The Big Bang Theory - Season 4 Bloopers




The Big Bang Theory - Season 4 Bloopers
More Posts from Selenophhile and Others




got inspired by @homosexual-having-tea ‘s post about the memes people would make while trying to rescue Watney in the Martian and whipped these up in about five minutes. bon appetite or whatever
I miss this.
literally one of the best feelings in the world is like. when you are keeping up with your studies enough to where you're still able to do your hobbies. and you're romanticizing your schoolwork. and you feel all academic. and your hobbies feel even more special because they're like a reward after completing your schoolwork
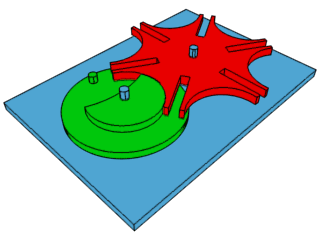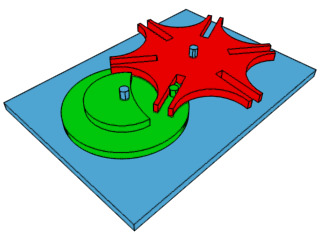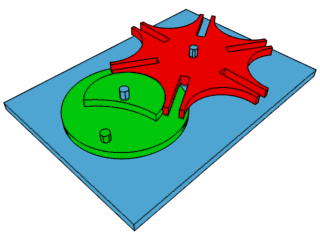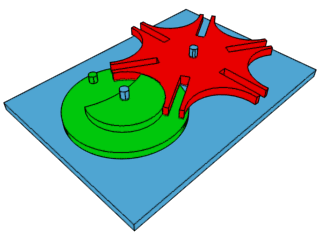
How the Geneva Drive (the mechanical step that makes the second hand on a clock work by turning constant rotation into intermittent motion) works.
i love you? no pls I'd rather hear the words "this paper is brilliantly researched and is worthy of a distinction"
the funniest part of the secret history is that even though it's a satirical commentary about the effects of elitism and pomposity of certain academia, the fandom is full of people WANTING to be those pretentious Greek students. tartt i think your writing had the opposite of the intended effects ....
Don't you just love it when women in stem

Engineer Karen Leadlay in a General Dynamics computer lab, 1964.

LaRue Burbank, mathematician and computer, is just one of the many women who were instrumental to NASA missions.
4 Little Known Women Who Made Huge Contributions to NASA
Women have always played a significant role at NASA and its predecessor NACA, although for much of the agency’s history, they received neither the praise nor recognition that their contributions deserved. To celebrate Women’s History Month – and properly highlight some of the little-known women-led accomplishments of NASA’s early history – our archivists gathered the stories of four women whose work was critical to NASA’s success and paved the way for future generations.
LaRue Burbank: One of the Women Who Helped Land a Man on the Moon
LaRue Burbank was a trailblazing mathematician at NASA. Hired in 1954 at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory (now NASA’s Langley Research Center), she, like many other young women at NACA, the predecessor to NASA, had a bachelor's degree in mathematics. But unlike most, she also had a physics degree. For the next four years, she worked as a "human computer," conducting complex data analyses for engineers using calculators, slide rules, and other instruments. After NASA's founding, she continued this vital work for Project Mercury.
In 1962, she transferred to the newly established Manned Spacecraft Center (now NASA’s Johnson Space Center) in Houston, becoming one of the few female professionals and managers there. Her expertise in electronics engineering led her to develop critical display systems used by flight controllers in Mission Control to monitor spacecraft during missions. Her work on the Apollo missions was vital to achieving President Kennedy's goal of landing a man on the Moon.
Eilene Galloway: How NASA became… NASA

Eilene Galloway wasn't a NASA employee, but she played a huge role in its very creation. In 1957, after the Soviet Union launched Sputnik, Senator Richard Russell Jr. called on Galloway, an expert on the Atomic Energy Act, to write a report on the U.S. response to the space race. Initially, legislators aimed to essentially re-write the Atomic Energy Act to handle the U.S. space goals. However, Galloway argued that the existing military framework wouldn't suffice – a new agency was needed to oversee both military and civilian aspects of space exploration. This included not just defense, but also meteorology, communications, and international cooperation.
Her work on the National Aeronautics and Space Act ensured NASA had the power to accomplish all these goals, without limitations from the Department of Defense or restrictions on international agreements. Galloway is even to thank for the name "National Aeronautics and Space Administration", as initially NASA was to be called “National Aeronautics and Space Agency” which was deemed to not carry enough weight and status for the wide-ranging role that NASA was to fill.
Barbara Scott: The “Star Trek Nerd” Who Led Our Understanding of the Stars

A self-described "Star Trek nerd," Barbara Scott's passion for space wasn't steered toward engineering by her guidance counselor. But that didn't stop her! Fueled by her love of math and computer science, she landed at Goddard Spaceflight Center in 1977. One of the first women working on flight software, Barbara's coding skills became instrumental on missions like the International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) and the Thermal Canister Experiment on the Space Shuttle's STS-3. For the final decade of her impressive career, Scott managed the flight software for the iconic Hubble Space Telescope, a testament to her dedication to space exploration.
Dr. Claire Parkinson: An Early Pioneer in Climate Science Whose Work is Still Saving Lives

Dr. Claire Parkinson's love of math blossomed into a passion for climate science. Inspired by the Moon landing, and the fight for civil rights, she pursued a graduate degree in climatology. In 1978, her talents landed her at Goddard, where she continued her research on sea ice modeling. But Parkinson's impact goes beyond theory. She began analyzing satellite data, leading to a groundbreaking discovery: a decline in Arctic sea ice coverage between 1973 and 1987. This critical finding caught the attention of Senator Al Gore, highlighting the urgency of climate change.
Parkinson's leadership extended beyond research. As Project Scientist for the Aqua satellite, she championed making its data freely available. This real-time information has benefitted countless projects, from wildfire management to weather forecasting, even aiding in monitoring the COVID-19 pandemic. Parkinson's dedication to understanding sea ice patterns and the impact of climate change continues to be a valuable resource for our planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!


In the face of overwhelming odds, I’m left with only one option: I’m gonna have to science the shit out of this.
quit brainrot. unfollow trolls. read essays. go down rabbit holes. have a calendar. maintain a todo list. read old books. watch old movies. turn on dnd. walk with intent. eat without youtube. chew more. train without music. plan for 15 mins. execute. organise your desk. take something seriously. read ancient scripts. act fast. find bread. eat clean. journal. save a life. learn to code. read poetry. create art. stay composed. refine your speech. optimise for efficiency. act sincere. help people. be kind. stop doing things that waste your time. follow your intuition. craft reputation. learn persuasion. systemise your day (or don't). write. write. write. write more. iterate violently. leave your phone at home. walk to the grocery store. talk to strangers. feed the dogs. visit bookstores. look for 1800s novels. experience art. then love. sit with a monk and offer them lunch. don't talk shit about people. embody virtue. sit alone. do something with your life. what do you want to create? turn off your mind. play. play a sport. combat sports. notice fonts in trees. fall in love. notice patterns on a table. visualise it. talk to people with respect. don't hate. be loving. be real. become yourself. cherrypick your qualities. discard the useless. rejections aren't permanent. invite what aligns. accept what does not. read great people. be different. choose different. do great work. let it consume you. lose your mind. value your time. experience life.
7 Reasons you might be procrastinating and how to solve them:



-
 ruuubt liked this · 1 month ago
ruuubt liked this · 1 month ago -
 ramblingsfromthytruly liked this · 7 months ago
ramblingsfromthytruly liked this · 7 months ago -
 mffer liked this · 11 months ago
mffer liked this · 11 months ago -
 selenophhile reblogged this · 11 months ago
selenophhile reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 selenophhile liked this · 11 months ago
selenophhile liked this · 11 months ago -
 podsrod liked this · 1 year ago
podsrod liked this · 1 year ago -
 transparentstrawberrysoul liked this · 1 year ago
transparentstrawberrysoul liked this · 1 year ago -
 prfctmarina liked this · 1 year ago
prfctmarina liked this · 1 year ago -
 autumnrose11 reblogged this · 1 year ago
autumnrose11 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 cheezbot liked this · 1 year ago
cheezbot liked this · 1 year ago -
 fudgewilde reblogged this · 1 year ago
fudgewilde reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 unusedmainlmao liked this · 1 year ago
unusedmainlmao liked this · 1 year ago -
 autumnrose11 reblogged this · 1 year ago
autumnrose11 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 joytri liked this · 1 year ago
joytri liked this · 1 year ago -
 anotherhotg4ywitch liked this · 2 years ago
anotherhotg4ywitch liked this · 2 years ago -
 mj04 liked this · 2 years ago
mj04 liked this · 2 years ago -
 lost-confused-brat liked this · 2 years ago
lost-confused-brat liked this · 2 years ago -
 raj0719 liked this · 2 years ago
raj0719 liked this · 2 years ago -
 boahey reblogged this · 2 years ago
boahey reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 boahey liked this · 2 years ago
boahey liked this · 2 years ago -
 behindthesefangirleyes reblogged this · 2 years ago
behindthesefangirleyes reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 behindthesefangirleyes liked this · 2 years ago
behindthesefangirleyes liked this · 2 years ago -
 zitronengurkenlimo liked this · 2 years ago
zitronengurkenlimo liked this · 2 years ago -
 mariaizabelbc liked this · 2 years ago
mariaizabelbc liked this · 2 years ago -
 instantflowerbeard liked this · 3 years ago
instantflowerbeard liked this · 3 years ago -
 cutieshamybabies liked this · 4 years ago
cutieshamybabies liked this · 4 years ago -
 always-believe-in-ur-dreams reblogged this · 4 years ago
always-believe-in-ur-dreams reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 always-believe-in-ur-dreams liked this · 4 years ago
always-believe-in-ur-dreams liked this · 4 years ago -
 homeofthedargon liked this · 4 years ago
homeofthedargon liked this · 4 years ago -
 afragmentada liked this · 4 years ago
afragmentada liked this · 4 years ago -
 mcdonaldslovert liked this · 4 years ago
mcdonaldslovert liked this · 4 years ago -
 nehali2002 liked this · 4 years ago
nehali2002 liked this · 4 years ago -
 everythingdaily-moved reblogged this · 4 years ago
everythingdaily-moved reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 anotherrandomnerd-blog liked this · 4 years ago
anotherrandomnerd-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 caitlin-1919 liked this · 5 years ago
caitlin-1919 liked this · 5 years ago -
 hungtotheoover liked this · 5 years ago
hungtotheoover liked this · 5 years ago -
 dbinmn liked this · 5 years ago
dbinmn liked this · 5 years ago -
 puchaku liked this · 5 years ago
puchaku liked this · 5 years ago -
 casual-decadence reblogged this · 5 years ago
casual-decadence reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 casual-decadence liked this · 5 years ago
casual-decadence liked this · 5 years ago -
 its-maemain liked this · 5 years ago
its-maemain liked this · 5 years ago
