Covering The Oceans In Darkness….
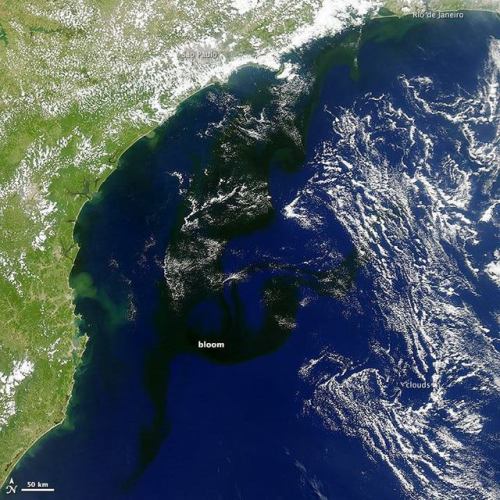

Covering the oceans in darkness….
Phytoplankton blooms produce some fascinating textures in Earth’s oceans, and consequently we’ve shared images of them taken from orbit many times (http://tinyurl.com/qhzwbr9, http://tinyurl.com/pwasxol). This bloom, however is a bit different from the others – in this photo from NASA’s Aqua satellite, it looks, well, black.
Keep reading
More Posts from Simplyphytoplankton and Others

Behold the blue glaucus (Glaucus atlanticus), a tiny sea slug that packs a powerful punch! Growing only about 1.2 in (3 cm) long, it’s also known as the blue dragon, and it specializes in eating venomous siphonophores—like the Portuguese man o' war. It then repurposes the toxic chemicals from its prey as a defense for itself. The blue glaucus’ sting has been known to induce nausea, vomiting, and agonizing pain. Their venom can remain active even after death!
Photo: drmattnimbs, CC BY-NC 4.0, iNaturalist





When wood turns into glitter
Many moons ago, in the area that is now Nevada ancient woodlands were living through events that would result in some stunning pieces that grace museums around the world. Some 14 million years ago in the Miocene, the area was thickly forested rather than displaying the arid environment of today. It was also much closer to sea level, since the area has been extensively uplifted since then, due to tectonic stresses caused by the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon plates under the North American one. The area also saw intense subduction related volcanism (ongoing along the USA’s west coast to this day), which periodically covered the forests in silica rich ash. As groundwater interacted with the magma below, weathering the layers of ash into clays, it dissolved silica, precipitating it when conditions such as temperature and pressure changed, replacing the ash covered trees with opal, sometimes so clearly that every cell is visible. While not really suitable for jewellery use due to its tendency to crack as it dries out (called crazing in the trade), these rare logs from the Virgin Valley of Nevada make for stunning collector’s specimens
Keep reading

Höfn
That was rather impressive

Mid Air Mid octopus
Changing main blog now. Everything before this is my study abroad experience in Costa Rica

“I make sure that when I am boating that nothing goes into the water, I try to recycle everything I can, and I don’t eat seafood unless it is invasive lionfish. I also participate in as many coastal cleanups to help to remove all of the garbage along our shorelines and I try to encourage others to do the same. We have a long ways to go in ocean conservation, but national marine sanctuaries, along with national parks, monuments, and wildlife refuges, afford us the best opportunity to help leverage limited resources to address coastal and marine conservation."
– Mark Chiappone, research associate at Nova Southeastern University and assistant professor at Miami Dade College
What inspires you about the ocean?
(Photo: Scrawled filefish in Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Credit: Daryl Duda)

DISCOVERING THE GIANTS OF THE DEEP: BATHYNOMUS JAMESI
A newly discovered species of giant isopod, Bathynomus vaderi, has recently been described from the deep waters around Spratly Islands, off Vietnam. The species, named after the infamous Sith Lord, Darth Vader, due to the striking resemblance of its helmet-like head, adds to the growing diversity of the Bathynomus genus. Bathynomus vaderi is characterized by several unique features, including a parallel-margin clypeal region, a raised dorsal surface on its pleotelson, and upwardly curved pleotelson spines.
Giant isopods like Bathynomus vaderi have become an expensive delicacy in Vietnam. Until 2017, local fishermen only sold them as an incidental product at low prices, but in recent years the media has drawn the public's attention to this unusual seafood. Some even claim that it is more delicious than lobster, the "king of seafood." This new species is described from several individual found at seafood markets in Hanoi, Vietnam.

-Seafood market in Hanoi, Vietnam, selling the newly described Bathynomus jamesi. Large specimens exceeding 2 kg in weight command premium prices.
In Vietnam, Bathynomus species, are often referred to as "sea bugs". Their unique appearance and large size make them a delicacy, and they can command high prices, with larger individuals of B. vaderi reaching up to 2 kg. In recent years, demand for these creatures has risen, especially in urban centers like Hanoi and Hồ Chí Minh City, where they are displayed in restaurants and sold through online seafood markets. This growing industry highlights the continued fascination with deep-sea species and the need for ongoing research to better understand their ecology and conservation.
Main photo: Bathynomus vaderi, male, colour in life. Photo by Nguyen Thanh Son
Reference (Open Access): Ng et al., 2025. A new species of supergiant Bathynomus A. Milne-Edwards, 1879 (Crustacea, Isopoda, Cirolanidae) from Vietnam, with notes on the taxonomy of Bathynomus jamesi Kou, Chen & Li, 2017. ZooKeys.










Trump’s War on Science continues

-
 mc-awsome liked this · 7 years ago
mc-awsome liked this · 7 years ago -
 askcodexone-blog liked this · 7 years ago
askcodexone-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 nurnielfa liked this · 7 years ago
nurnielfa liked this · 7 years ago -
 carol1st reblogged this · 7 years ago
carol1st reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bugger897 liked this · 7 years ago
bugger897 liked this · 7 years ago -
 simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 7 years ago
simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 bunnnyhannny liked this · 7 years ago
bunnnyhannny liked this · 7 years ago -
 cannibal-captain-hannibal reblogged this · 7 years ago
cannibal-captain-hannibal reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 rockparadiseworld-blog liked this · 7 years ago
rockparadiseworld-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 cloudair liked this · 7 years ago
cloudair liked this · 7 years ago -
 therodentqueen liked this · 7 years ago
therodentqueen liked this · 7 years ago -
 catshapeddarkness liked this · 7 years ago
catshapeddarkness liked this · 7 years ago -
 thequietchorusgirl liked this · 7 years ago
thequietchorusgirl liked this · 7 years ago -
 toytulini reblogged this · 7 years ago
toytulini reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 toytulini liked this · 7 years ago
toytulini liked this · 7 years ago -
 averydappercat liked this · 7 years ago
averydappercat liked this · 7 years ago -
 fotoecke-blog liked this · 7 years ago
fotoecke-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 just-dont-even liked this · 7 years ago
just-dont-even liked this · 7 years ago -
 supermermaids reblogged this · 7 years ago
supermermaids reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 etakeh liked this · 7 years ago
etakeh liked this · 7 years ago -
 tooloco reblogged this · 7 years ago
tooloco reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 daemonicsatinworship liked this · 7 years ago
daemonicsatinworship liked this · 7 years ago -
 balkanbruiser reblogged this · 7 years ago
balkanbruiser reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ladythmpr liked this · 7 years ago
ladythmpr liked this · 7 years ago -
 poeticrin1 reblogged this · 7 years ago
poeticrin1 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ariesinspace reblogged this · 7 years ago
ariesinspace reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 poeticrin1 liked this · 7 years ago
poeticrin1 liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-telescope-times liked this · 7 years ago
the-telescope-times liked this · 7 years ago -
 the-telescope-times reblogged this · 7 years ago
the-telescope-times reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 webwormmm liked this · 7 years ago
webwormmm liked this · 7 years ago -
 sin-city-sights liked this · 7 years ago
sin-city-sights liked this · 7 years ago -
 geologychick reblogged this · 7 years ago
geologychick reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 geologychick liked this · 7 years ago
geologychick liked this · 7 years ago -
 spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 7 years ago
spacetimewithstuartgary reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 kindahotintheserhinoss liked this · 7 years ago
kindahotintheserhinoss liked this · 7 years ago -
 you-gotta-be-hawkidding-me liked this · 7 years ago
you-gotta-be-hawkidding-me liked this · 7 years ago -
 imjustamonster liked this · 7 years ago
imjustamonster liked this · 7 years ago -
 paleontologylife reblogged this · 7 years ago
paleontologylife reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 paleontologylife liked this · 7 years ago
paleontologylife liked this · 7 years ago -
 indelliblemercinary reblogged this · 7 years ago
indelliblemercinary reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 indelliblemercinary reblogged this · 7 years ago
indelliblemercinary reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 walterlegui-67 liked this · 7 years ago
walterlegui-67 liked this · 7 years ago

Blog dedicted to phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that are responsible for half of the photosynthesis that occurs on Earth. Oh, and they look like art... Follow to learn more about these amazing litter critters! Caution: Will share other ocean science posts!Run by an oceanographer and phytoplankton expert. Currently a postdoctoral researcher.Profile image: False Colored SEM image of Emiliania huxleyi, a coccolithophore, and the subject of my doctoral work. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/ Science Photo Library/ Getty ImagesHeader image: Satellite image of a phytoplankton bloom off the Alaskan Coast, in the Chukchi SeaCredit: NASA image by Norman Kuring/NASA's Ocean Color Web https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/92412/churning-in-the-chukchi-sea
158 posts