March For Science, CSU Chico!
March for Science, CSU Chico!
More Posts from Karlfelersii and Others
Split brain does not lead to split consciousness
A new research study contradicts the established view that so-called split-brain patients have a split consciousness. Instead, the researchers behind the study, led by UvA psychologist Yair Pinto, have found strong evidence showing that despite being characterised by little to no communication between the right and left brain hemispheres, split brain does not cause two independent conscious perceivers in one brain. Their results are published in the latest edition of the journal Brain.

Split brain is a lay term to describe the result of a corpus callosotomy, a surgical procedure first performed in the 1940s to alleviate severe epilepsy among patients. During this procedure, the corpus callosum, a bundle of neural fibres connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, is severed to prevent the spread of epileptic activity between the two brain halves. While mostly successful in relieving epilepsy, the procedure also virtually eliminates all communication between the cerebral hemispheres, thereby resulting in a ‘split brain’.
This condition was made famous by the work of Nobel laureate Roger Sperry and Michael Gazzaniga. In their canonical work, Sperry and Gazzaniga discovered that split-brain patients can only respond to stimuli in the right visual field with their right hand and vice versa. This was taken as evidence that severing the corpus callosum causes each hemisphere to gain its own consciousness.
Divided perception
For their study, Pinto and his fellow researchers conducted a series of tests on two patients who had undergone a full callosotomy. In one of the tests, the patients were placed in front of a screen and shown various objects displayed in several locations. The patients were then asked to confirm whether an object appeared and to indicate its location. In another test, they had to correctly name the object they had seen, a notorious difficulty among spit-brain patients. ‘Our main aim was to determine whether the patients performed better when responding to the left visual field with their left hand instead of their right hand and vice versa’, says Pinto, assistant professor of Cognitive Psychology. ‘This question was based on the textbook notion of two independent conscious agents: one experiencing the left visual field and controlling the left hand, and one experiencing the right visual field and controlling the right hand.’
To the researchers’ surprise, the patients were able to respond to stimuli throughout the entire visual field with all the response types: left hand, right hand and verbally. Pinto: ‘The patients could accurately indicate whether an object was present in the left visual field and pinpoint its location, even when they responded with the right hand or verbally. This despite the fact that their cerebral hemispheres can hardly communicate with each other and do so at perhaps 1 bit per second, which is less than a normal conversation. I was so surprised that I decide repeat the experiments several more times with all types of control.’

(Image caption: A depiction of the traditional view of the split brain syndrome (top) versus what the researchers actually found in two split-brain patients across a wide variety of tasks (bottom). Credit: Yair Pinto)
Undivided consciousness
According to Pinto, the results present clear evidence for unity of consciousness in split-brain patients. ‘The established view of split-brain patients implies that physical connections transmitting massive amounts of information are indispensable for unified consciousness, i.e. one conscious agent in one brain. Our findings, however, reveal that although the two hemispheres are completely insulated from each other, the brain as a whole is still able to produce only one conscious agent. This directly contradicts current orthodoxy and highlights the complexity of unified consciousness.’
In the coming period, Pinto plans to conduct research on more split-brain patients to see whether his findings can be replicated. ‘These patients, who are rapidly decreasing in numbers, are our only way to find out what happens when large subsystems in the brain no longer communicate with each other. This phenomenon raises important questions that cannot be investigated in healthy adults because we have no technique to isolate large subsystems in healthy brains.’

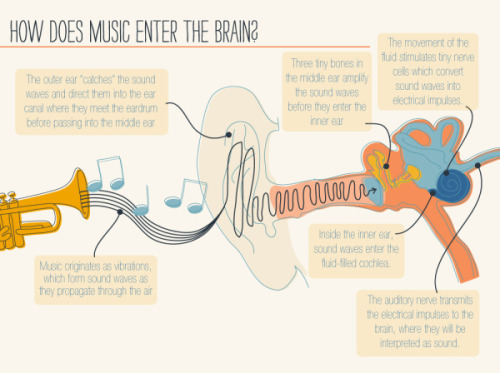
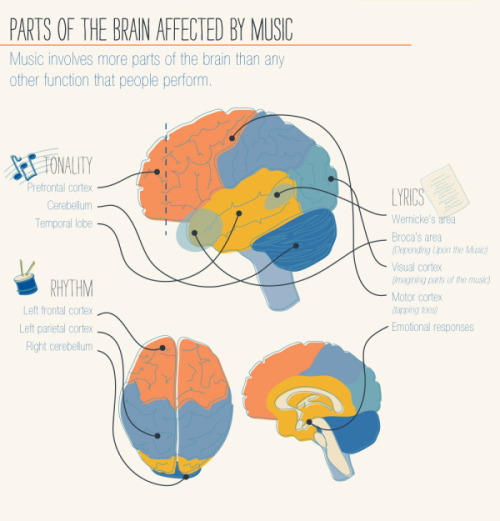
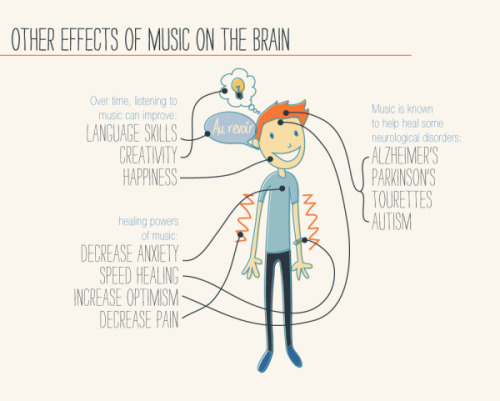

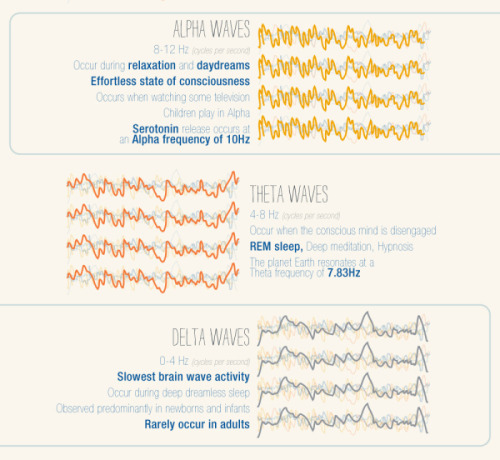

For more posts like these, go to @mypsychology

Submitted by musiq4thieves
For more posts like these, go visit psych2go
Psych2go features various psychological findings and myths. In the future, psych2go attempts to include sources to posts for the for the purpose of generating discussions and commentaries. This will give readers a chance to critically examine psychology.
How to Study Effectively | Psych2Go
4 Ways To Improve Exam Memory | Psych2Go

The 5 Languages of Love: Can You Read Your Lover as Well as You Think?

Communication problems are an extremely common issue in budding relationships. Why don’t they compliment you more often? Don’t they appreciate it when you present them with thoughtful gifts? More often than not, small questions like this can lead to much larger arguments that question affections and intentions. But what if (stay with me here) they aren’t trying to purposely hurt your feelings by brushing off your displays of affection? What if your way of saying “I love you” is just different than theirs (whaaaaat!?)?
Let me tell you about Dr. Gary Demonte Chapman. Chapman is a Ph.D. and church pastor who has dedicated his time to understanding the interworkings of relationships. Chapman coined the concept of “love languages”, explaining that we tend to express and receive love in five ways:
Words of affirmation
…..
…..
…..
…..
Continue Reading Here


Top 10 Biggest Brain Damaging Habits
1. No Breakfast
People who do not take breakfast are going to have a lower blood sugar level.This leads to an insufficient supply of nutrients to the brain causing brain degeneration.
2. Overreacting
It causes hardening of the brain arteries, leading to a decrease in mental power.
3. Smoking
It causes multiple brain shrinkage and may lead to Alzheimer disease.
4. High Sugar consumption
Too much sugar will interrupt the absorption of proteins and nutrients causing malnutrition and may interfere with brain development.
5. Air Pollution
The brain is the largest oxygen consumer in our body. Inhaling polluted air decreases the supply of oxygen to the brain, bringing about a decrease in brain efficiency.
6. Sleep Deprivation
Sleep allows our brain to rest. Long term deprivation from sleep will accelerate the death of brain
7. Head covered while sleeping
Sleeping with the head covered, increases the concentration of carbon dioxide and decrease concentration of oxygen that may lead to brain damaging effects.
8. Working your brain during illness
Working hard or studying with sickness may lead to a decrease in effectiveness of the brain as well as damage the brain.
9. Talking Rarely
Intellectual conversations will promote the efficiency of the brain.
10. Lacking in stimulating thoughts
Thinking is the best way to train our brain, lacking in brain stimulation thoughts may cause brain shrinkage.

Knowledge is power, the old saying goes, but it isn’t much use if it’s hidden away – so we’re excited to learn that the US Library of Congress is making 25 million of its records available for free, for anyone to access online.
The bibliographic data sets, like digital library cards, cover music, books, maps, manuscripts, and more, and their publication online marks the biggest release of digital records in the Library’s history.
“The Library of Congress is our nation’s monument to knowledge and we need to make sure the doors are open wide for everyone, not just physically but digitally too,” says Librarian of Congress Carla Hayden.
“Unlocking the rich data in the Library’s online catalogue is a great step forward. I’m excited to see how people will put this information to use.”
Continue Reading.
