Top Study Tips From NASA
Top Study Tips from NASA

Study smarter this school year! We asked scientists, engineers, astronauts, and experts from across NASA about their favorite study tips – and they delivered. Here are a few of our favorites:

Study with friends
Find friends that are like-minded and work together to understand the material better. Trading ideas with a friend on how to tackle a problem can help you both strengthen your understanding.

Create a study environment
Find a quiet space or put on headphones so you can focus. You might not be able to get to the International Space Station yet, but a library, a study room, or a spot outside can be a good place to study. If it’s noisy around you, try using headphones to block out distractions.

Take breaks
Don’t burn yourself out! Take a break, go for a walk, get some water, and come back to it.
Looking for more study tips? Check out this video for all ten tips to start your school year off on the right foot!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What is it Like to be a NASA Intern?
We asked prospective interns that follow us on social media what questions they had for our current interns.
You asked…they answered! Let’s take a look:

Answer: “Yes, sometimes astronauts request to run through the International Space Station simulation that we have using the hyper-reality lab.”

Answer: “Persistence is the key to getting your first NASA internship. Work hard, study hard, keep applying and persevere.”

Answer: “NASA is looking for passionate, smart and curious, full-time students, who are U.S. citizens, at least 16 years of age and have a minimum 3.0 GPA.”

Answer: “In addition to STEM majors, NASA has many opportunities for students studying business, photography, English, graphics and public relations.”

Answer: “The highlight has been the chance to learn a lot more about embedded systems and coding for them, and just seeing how everyone’s efforts in lab come together for our small part in the AVIRIS-NG project.”

Answer: Yes! Here at the Kennedy Space Center is where all the action takes place. Check out the schedule on our website!”

Answer: “There are 10 NASA field centers and they all accept interns.”

Answer: "Yes, we do! I am currently working in tech development for an X-ray telescope that is launched into space to take pictures of our galaxy.”

Answer: “The greatest thing I’ve learned as a NASA intern is to not be afraid of failing and to get involved in any way you can. NASA is a very welcoming environment that offers a lot of opportunities for its interns to learn.”

Answer: My favorite experience from being a NASA intern is meeting people from all around the world and being exposed to the different cultures.”
Want to become a NASA intern? Visit intern.nasa.gov to learn about the open opportunities and follow @NASAInterns on Twitter and Facebook for regular updates!
Watch the full story on NASA Snapchat or Instagram until it expires on April 6.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Hitchhiking a Ride to Space
Have you ever packed for a long trip with a friend and ran out of space in your suitcase? Maybe your friend was nice and let your spare items hitchhike a ride in their bag? The following science experiments are doing something similar on our Space Launch System rocket.

Our Space Launch System (SLS) will be the most powerful rocket we’ve ever built and will enable astronauts in the Orion spacecraft to travel deeper into the solar system. This advanced launch vehicle will launch astronauts to an asteroid and eventually to Mars, while opening new possibilities for other payloads including robotic scientific missions to places like Mars, Saturn and Jupiter.

The primary goal of SLS and the Orion spacecraft is to launch future crewed, deep space missions. That said, an added bonus of this powerful rocket is the extra science it can carry. On it’s first mission (known as Exploration Mission-1, EM-1) SLS will carry 13 CubeSats (small satellites, each the size of a large shoebox) on its first flight as secondary payloads. These small satellites will perform various in-space experiments. In a way, these 13 CubeSats are ‘space hitchhikers’, catching a ride to deep space where they can gather data valuable to future exploration missions.

How were these 13 experiments selected? Great question. They were selected through a series of announcements of flight opportunities, a public contest and negations with our international partners.
These secondary payloads have a vast array of functions, from taking pictures of asteroids, to using yeast to detect impacts of deep-space radiation. Each month we will highlight one of these experiments on Tumblr and talk about all the exciting science they will do. Just to give you an idea of what these shoebox-sized satellites will do, we’ll give you a preview:
1. NEA Scout

NEA Scout, stands for: Near-Earth Asteroid Scout. This CubeSat will investigate an asteroid, taking pictures and observe its position in space.
2. BioSentinel

BioSentinel will be the first time living organisms have traveled to deep space in more than 40 years. It will use yeast to detect, measure and compare the impact of deep-space radiation on living organisms over long durations in deep space.
3. Lunar Flashlight

This experiment will look for ice deposits and identify locations where resources may be extracted from the lunar surface. It will demonstrate the capability to scout for useful materials and resources from lunar orbit.
4. Skyfire

Lockheed Martin’s Skyfire will perform a lunar flyby, collecting data to address both Moon and Mars Strategic Knowledge Gaps, or gaps in information required to reduce risk, increase effectiveness and improve the design of robotic and human space exploration missions, for surface characterization, remote sensing and site selection.
5. Lunar IceCube

Morehead State University’s Lunar IceCube will look for water in ice, liquid and vapor forms from a very low orbit of only 62 miles above the surface of the moon. The ability to search for useful resources can potentially help astronauts manufacture fuel and necessities to sustain a crew.
6. CuSP

The CubeSat mission to study Solar Particles, or CuSP, will be the first protype of an interplanetary CubeSat space weather station. It will observe space weather events hours before they reach Earth.
7. Luna-H-Map

Lunar Polar Hydrogen Mapper (LunaH) will enter a polar orbit around the moon with a low altitude. From there, it will produce maps of near-surface hydrogen.
8, 9, 10. Three Tournament Payloads

Three of the payloads riding along on this journey will be the winners of the Ground Tournaments portion of our CubeQuest Challenge. This challenge is designed to foster innovation in small spacecraft propulsion and communications techniques. Learn more about this challenge HERE.
11, 12, 13. International Partners
The remaining three payloads are reserved for international partners, and will be announced at a later time.
To stay updated on these experiments, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/launching-science-and-technology.html
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Leap Day…Why Does It Exist?
Once every four years, an extra calendar day is added: a leap day. But why?
The reason for adding leap days to the calendar is to align the calendar year with the actual year – which is defined by the time it takes Earth to circle the sun. It is equal to 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 46 seconds, or 365.24219 days.

If all calendar years contained exactly 365 days, they would drift from the actual year by about 1 day every 4 years. Eventually, July would occur during the northern hemisphere winter! Wouldn’t that be weird?
To correct (approximately), we add 1 day every 4 years...resulting in a leap year.
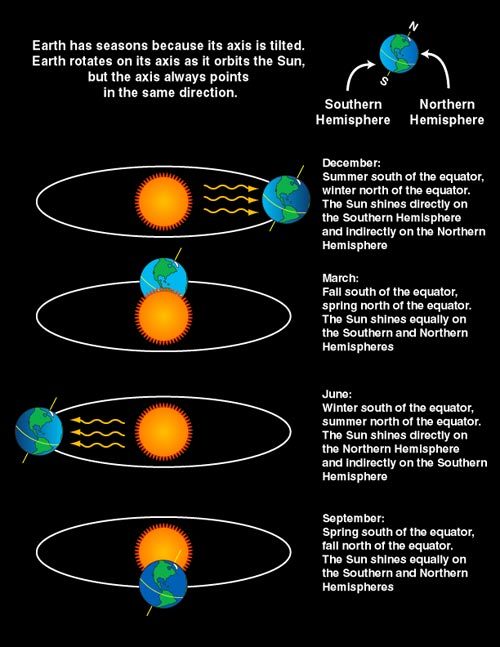
By making most years 365 days but every fourth year 366 days, the calendar year and the actual year remain more nearly in step.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 2015 Year in Review

Two mysterious worlds explored for the first time. Liquid water seen flowing on Mars. A global ocean discovered hiding inside a moon of Saturn. Even during our Era of audacious solar system exploration, 2015 stands out. Here are a few highlights:
1. New Horizons Reveals the Face of Pluto

Whether or not you call it a planet, Pluto entranced the people of Earth when it sent a love note from three billion miles away via our New Horizons spacecraft.
2. Dawn Comes to Ceres

The dwarf planet Ceres, the largest object in the main asteroid belt, teased explorers with its bizarre bright spots before finally giving up some of its secrets to the Dawn spacecraft. HERE are the latest findings.
3. Cassini Marks Discoveries and Milestones at Enceladus

When the Cassini spacecraft performs its final close flyby of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus on Dec. 19, it will be a true milestone. Scientists using data from Cassini’s instruments have uncovered astounding secrets about this small moon, including (confirmed this year) the fact that its underground ocean of liquid water is global, and is home to hydrothermal vents.
4. We Confirmed Evidence that Liquid Water Flows on Today’s Mars

Findings from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) provided the strongest evidence yet that liquid water flows intermittently — on present-day Mars.
5. Rosetta Passes Perihelion

The European Space Agency’s Rosetta mission had a remarkable year, re-establishing contact with the Philae lander and following comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko as it swung near the sun.
6. Mars Explorers Confirm Lakes Once Dotted Mars

A study from the team behind our Mars Science Laboratory/Curiosity Rover confirmed that Mars was once, billions of years ago, capable of storing water in lakes over an extended period of time.
7. MAVEN Finds a Culprit in the Loss of Mars’ Atmosphere

The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission identified the process that appears to have played a key role in the transition of the Martian climate from an early, warm and wet environment that might have supported surface life to the cold, arid planet that Mars is today.
8. Akatsuki Gets a Second Chance at Venus

Five years after a mishap sent the spacecraft off course, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) successfully inserted the Venus Climate Orbiter “Akatsuki” into orbit around Venus. While the mission is not funded by NASA, an agency partnership with JAXA provides an opportunity for eight of our scientists to work with the Akatsuki team and study data from the spacecraft over the next year or so.
9. A Trailblazing Mission Sends Its Final Message from Mercury

After a flight of nearly 11 years, the highly successful MESSENGER mission ended when, as planned, the spacecraft slammed into the surface of Mercury.
10. Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Completes 40,000 Orbits

Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, at Mars since 2006, has orbited the Red Planet more than 40,000 times. The mission, which studies the whole planet from space, has shown that Mars is diverse and dynamic by way of many thousands of spectacular images and other kinds of data.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Is your health affected from being in outer space?
Solar System: 10 Things to Know
Movie Night
Summer break is just around the corner. Hang a sheet from the clothesline in the backyard and fire up the projector for a NASA movie night.
1. Mars in a Minute

Back in the day, movies started with a cartoon. Learn the secrets of the Red Planet in these animated 60 second chunks.
2. Crash of the Titans

Watch two galaxies collide billions of years from now in this high-definition visualization.
3. Tour the Moon in 4K

Wait for the dark of the waning Moon next weekend to take in this 4K tour of our constant celestial companion.
4. Seven Years of the Sun

Watch graceful dances in the Sun’s atmosphere in this series of videos created by our 24/7 Sun-sentinel, the Solar Dynamic Observatory (SDO).
5. Light ‘Em Up

Crank up the volume and learn about NASA science for this short video about some of our science missions, featuring a track by Fall Out Boy.
6. Bennu’s Journey

Follow an asteroid from its humble origins to its upcoming encounter with our spacecraft in this stunning visualization.
7. Lunar Landing Practice
Join Apollo mission pilots as they fly—and even crash—during daring practice runs for landing on the Moon.
8. Earthrise

Join the crew of Apollo 8 as they become the first human beings to see the Earth rise over the surface of the Moon.
9. Musical Descent to Titan

Watch a musical, whimsical recreation of the 2005 Huygens probe descent to Titan, Saturn’s giant moon.
10. More Movies

Our Goddard Scientific Visualization Studio provides a steady stream of fresh videos for your summer viewing pleasure. Come back often and enjoy.
Read the full version of this article on the web HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our Dawn mission to the asteroid belt is no ordinary deep space expedition.
Instead of traditional chemical rockets, the spacecraft uses sophisticated ion engines for propulsion. This enabled Dawn to become the first mission to orbit not one, but two different worlds — first the giant asteroid Vesta and now the dwarf planet Ceres. Vesta and Ceres formed early in the solar system's history, and by studying them, the mission is helping scientists go back in time to the dawn of the planets. To mark a decade since Dawn was launched on Sept. 27, 2007, here are 10 things to know about this trailblazing mission.
1. Ion Engines: Not Just for Sci-Fi Anymore

Most rocket engines use chemical reactions for propulsion, which tend to be powerful but short-lived. Dawn's futuristic, hyper-efficient ion propulsion system works by using electricity to accelerate ions (charged particles) from xenon fuel to a speed seven to 10 times that of chemical engines. Ion engines accelerate the spacecraft slowly, but they're very thrifty with fuel, using just milligrams of xenon per second (about 10 ounces over 24 hours) at maximum thrust. Without its ion engines, Dawn could not have carried enough fuel to go into orbit around two different solar system bodies. Try your hand at an interactive ion engine simulation.
2. Time Capsules

Scientists have long wanted to study Vesta and Ceres up close. Vesta is a large, complex and intriguing asteroid. Ceres is the largest object in the entire asteroid belt, and was once considered a planet in its own right after it was discovered in 1801. Vesta and Ceres have significant differences, but both are thought to have formed very early in the history of the solar system, harboring clues about how planets are constructed. Learn more about Ceres and Vesta—including why we have pieces of Vesta here on Earth.
3. Portrait of a Dwarf Planet

This view of Ceres built from Dawn photos is centered on Occator Crater, home of the famous "bright spots." The image resolution is about 460 feet (140 meters) per pixel.
Take a closer look.
4. What's in a Name?
Craters on Ceres are named for agricultural deities from all over the world, and other features carry the names of agricultural festivals. Ceres itself was named after the Roman goddess of corn and harvests (that's also where the word "cereal" comes from). The International Astronomical Union recently approved 25 new Ceres feature names tied to the theme of agricultural deities. Jumi, for example, is the Latvian god of fertility of the field. Study the full-size map.
5. Landslides or Ice Slides?

Thanks to Dawn, evidence is mounting that Ceres hides a significant amount of water ice. A recent study adds to this picture, showing how ice may have shaped the variety of landslides seen on Ceres today.
6. The Lonely Mountain

Ahuna Mons, a 3-mile-high (5-kilometer-high) mountain, puzzled Ceres explorers when they first found it. It rises all alone above the surrounding plains. Now scientists think it is likely a cryovolcano — one that erupts a liquid made of volatiles such as water, instead of rock. "This is the only known example of a cryovolcano that potentially formed from a salty mud mix, and that formed in the geologically recent past," one researcher said. Learn more.
7. Shining a Light on the Bright Spots

The brightest area on Ceres, located in the mysterious Occator Crater, has the highest concentration of carbonate minerals ever seen outside Earth, according to studies from Dawn scientists. Occator is 57 miles (92 kilometers) wide, with a central pit about 6 miles (10 kilometers) wide. The dominant mineral of this bright area is sodium carbonate, a kind of salt found on Earth in hydrothermal environments. This material appears to have come from inside Ceres, and this upwelling suggests that temperatures inside Ceres are warmer than previously believed. Even more intriguingly, the results suggest that liquid water may have existed beneath the surface of Ceres in recent geological time. The salts could be remnants of an ocean, or localized bodies of water, that reached the surface and then froze millions of years ago. See more details.
8. Captain's Log
Dawn's chief engineer and mission director, Marc Rayman, provides regular dispatches about Dawn's work in the asteroid belt. Catch the latest updates here.
9. Eyes on Dawn
Another cool way to retrace Dawn's decade-long flight is to download NASA's free Eyes on the Solar System app, which uses real data to let you go to any point in the solar system, or ride along with any spacecraft, at any point in time—all in 3-D.
10. No Stamp Required

Send a postcard from one of these three sets of images that tell the story of dwarf planet Ceres, protoplanet Vesta, and the Dawn mission overall.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Our water-seeking robotic Moon rover just booked a ride to the Moon’s South Pole. Astrobotic of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, has been selected to deliver the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, to the Moon in 2023. During its 100-Earth-day mission, the approximately 1,000-pound rover will roam several miles and use its four science instruments to sample various soil environments in search of water ice. Its survey will help pave the way for a new era of human missions to the lunar surface and will bring us a step closer to developing a sustainable, long-term robotic and human presence on the Moon as part of the Artemis program.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Spot the International Space Station
Right now, there are humans living and working off the Earth on the International Space Station. They orbit our planet from 250 miles above every 90 minutes, which means the crew sees 16 sunrises and sunsets every day.

If you’re in the right place, at the right time, the space station is visible to the naked eye. It looks like a fast-moving plane, only much higher and traveling thousands of miles an hour faster. The fact that it’s the third brightest object in the sky makes it easier to spot…if you know when to look up.
That’s where we can help! Our Spot the Station site allows you to enter your location and find out when the space station will be flying overhead. You can even sign up to receive alerts that will send you email or text messages to let you know when and where to look up.

Why is the space station visible? It reflects the light of the Sun, the same reason we can see the Moon. However, unlike the Moon, the space station isn’t bright enough to see during the day.
To find out when the space station is flying over your area, visit: http://spotthestation.nasa.gov/
Learn more about the International Space Station and the crew HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What is some advice that really helped you get to where you are now?
-
 thetranstwink liked this · 1 month ago
thetranstwink liked this · 1 month ago -
 andy202405 liked this · 1 month ago
andy202405 liked this · 1 month ago -
 snazzycartoongal liked this · 3 months ago
snazzycartoongal liked this · 3 months ago -
 y0on-son reblogged this · 3 months ago
y0on-son reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 y0on-son liked this · 3 months ago
y0on-son liked this · 3 months ago -
 sighingbrrkitten liked this · 4 months ago
sighingbrrkitten liked this · 4 months ago -
 ramonajan liked this · 6 months ago
ramonajan liked this · 6 months ago -
 megacrawling liked this · 6 months ago
megacrawling liked this · 6 months ago -
 paper0wls reblogged this · 6 months ago
paper0wls reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 paper0wls liked this · 6 months ago
paper0wls liked this · 6 months ago -
 pinkish-orange liked this · 6 months ago
pinkish-orange liked this · 6 months ago -
 simsimousse liked this · 6 months ago
simsimousse liked this · 6 months ago -
 r4y4m3 liked this · 7 months ago
r4y4m3 liked this · 7 months ago -
 sparcky liked this · 7 months ago
sparcky liked this · 7 months ago -
 notyeeyee liked this · 7 months ago
notyeeyee liked this · 7 months ago -
 anonymitie liked this · 7 months ago
anonymitie liked this · 7 months ago -
 bellarose80 liked this · 8 months ago
bellarose80 liked this · 8 months ago -
 blevkuu liked this · 8 months ago
blevkuu liked this · 8 months ago -
 caringfroge reblogged this · 8 months ago
caringfroge reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 pzlqpibz liked this · 8 months ago
pzlqpibz liked this · 8 months ago -
 wayfaring-wynn reblogged this · 8 months ago
wayfaring-wynn reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 rockthesebraids liked this · 8 months ago
rockthesebraids liked this · 8 months ago -
 notsocasualenjoyer liked this · 8 months ago
notsocasualenjoyer liked this · 8 months ago -
 psyantics liked this · 9 months ago
psyantics liked this · 9 months ago -
 wiaterwieje liked this · 9 months ago
wiaterwieje liked this · 9 months ago -
 orphic-studies liked this · 9 months ago
orphic-studies liked this · 9 months ago -
 asimpforallthingsfictional liked this · 9 months ago
asimpforallthingsfictional liked this · 9 months ago -
 atrainpassenger reblogged this · 9 months ago
atrainpassenger reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 1lovcn liked this · 9 months ago
1lovcn liked this · 9 months ago -
 sleepy-autumns-world liked this · 9 months ago
sleepy-autumns-world liked this · 9 months ago -
 booreadmims liked this · 9 months ago
booreadmims liked this · 9 months ago -
 beautifulghostvoidpeach liked this · 9 months ago
beautifulghostvoidpeach liked this · 9 months ago -
 mijnmijntje liked this · 9 months ago
mijnmijntje liked this · 9 months ago -
 accidentallyoccidental reblogged this · 10 months ago
accidentallyoccidental reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 ilovelayingonthefloor liked this · 10 months ago
ilovelayingonthefloor liked this · 10 months ago -
 timothywinters liked this · 10 months ago
timothywinters liked this · 10 months ago -
 hattedaviator reblogged this · 10 months ago
hattedaviator reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 acciowriting liked this · 11 months ago
acciowriting liked this · 11 months ago -
 lady-bizarre liked this · 11 months ago
lady-bizarre liked this · 11 months ago -
 juncheol-17 liked this · 11 months ago
juncheol-17 liked this · 11 months ago -
 stellarskyes liked this · 11 months ago
stellarskyes liked this · 11 months ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts