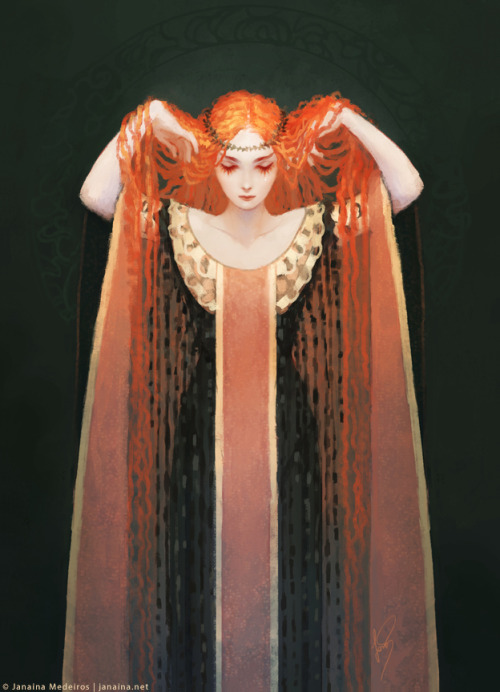
“Dionysus Is Powerful Because He Is A God; But In Myth, At Least, The God Conceals His Divinity In
“Dionysus is powerful because he is a god; but in myth, at least, the god conceals his divinity in order to impress his presence all the more forcefully on mortals. In his mythical epiphanies, he exercises his destructive power from a position of apparent weakness and inferiority… the punishment he inflicts is often indirect, deceptive and designed to hide his presence and downplay his power; unlike Apollo or Artemis, he does not kill his victims through direct divine intervention, but relies on those self-destructive drives within their human nature that case madness, self-mutilation or transformation.”
— Albert Henrichs, “He Has a God in Him”: Human and Divine in the Modern Perception of Dionysus
More Posts from Ro0hafz4 and Others
This is Amal and her family. My children are living under bombardment in the war 😭 Please consider them your children and help them 🙏🙏 Stand by my side to save and protect my children. They haven't gone to school for a year 🙏😢😢 Donate to save my children's lives 🍉 🙏🇵🇸 We live in very difficult and desperate circumstances, and what is worst of all is that the fear that haunts me increases day by day. Help me provide them with basic life needs. @gazavetters is verified, my verified number in the list is (#55)
Please help Amal and her family get food, water and shelter!!

Their campaign has been vetted here at #55 by @gazavetters, $7,760/$30,000 (26%) has been raised (as of 20/11/2024). Please donate if you can and share as much as possible to get Amal and her family to safety!!
Source: Redefining Ancient Orphism: A Study in Greek Religion by Radcliffe G. Edmonds
FASCINATING stuff where this scholar on orphism argues that several texts on persephone explicitly (and the homeric hymn implicitly) claim that mortals pay the recompense (ποινη) for the grief (πενθος) that persephone underwent at her abduction. not hades, but mortals try to appease the goddess for her mistreatment, and in return they earn her favour and a blessed afterlife (or even next life). there's this irreconcilable problem here in that hades was culturally justified, but persephone as a goddess still warrants respect/pity/appeasement, and so mortals through rites and sacrifices console her.
decolonial art history starter guide
really tired of seeing AH on the internet/tumblr talked about w the same extreme reverence for the classics that has dominated the field since its conception and has led to the proliferation of white supremacist ideals in this course of study i love very much so decided to channel that by collecting some of my favorite readings on decolonizing art history, with a particular focus on the ancient/classical world. note: this is by no means an extensive list, but rather a selection of pieces i found helpful when starting to explore decolonial art history - with this list i'm focusing more on broad issues than highly specific case studies
reflections on the painting and sculptures of the greeks. jj winckelmann: giving this one a preface as it is quite literally the least decolonial art historical text you can find but also the one that kicked off classical art history studies as we know it (winckelmann is largely seen as the father of art history). as such it is worth a read to understand what these arguments are based around - in more recent years this text has been used extensively to support the white supremacist idea that aryan art came from the great green past and that anything not pertaining to the greeks was ‘degenerate’
decolonization is not a metaphor. tuck and yang.
empty the museum, decolonize the curriculum, open theory. nicholas mirzeoff.
decolonizing art history. grant and price.
decolonization: we aren't going to save you. puawai cairns.
why we need to start seeing the classical world in color. sarah bond.
beyond classical art. caroline vout.
classics and the alt-right: historicizing visual rhetorics of white supremacy. heidi morse.
decolonizing greek archaeology: indigenous archaeologies, modernist archaeology and the post-colonial critique. yannis hamilakis.
how academics, egyptologists, and even melania trump benefit from colonialist cosplay. blouin, hanna, and bond. (i'd like to flag this one in particular with a nod to tumblr's obsession with maintaining a certain aesthetic linked to what you study).
Persephone the Wanderer (II)
by Louise Glück
In the second version, Persephone is dead. She dies, her mother grieves– problems of sexuality need not trouble us here. Compulsively, in grief, Demeter circles the earth. We don’t expect to know what Persephone is doing. She is dead, the dead are mysteries. We have here a mother and a cipher: this is accurate to the experience of the mother as she looks into the infant’s face. She thinks: I remember when you didn’t exist. The infant is puzzled: later, the child’s opinion is she has always existed, just as her mother had always existed in her present form. Her mother is like a figure at a bus stop, an audience for the bus’s arrival. Before that, she was the bus, a temporary home or convenience. Persephone, protected, stares out of the window of the chariot. What does she see? A morning in early spring, in April. Now her whole life is beginning–unfortunately, it’s going to be a short life. She’s going to know, really, only two adults: death and her mother. But two is twice what her mother has: her mother has one child, a daughter. As a god, she could have had a thousand children. We begin to see here the deep violence of the earth whose hostility suggests she has no wish to continue as a source of life. And why is this hypothesis never discussed? Because it is not in the story; it only creates the story. In grief, after the daughter dies, the mother wanders the earth. She is preparing her case; like a politician she remembers everything and admits nothing. For example, her daughter’s birth was unbearable, her beauty was unbearable: she remembers this. She remembers Persephone’s innocence, her tenderness– What is she planning, seeking her daughter? She is issuing a warning whose implicit message is: what are you doing outside my body? You ask yourself: why is the mother’s body safe? The answer is this is the wrong question, since the daughter’s body doesn’t exist, except as a branch of the the mother’s body that needs to be reattached any any cost. When a god grieves it meas destroying others (as in war) while at the same time petitioning to reverse agreements (as in war also): if Zeus will get her back, winter will end. Winter will end, spring will return. The small pestering breezes that I so loved, the idiot yellow flowers– Spring will return, a dream based on a falsehood: that the dead return. Persephone was used to death. Now over and over her mother hauls her out again– You must ask yourself: are the flowers real? If Persephone “returns” there will be one of two reasons: either she was not dead or she is being used to support a fiction– I think I can remember being dead. Many times, in winter, I approached Zeus. Tell me, I would ask him, how can I endure the earth? And he would say, in a short time you will be here again. And in the time between you will forget everything: those fields of ice will be the meadows of Elysium.
In other words, Cassandra is not just a translator, she is also an embodiment of the very function of translation: her prophetic speech often appears to be suspended between languages, like Benjamin's translator who operates in the realm of 'pure language' that is beyond any single linguistic code. Cassandra takes and reformulates and incomprehensible message from the future and becomes incomprehensible in the process, (re)producing a message in such a way that it demands a second, or third or fourth translation. Sometimes she descends from a trance-like state of prophecy to initiate the next link in the chain of interpretations herself, reframing her own message in more prosaic language, only to find that this speech too is received with confusion. Her utterance is always both a target and source text at the same time. The proliferation of translation acts within her single body evokes a kind of never-ending self-translation; like the self-translator, Cassandra suffers a splitting of the self, one part of which is committed to the spirit of the original composition, while the other struggles to reframe it for a new audience that can never grasp the meaning of the original.
Emily Pillinger, Cassandra and the Poetics of Prophecy in Greek and Latin Literature
Here are some diversified open-source syllabi and reading lists on race, gender, Kashmir, Palestine, caste, sexuality, colonialism and modernism, design and systems, feminism, anthropology, sociology, economics, political science, data and tech, labour studies, African studies, disability studies, violence and it’s textures by some amazing educators and activists. Reblog, share and email decolonis.zing@gmail.com to include more in the list!
Decoloniszing Gender - khari jackson, Malcolm Shanks
Modernity and Coloniality - Ahmed Ansari
Design Thinking For Complex Systems- Ahmed Ansari
Feminist and Social Justice Studies- Dr. Alex Ketchum
Afrotectopia
Design + Anthropology - Shannon Mattern
“Shakespeare in the ‘Post'Colonies” -Amrita Dhar
At the Intersection of Critical Race and Disability Studies: A Bibliography - Amrita Dhar
Testimonials + local literature - Mountain Voices
Introduction to Critical Race Theory for 2017- Adrienne Keene
Mini Courses on Art and Culture - Asia Art Archive
Sound and Violence, Sound as Violence - Pedro Oliveira
Violence - Pedro Oliveira
Border thinking and Border as culture - Pedro Oliveira
Introduction to decolonial thinking and decolonising methodologies -Pedro Oliveira
The Kashmir Syllabus - Stand With Kashmir
Palestine Reading List - Danah Abdulla
A Bibliography of Caste Readings - Jyothi James
Decolonizing the Malabari Mind - Jyothi James
Labour and Tech Reading List - Alexandra Mateescu and Eve Zelickson
Diversifying your Design Syllabus: Recommended Readings by Women, Non-binary, and Culturally Diverse Authors - Hillary Carey
Between Scarcity and Excess: Capitalism, Population Control and the Climate Crisis - Luiza Prado
Decolonising Science Reading List - Chanda Prescod-Weinstein
Everyday Orientalism - Katherine Blouin, Usama Ali Gad, Rachel Mairs
-
 breadandsalt liked this · 6 days ago
breadandsalt liked this · 6 days ago -
 caintooth liked this · 3 weeks ago
caintooth liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 gabidogragoata liked this · 1 month ago
gabidogragoata liked this · 1 month ago -
 korenbellcullen liked this · 1 month ago
korenbellcullen liked this · 1 month ago -
 theratcircus liked this · 1 month ago
theratcircus liked this · 1 month ago -
 phantonmme liked this · 2 months ago
phantonmme liked this · 2 months ago -
 argentpalace reblogged this · 2 months ago
argentpalace reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 dionysianivy liked this · 2 months ago
dionysianivy liked this · 2 months ago -
 pomeloeater liked this · 3 months ago
pomeloeater liked this · 3 months ago -
 byhaphs liked this · 4 months ago
byhaphs liked this · 4 months ago -
 azzagrazt reblogged this · 4 months ago
azzagrazt reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 ro0hafz4 reblogged this · 6 months ago
ro0hafz4 reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 lunarnoctiluca liked this · 9 months ago
lunarnoctiluca liked this · 9 months ago -
 manythingsarewrong reblogged this · 9 months ago
manythingsarewrong reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 manythingsarewrong liked this · 9 months ago
manythingsarewrong liked this · 9 months ago -
 thetemperancecard reblogged this · 9 months ago
thetemperancecard reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 a-backlog-of-a-man reblogged this · 11 months ago
a-backlog-of-a-man reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 toodreamercollector liked this · 11 months ago
toodreamercollector liked this · 11 months ago -
 hineinihineini-moving liked this · 1 year ago
hineinihineini-moving liked this · 1 year ago -
 kamamo1 liked this · 1 year ago
kamamo1 liked this · 1 year ago -
 the-biggest-mt liked this · 1 year ago
the-biggest-mt liked this · 1 year ago -
 kingdomkome liked this · 1 year ago
kingdomkome liked this · 1 year ago -
 ibelonginthesun liked this · 1 year ago
ibelonginthesun liked this · 1 year ago -
 werewolftism reblogged this · 1 year ago
werewolftism reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lit-archive reblogged this · 1 year ago
lit-archive reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 missingbarbie liked this · 1 year ago
missingbarbie liked this · 1 year ago -
 movedd liked this · 1 year ago
movedd liked this · 1 year ago -
 halfdusthalfdeitysan liked this · 2 years ago
halfdusthalfdeitysan liked this · 2 years ago -
 hadrian69 liked this · 2 years ago
hadrian69 liked this · 2 years ago -
 lookthenleap reblogged this · 2 years ago
lookthenleap reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 lookthenleap reblogged this · 2 years ago
lookthenleap reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 truthofthewell liked this · 2 years ago
truthofthewell liked this · 2 years ago -
 myckicade liked this · 2 years ago
myckicade liked this · 2 years ago -
 mightyaubs liked this · 2 years ago
mightyaubs liked this · 2 years ago -
 balljointedfairy liked this · 2 years ago
balljointedfairy liked this · 2 years ago -
 galaxywitchwolf13 liked this · 2 years ago
galaxywitchwolf13 liked this · 2 years ago -
 lorwans liked this · 2 years ago
lorwans liked this · 2 years ago -
 roadkillahead reblogged this · 2 years ago
roadkillahead reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 calendularose liked this · 2 years ago
calendularose liked this · 2 years ago -
 eddhegg liked this · 3 years ago
eddhegg liked this · 3 years ago -
 fantasmaton reblogged this · 3 years ago
fantasmaton reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 papi-serpiente liked this · 3 years ago
papi-serpiente liked this · 3 years ago









