Barbados Caribbean Cloudscape By Mike Toy


Barbados Caribbean Cloudscape by Mike Toy
More Posts from Night-hides-the-world and Others


Venezuela by Jonas Piontek

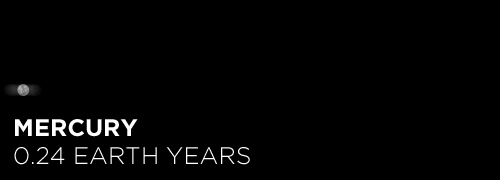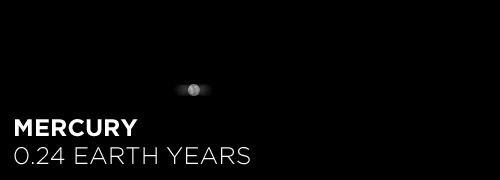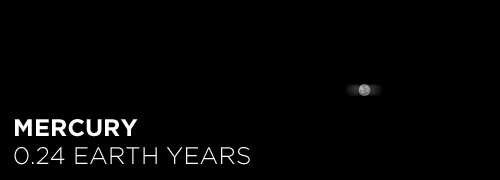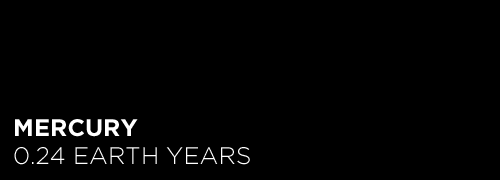
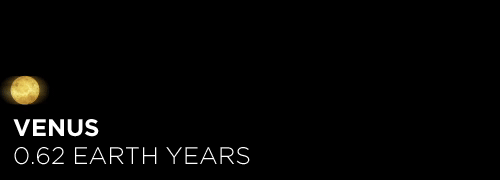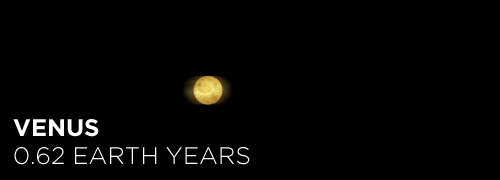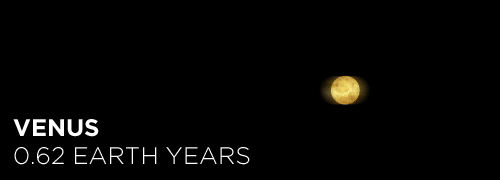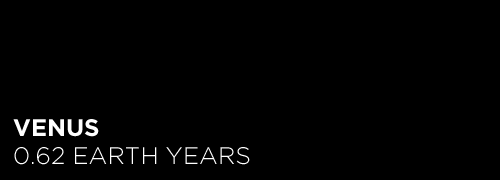

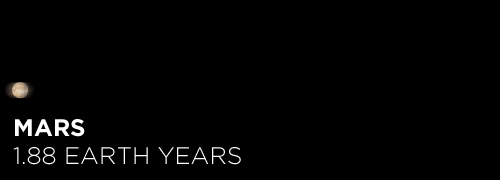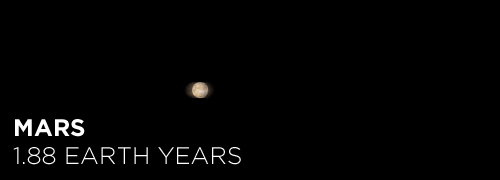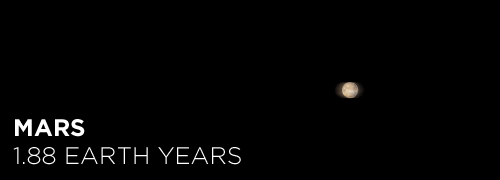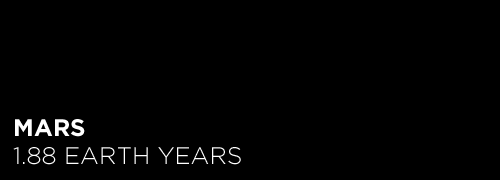
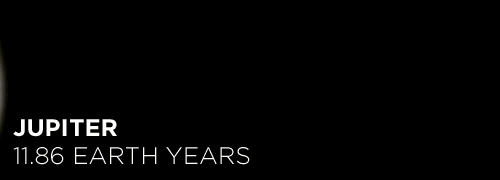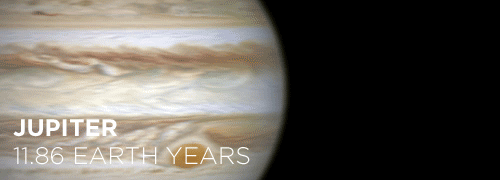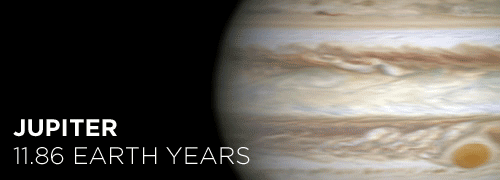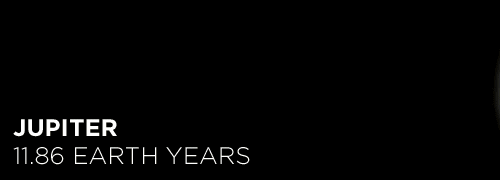
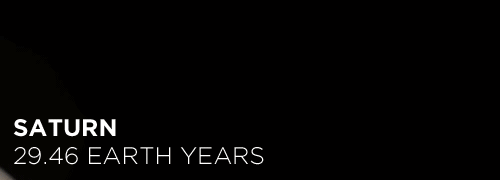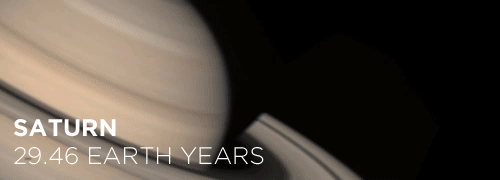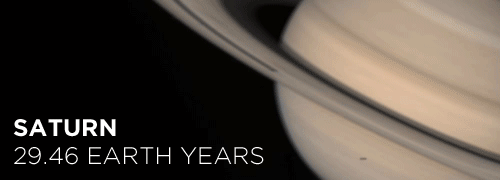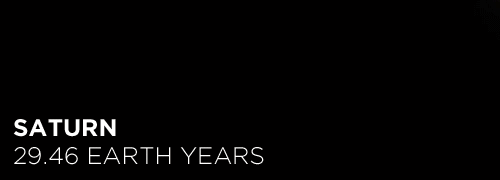
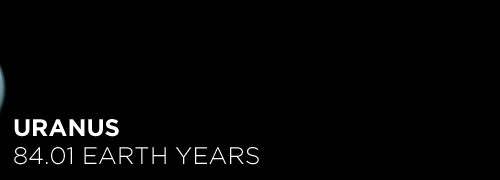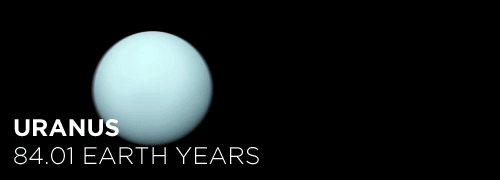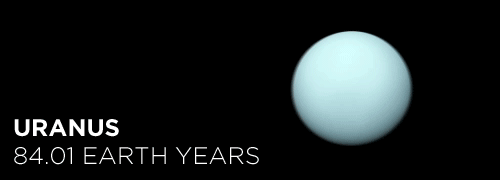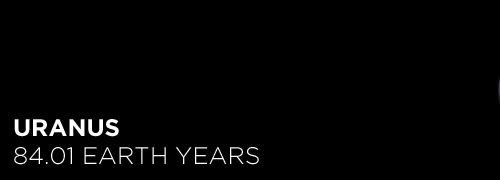

Here’s the orbital period of our solar system’s 8 major planets (how long it takes each to travel around the sun). Their size is to scale and their speed is accurate relative to Earth’s. The repetition of each GIF is proportional to their orbital period. Mercury takes less than 3 months to zoom around Sol, Neptune takes nearly 165 years.




Clouds cast thousand-mile shadows into space when viewed aboard the International Space Station







In this 2 part series, Planet X will teach you about the formation of donut planets using the power of physics!
http://io9.gizmodo.com/what-would-the-earth-be-like-if-it-was-the-shape-of-a-d-1515700296

NGC 1999
Just south of the Orion nebula is a dense area of dust and gas forming stars, in fact, the first Herbig-Haro stars were located here, protostars pushing intense beams of matter out at the poles.
The mystery is the black blob in the white region, a reflective nebula from the star V380 Ori, but what is the dark patch ?

Originally it was thought to be a dense dark cloud of dust, hiding the light, however further analysis has found it is indeed a hole, made to look black in contrast to the bright reflective surroundings.
![A Multi-Camera 360° Panoramic Timelapse Of The Stars By Vincent Brady [VIDEO]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/4e12ed79b6fa93fbd2f17ccd004921d6/tumblr_n7h573O5RR1rte5gyo1_500.gif)
A Multi-Camera 360° Panoramic Timelapse of the Stars by Vincent Brady [VIDEO]

The Einstein Cross Gravitational Lens : Most galaxies have a single nucleus – does this galaxy have four? The strange answer leads astronomers to conclude that the nucleus of the surrounding galaxy is not even visible in this image. The central cloverleaf is rather light emitted from a background quasar. The gravitational field of the visible foreground galaxy breaks light from this distant quasar into four distinct images. The quasar must be properly aligned behind the center of a massive galaxy for a mirage like this to be evident. The general effect is known as gravitational lensing, and this specific case is known as the Einstein Cross. Stranger still, the images of the Einstein Cross vary in relative brightness, enhanced occasionally by the additional gravitational microlensing effect of specific stars in the foreground galaxy. via NASA

12072022: Edge of the Carina Nebula | First Images from The James Webb Space Telescope. Photography credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI

Making a Spectacle of Star Formation in Orion
Looking like a pair of eyeglasses only a rock star would wear, this nebula brings into focus a murky region of star formation. NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope exposes the depths of this dusty nebula with its infrared vision, showing stellar infants that are lost behind dark clouds when viewed in visible light.
Best known as Messier 78, the two round greenish nebulae are actually cavities carved out of the surrounding dark dust clouds. The extended dust is mostly dark, even to Spitzer’s view, but the edges show up in mid-wavelength infrared light as glowing, red frames surrounding the bright interiors. Messier 78 is easily seen in small telescopes in the constellation of Orion, just to the northeast of Orion’s belt, but looks strikingly different, with dominant, dark swaths of dust. Spitzer’s infrared eyes penetrate this dust, revealing the glowing interior of the nebulae.
Credit: NASA/JPL/Spitzer
-
 segebuildings reblogged this · 11 months ago
segebuildings reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 thebougieblackgirl reblogged this · 3 years ago
thebougieblackgirl reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 havatabanca reblogged this · 3 years ago
havatabanca reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 mymusicbias liked this · 3 years ago
mymusicbias liked this · 3 years ago -
 4leurs liked this · 5 years ago
4leurs liked this · 5 years ago -
 entremesj liked this · 5 years ago
entremesj liked this · 5 years ago -
 sammo-has-nice-thighs reblogged this · 5 years ago
sammo-has-nice-thighs reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 whiskey-muse reblogged this · 5 years ago
whiskey-muse reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mahmoudkabbout liked this · 5 years ago
mahmoudkabbout liked this · 5 years ago -
 pvnk-bitch reblogged this · 5 years ago
pvnk-bitch reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago
happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 happylilthangsmh liked this · 5 years ago
happylilthangsmh liked this · 5 years ago -
 happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago
happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago
happylilthangsmh reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 daphnectar liked this · 5 years ago
daphnectar liked this · 5 years ago -
 restlessdaydreams reblogged this · 5 years ago
restlessdaydreams reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 elliepantazilove reblogged this · 5 years ago
elliepantazilove reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 elliepantazilove liked this · 5 years ago
elliepantazilove liked this · 5 years ago -
 wolffeyess reblogged this · 6 years ago
wolffeyess reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 sparklesnsparrows-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
sparklesnsparrows-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 sparklesnsparrows-blog liked this · 6 years ago
sparklesnsparrows-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 k-illaky liked this · 6 years ago
k-illaky liked this · 6 years ago -
 dumbbench liked this · 6 years ago
dumbbench liked this · 6 years ago -
 imjustthatcoolguy liked this · 6 years ago
imjustthatcoolguy liked this · 6 years ago -
 palothav liked this · 7 years ago
palothav liked this · 7 years ago -
 diorwhore19 reblogged this · 7 years ago
diorwhore19 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 threadbakery reblogged this · 7 years ago
threadbakery reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 balfabooty reblogged this · 7 years ago
balfabooty reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 artanis-knarf reblogged this · 7 years ago
artanis-knarf reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 pirate-inconnue-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
pirate-inconnue-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 below-fucking-average reblogged this · 7 years ago
below-fucking-average reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 thegrimmgrimm reblogged this · 7 years ago
thegrimmgrimm reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sparkler-v liked this · 7 years ago
sparkler-v liked this · 7 years ago
Astronomy and the other wonders you witness when you look to the skies.
115 posts