One Month
One Month
One month down
Cultural differences
Language barrier
On Friday, my first month in Costa Rica ended and marked the beginning of my second month here. Over the course of this month, I have noticed a lot of differences between Costa Rican culture and U.S. culture, although there are probably more that I have not noticed because I have not thought about them. Personal space and your personal bubble do not exist in the way they do in the U.S. It is common to hug and kiss people on the cheek as a sign of greeting and farewell, which as someone who likes their personal bubble, is taking a bit of time to get used to. It is very common for men to catcall, whistle, honk their horns, and stare at women walking, although every time that I have seen it, that's all it was. It makes me think that instead of men just lacking in all forms of self control, it is more of a cultural norm to do it and it would be out of place for men not to do it. Although, it still makes my female friends from the U.S. very uncomfortable for obvious reasons. Rules of the road really just seem like suggestions and it seems that drivers make up their own rules as they go, including motorcycles and scooters that always pass cars, buses, trucks, SUVs, etc... when they shouldn't. Most classes at the university are only once a week and there is a lot less busy work and a lot more group work. It is acceptable for people to show up late for classes and events (tico time), however, it does not apply to my science classes.
By far, my biggest struggle has been the language barrier. Looking back at a month ago, I can tell that there has been at least a subtle increase in my proficiency with Spanish. I try to listen and follow my professors, my parents, and other people that I encounter, but at times I can't understand what they are saying, although my listening skills are still a lot better than my speaking skills. I try to talk as much as possible but my problems are when I don't a word I need and cannot get around (although today I had a conversation about my opinion genetic modification with classmates for fun and it went really well) and if I don't have anything to say, I usually don't say anything. To mediate this, I've tried to force myself to talk more with mixed success. But I have learned that even if I understand 95% of what everyone says, the only way my speaking will improve is if I speak as much as I possibly can, knowing that I will make a lot of mistakes in the beginning.
More Posts from Simplyphytoplankton and Others

Shark Week Takeover with photos by @BrianSkerry ! • • • Like a living wreath, small fish encircle the head of a whale shark cruising through coastal waters off Mexico’s Isla Holbox. The small fish have little to fear from this shark, since whale sharks are filter feeders, eating mainly plankton and fish eggs. Whale sharks are currently listed as ‘vulnerable’ due to human pollution and hunting, and populations remain unstable due to the slow reproductive habits of these magnificent creatures.
Swimming with whale sharks is one of my favorite experiences in the sea. Their massive size and gentle nature make for exhilarating encounters. • • • To see more shark photos and other ocean wildlife follow @BrianSkerry And keep following our feed all week to keep up with Brian Skerry’s very sharky takeover! #takeover #sharks #sharkweek #sharkweek2018 #allsharksallthetime #newenglandaquarium
Annual Arctic sea ice minimum, 1979-2016
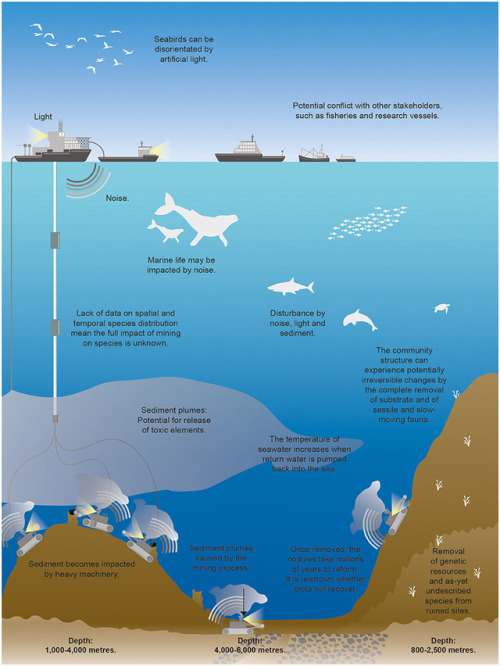
DEEP-SEA MINING COULD DESTROY MARINE ECOSYSTEMS
Despite deep-sea environments covers about half of the Earth’s surface and is home to a vast range of species, little is known about these environments, and mining could have long-lasting and unforeseen consequences, not just at mining sites but also across much larger areas.
According to a study published in scientific journal Frontiers in Marine Science, which is the first to give a global overview of all current plans to mine the seabed, in both national and international waters, and looks at the potential impacts including physical destruction of seabed habitats, creation of large underwater plumes of sediment and the effects of chemical, noise and light pollution arising from mining operations.
Rising demand for minerals and metals, including for use in the technology sector, has led to a resurgence of interest in exploration of mineral resources located on the seabed. Such resources, whether seafloor massive sulfides around hydrothermal vents, cobalt-rich crusts on the flanks of seamounts or fields of manganese nodules on the abyssal plains, cannot be considered in isolation of the distinctive, in some cases unique, assemblages of marine species associated with the same habitats and structures.
Some operations are already taking place, generally at relatively shallow depths near national coastlines. The first commercial enterprise, expected to target mineral-rich sulfides in deeper waters, at depths between 1,500 and 2,000 m on the continental shelf of Papua New Guinea, is scheduled to begin early in 2019.
Illustration: A schematic showing the potential impacts of deep-sea mining on marine ecosystems. Schematic not to scale.
Reference: Miller et al., 2018. An Overview of Seabed Mining Including the Current State of Development, Environmental Impacts, and Knowledge Gaps. Frontiers in Marine Science.
A mariachi band playing at my host dad’s mom’s 86th birthday party.

THE PARADOX OF THE PLANKTON EXPLAINED BY COMPUTER SIMULATION
The paradox of the plankton results from the clash between the observed diversity of plankton and the competitive exclusion principle, which states that, when two species compete for the same resource, ultimately only one will persist and the other will be driven to extinction. With phytoplankton this is different, despite the limited range of resources, as is light, nitrate, phosphate, silicic acid, iron, a large number of species coexist, all competing for the same sorts of resources.
Now, a new math model explains such biodiversity. To understand this paradox researchers created a conceptual model for a theoretical community. Where each member of that community consumes one type of resource, and consuming it causes the production of exactly two new resources. Also, any new member could only survive if there is an open niche, or if it was better to exploit a resource than a current member. But with this computer simulation, researchers discovered that its simple rules led to a virtual community that, like the bacterial or phytoplankton communities, this hypotethical community was diverse and stable, and in fact became increasingly stable to as organisms diversified.
Resource competition and metabolic commensalism -where one organism benefits from the other without affecting it- drive a healty and diverse ecosystem. Researchers demonstrate that even when supplied with just one resource, ecosystems can exhibit high diversity and increasing stability. Despite early stages where massive die-offs scenes occured, as time passed and community grew more stable, these became less common. Affortunately to phytoplancton species, two communities under ideal conditions can develop so differently from one another, without producing extintions.
Photo: Gordon T. Taylor.
Reference: Goyal and Maslov, 2018. Diversity, Stability, and Reproducibility in Stochastically Assembled Microbial Ecosystems, Physical Review Letters

From Kane Lynch and our stats dept.
NSF cancels grant reviews due to WH executive order
The National Science Foundation (NSF)—the major funding agency for basic science—has canceled all grant review panels this week to comply with an executive order from the new administration. This is where independent panels of scientists discuss grant proposals they’ve reviewed for scientific merit and recommend which projects get funded to NSF project managers. A LOT of work goes into setting up and scheduling grant reviews. It will take time to reschedule these panels, delaying key decisions for many promising projects. This will wreak havoc on science grant funding for months to come.
Put simply, this action along with the halting of NIH-funded grants are blatant and reckless political attacks on science, from an administration that seeks blinding loyalty.

Meet “the sheep of the Mesozoic,” Protoceratops andrewsi. This herbivore was a very common animal and is remarkably well-represented in the fossil record.
Delta
Flight 1235- 12:05pm
Harrisburg to Atlanta
Right now, my first flight is almost over and we will soon land in Atlanta. I should be on my way to Atlanta. But I am not on that flight. I am sitting in Harrisburg International Airport (Canada counts).
IFSA-Butler sent everyone multiple emails in the months leading up to departure about visas. Each email was clear and concise, and I reread everyone to make sure there was nothing else I had to do. So, it was surprising (and very stressful) when the boarding agent would not allow me on the plane because I didn't have a visa. I told him I didn’t need one and showed him the documents from IFSA-Butler. Nope. He needed something from the Costa Rican government. So I called IFSA-Butler and my advisor told me the same thing every email said. I didn’t need a visa because I would apply for a tourist visa after landing in San Jose and then apply for an extension of it.
I told the agent this, but he needed official documentation. I relayed the message that he could call the Costa Rican Consulate and they would verify what I was saying. That wasn't his responsibility (I'd like to point out here that if I called and tried to tell him what they said, he would have had to speak with them to verify it, meaning it technically was his responsibility). As everyone was boarding, one kind stranger showed the agent the website of the Costa Rican Embassy saying that you did not need a visa to enter the visa and you would apply for a visa after landing. He said that the date of my departure was after the 90-day tourist visa expired. I repeated that I would get an extension in Costa Rica and it was impossible for me to have a tourist visa before arriving in Costa Rica (from what IFSA-Butler told me).
By the time my advisor got me documentation from Costa Rican immigration and emailed it to me, it was too late. Oh, and it was in Spanish and they would have had to find a way to translate it since I would not be able to. And my bag was on the plane.
So here I am, sitting in Harrisburg International Airport after figuring out how I would get to Costa Rica. Everything is taken care of now after many phone calls and my flight is tomorrow at 3:34pm out of Washington, D.C. But my back won't be back until 5ish and I'm waiting for my parents to comeback.
So I will conclude by quoting my travel agent at Advantage Travel (IFSA's travel agency), "Delta can go pound salt."
What will scientists find in the deep waters off California?
Deep-sea corals and sponges are some of the oldest animals on Earth, living for hundreds of years at depths beyond direct human observation. Coral, sponge, and fish communities thrive in the cold, deep waters off California’s coast, but are rarely – if ever – visited or observed.
In late July and early August, scientists using advanced technology aboard the NOAA Ship Bell M. Shimada will study unexplored seafloor habitats off North-Central California in NOAA’s Greater Farallones and Cordell Bank national marine sanctuaries. Their focus includes coral, sponge, and groundfish communities. What they learn will help inform the management of these special ocean areas, and add to knowledge about deep-sea habitats and the biological communities that live there.

A crinoid and bubblegum coral grow in the deep sea in Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary. Photo: OET/NOAA
Using a robot to explore the deep
To survey the seafloor and record images of the habitats as deep as 2,000 feet (600 meters), scientists are using a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), launched from the ship and sent into the depths of the ocean. In addition to sending real-time video and images via a cable connected to the ship, the unmanned ROV will collect geological and biological specimens for identification. Scientists will also conduct seafloor mapping, an important tool for management of marine areas.

A remotely operated vehicle collects a sponge sample. The yellow sponge is a new species that was found on the wreck of the USS Independence. Photo: OET/NOAA
Why journey to the deep?
The deep sea is vastly unknown because it is largely inaccessible by humans. However, it affects us in many ways. A healthy ocean is essential to the health of our planet, and deep-sea communities are an important part of marine ecosystems. The deep sea nurtures fish stocks and hosts life-forms like bacteria and sponges that have contributed to medical discoveries.
Coral and sponge habitats are among the most biodiverse and productive ecosystems throughout the entire ocean. Increasing global human demand for resources has created a need for expanded science and conservation of these deep-ocean ecosystems and the benefits they may yield. Both living and dead corals and sponges are “biogenic habitats,” where the organisms themselves provide habitat for other marine life.
Previous NOAA expeditions off California’s coast have identified several new species of corals and sponges, including Swiftia farallonesica, a slender white coral, in the deep waters of Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary, off the Sonoma County coast. New sponge species were discovered living on the wreck of the USS Independence off the San Mateo County coast. They were also discovered in Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary, both in Bodega Canyon and on the deep slope near Cordell Bank to the north. New species discoveries indicate that we still have much to learn about the deep sea.
The ocean supports hundreds of billions of dollars of the U.S. economy through food, jobs, transportation, recreation, and other services. NOAA’s mission is “to understand and predict changes in climate, weather, oceans, and coasts, to share that knowledge and information with others, and to conserve and manage coastal and marine ecosystems and resources.” Assessing the conditions of ocean ecosystems can lead to better management of those areas to support the ocean economy.

Swiftia farallonesica is a new species of coral that was discovered in the deep waters of Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary. Photo: NOAA
Stay tuned for more pictures and information after the expedition!
-
 ididitforthedogs liked this · 9 years ago
ididitforthedogs liked this · 9 years ago -
 simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 9 years ago
simplyphytoplankton reblogged this · 9 years ago

Blog dedicted to phytoplankton. Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that are responsible for half of the photosynthesis that occurs on Earth. Oh, and they look like art... Follow to learn more about these amazing litter critters! Caution: Will share other ocean science posts!Run by an oceanographer and phytoplankton expert. Currently a postdoctoral researcher.Profile image: False Colored SEM image of Emiliania huxleyi, a coccolithophore, and the subject of my doctoral work. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/ Science Photo Library/ Getty ImagesHeader image: Satellite image of a phytoplankton bloom off the Alaskan Coast, in the Chukchi SeaCredit: NASA image by Norman Kuring/NASA's Ocean Color Web https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/92412/churning-in-the-chukchi-sea
158 posts