked this · 4 years ago -
 zulacent liked this · 4 years ago
zulacent liked this · 4 years ago -
 biromantic-disaster liked this · 4 years ago
biromantic-disaster liked this · 4 years ago -
 teh-repository reblogged this · 4 years ago
teh-repository reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 phil-2268 reblogged this · 4 years ago
phil-2268 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 phil-2268 liked this · 4 years ago
phil-2268 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ramirokai liked this · 4 years ago
ramirokai liked this · 4 years ago -
 sparsenote liked this · 4 years ago
sparsenote liked this · 4 years ago -
 utot-atbp liked this · 4 years ago
utot-atbp liked this · 4 years ago -
 axromo458 liked this · 4 years ago
axromo458 liked this · 4 years ago -
 shyclaws liked this · 4 years ago
shyclaws liked this · 4 years ago -
 maviacomic liked this · 4 years ago
maviacomic liked this · 4 years ago -
 laellia liked this · 4 years ago
laellia liked this · 4 years ago -
 leahazel reblogged this · 4 years ago
leahazel reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 john-e-cage liked this · 4 years ago
john-e-cage liked this · 4 years ago -
 starshineselkie liked this · 4 years ago
starshineselkie liked this · 4 years ago -
 bemenotyou liked this · 4 years ago
bemenotyou liked this · 4 years ago -
 reincarnated2a3cycle liked this · 4 years ago
reincarnated2a3cycle liked this · 4 years ago -
 give-me-back-my-legions liked this · 4 years ago
give-me-back-my-legions liked this · 4 years ago -
 pendulum909 liked this · 4 years ago
pendulum909 liked this · 4 years ago -
 yannjo liked this · 4 years ago
yannjo liked this · 4 years ago -
 0dannyphantom0 reblogged this · 4 years ago
0dannyphantom0 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 0dannyphantom0 liked this · 4 years ago
0dannyphantom0 liked this · 4 years ago -
 teressadraher liked this · 4 years ago
teressadraher liked this · 4 years ago -
 asteriscuz-m liked this · 4 years ago
asteriscuz-m liked this · 4 years ago -
 lamememes101 liked this · 4 years ago
lamememes101 liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts