Space Craft! Make NASA-Inspired Creations For World Embroidery Day

Space Craft! Make NASA-Inspired Creations for World Embroidery Day
It’s time to get crafty with some needle and thread. At NASA, we hope to inspire art of all kinds. To highlight #WorldEmbroideryDay on July 30, we want to know: does our imagery inspire you? Show us your art and we may feature it on social media.
How?
Search for a NASA image that inspires you. Here are a few places to get you started: Hubble, James Webb Space Telescope, Ocean Color, Landsat and Earth Observatory
Create. Over the years, we've seen a growing number of embroidered pieces that showcase our organization's research, especially with needlepoint.
Share your creation, along with the image it was inspired by, on social media using the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery. We will share selected pieces on July 30 for World Embroidery Day
Why?

NASA imagery has many functions. From studying distant galaxies to tracking ocean health, our scientists use these images to not only monitor our home planet, but better understand life beyond our solar system.
Embroidery is an ancient craft that has experienced a revival over the years. It involves decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Have you recently taken up embroidery? What images are you inspired by? We’d love to see it.
Image Resources for #NASAEmbroidery Inspiration
NASA Images
Hubble Image Gallery
NASA’s Ocean Color Image Gallery
James Webb Space Telescope
Landsat Image Gallery
Create and Share Your #NASAEmbroidery
Take a picture of your piece and upload it to Twitter, Instagram, Tumblr or Facebook. Make sure you use the hashtag #NASAEmbroidery so we know that you are taking part in the event and make sure that your privacy permissions allow us to view your post.
If the piece catches our eye, we may share your work on NASA’s main social media accounts as well as theme-related ones. We may also feature your art in a NASA Flickr gallery and our Tumblr pages. We’ll contact you directly to grant us permission to feature your work. You can follow @NASA on Twitter, Instagram and Facebook for embroidery creations, which will be featured from July 30-Aug. 1
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What’s On Board the Next SpaceX Cargo Launch?
Cargo and supplies are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station on Monday, July 18 at 12:45 a.m. EDT. The SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft will liftoff from our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Among the arriving cargo is the first of two international docking adapters, which will allow commercial spacecraft to dock to the station when transporting astronauts in the near future as part of our Commercial Crew Program.

This metallic ring, big enough for astronauts and cargo to fit through represents the first on-orbit element built to the docking measurements that are standardized for all the spacecraft builders across the world.

Its first users are expected to be the Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft, which are both now in development.
What About the Science?!
Experiments launching to the station range from research into the effects of microgravity on the human body, to regulating temperature on spacecraft. Take a look at a few:
A Space-based DNA Sequencer

DNA testing aboard the space station typically requires collecting samples and sending them back to Earth to be analyzed. Our Biomolecule Sequencer Investigation will test a new device that will allow DNA sequencing in space for the first time! The samples in this first test will be DNA from a virus, a bacteria and a mouse.
How big is it? Picture your smartphone…then cut it in half. This miniature device has the potential to identify microbes, diagnose diseases and evaluate crew member health, and even help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
OsteoOmics
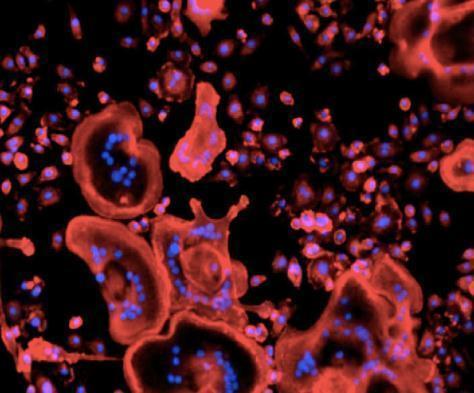
OsteoOmics is an experiment that will investigate the molecular mechanisms that dictate bone loss in microgravity. It does this by examining osteoblasts, which form bone; and osteoclasts, which dissolves bone. New ground-based studies are using magnetic levitation equipment to simulate gravity-related changes. This experiment hopes to validate whether this method accurately simulates the free-fall conditions of microgravity.
Results from this study could lead to better preventative care or therapeutic treatments for people suffering bone loss, both on Earth and in space!
Heart Cells Experiment

The goals of the Effects of Microgravity on Stem Cell-Derived Heart Cells (Heart Cells) investigation include increasing the understanding of the effects of microgravity on heart function, the improvement of heart disease modeling capabilities and the development of appropriate methods for cell therapy for people with heart disease on Earth.
Phase Change Material Heat Exchanger (PCM HX)

The goal of the Phase Change Material Heat Exchanger (PCM HX) project is to regulate internal spacecraft temperatures. Inside this device, we're testing the freezing and thawing of material in an attempt to regulate temperature on a spacecraft. This phase-changing material (PCM) can be melted and solidified at certain high heat temperatures to store and release large amounts of energy.
Watch Launch!
Live coverage of the SpaceX launch will be available starting at 11:30 p.m. EDT on Sunday, July 17 via NASA Television.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Urban Growth of New Delhi

The capital of India, New Delhi, has been experiencing one of the fastest urban expansions in the world. Vast areas of croplands and grasslands are being turned into streets, buildings, and parking lots, attracting an unprecedented amount of new residents. By 2050, the United Nations projects India will add 400 million urban dwellers, which would be the largest urban migration in the world for the thirty-two year period.
These images show the growth in the city of New Delhi and its adjacent areas—a territory collectively known as Delhi—from December 5, 1989 to June 5, 2018.
Most of the expansion in Delhi has occurred on the peripheries of New Delhi, as rural areas have become more urban. The geographic size of Delhi has almost doubled from 1991 to 2011, with the number of urban households doubling while the number of rural houses declined by half. Cities outside of Delhi—Bahadurgarh, Ghaziabad, Noida, Faridabad, and Gurugram—have also experienced urban growth over the past three decades, as shown in these images.
Read more: https://go.nasa.gov/2y32G7h
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Why are bacteria resistant polymers being experimented, specifically in microgravity?
I love astrophysics and especially black holes and I want to pursue a career on them, but to be honest I'm scared to be not good enough or not clever enough. How did you decide to work on black holes? How did you become the person you are today?
NASA and Veterans

November 11 each year is a day we honor those who have served in our nation’s armed forces.

Discover how we have close ties to the military, even to this day, and see who has traded in their camouflage uniform for an astronaut flight suit.

There have been veterans working for us since the beginning, even when it was still called the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA).
Additionally, there are several active duty military members working at NASA facilities through special government programs.


Today, there are more than 1500 veterans currently employed with us. Their experiences in the military make their expertise invaluable around the agency. We value the unique leadership style they bring to the work place. Above and below are some astronaut veterans.



A Partnership for the Space Age
Since the early days of NASA, we’ve partnered with all branches of the military. We still work closely with the military today and rely on the expertise of our service members to support our missions both while in active duty and in the civilian workforce. Here are some examples of this close partnership:

The Marines helped with recovery efforts of Astronaut Alan Shepard at the end of his sub-orbital flight on May 5, 1961...a task performed across several of our missions.

Today, the Navy helps us recover spacecraft, just like the Orion space capsule...which will one day carry astronauts into deep space and eventually on our journey to Mars.

. . .and the Air Force has traditionally and continues to help us transport sensitive and critical space hardware around the globe.

The Coast Guard has even helped us access remote locations to collect oceanographic data as part of our efforts to study and learn more about the Earth.

We’ve partnered with the Army to use their unique capabilities at the Yuma Proving Ground to test the entry, descent and landing of our spacecraft systems.

To all the Veteran’s out there, we thank you for your service to America and your continued support of America’s space program.
Happy Veteran’s Day!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What is your advise to people who wanna be astronaut?
What’s Up - June 2018
What’s Up For June?
Jupiter and Venus at sunset, Mars, Saturn and Vesta until dawn.

First up is Venus. It reaches its highest sunset altitude for the year this month and sets more than two hours after sunset.

You can't miss Jupiter, only a month after its opposition--when Earth was directly between Jupiter and the Sun.

The best time to observe Jupiter through a telescope is 10:30 p.m. at the beginning of the month and as soon as it's dark by the end of the month.

Just aim your binoculars at the bright planet for a view including the four Galilean moons. Or just enjoy Jupiter with your unaided eye!

Saturn is at opposition June 27th, when it and the Sun are on opposite sides of Earth. It rises at sunset and sets at sunrise. Great Saturn viewing will last several more months. The best views this month will be just after midnight.

All year, the rings have been tilted wide open--almost 26 degrees wide this month--giving us a great view of Saturn's distinctive rings.

The tilt offers us a view of the north polar region, so exquisitely imaged by the Cassini spacecraft.

Near Saturn, the brightest asteroid--Vesta--is so bright that it can be seen with your unaided eye. It will be visible for several months.

A detailed star chart will help you pick out the asteroid from the stars. The summer Milky way provides a glittery backdrop.

Finally, Mars grows dramatically in brightness and size this month and is visible by 10:30 p.m. by month end.

The best views are in the early morning hours. Earth's closest approach with Mars is only a month away. It's the closest Mars has been to us since 2003.

Watch the full What’s Up for June Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
TESS: The Planet Hunter
So you’re thinking...who’s TESS? But, it’s more like: WHAT is TESS?
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is an explorer-class planet finder that is scheduled to launch in April 2018. This mission will search the entire sky for exoplanets — planets outside our solar system that orbit sun-like stars.

In the first-ever space borne all-sky transit survey, TESS will identify planets ranging from Earth-sized to gas giants, orbiting a wide range of stellar types and orbital distances.
The main goal of this mission is to detect small planets with bright host stars in the solar neighborhood, so that we can better understand these planets and their atmospheres.

TESS will have a full time job monitoring the brightness of more than 200,000 stars during a two year mission. It will search for temporary drops in brightness caused by planetary transits. These transits occur when a planet’s orbit carries it directly in front of its parent star as viewed from Earth (cool GIF below).

TESS will provide prime targets for further, more detailed studies with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), as well as other large ground-based and space-based telescopes of the future.
What is the difference between TESS and our Kepler spacecraft?
TESS and Kepler address different questions: Kepler answers "how common are Earth-like planets?" while TESS answers “where are the nearest transiting rocky planets?”

What do we hope will come out of the TESS mission?
The main goal is to find rocky exoplanets with solid surfaces at the right distance from their stars for liquid water to be present on the surface. These could be the best candidates for follow-up observations, as they fall within the “habitable zone” and be at the right temperatures for liquid water on their surface.
TESS will use four cameras to study sections of the sky’s north and south hemispheres, looking for exoplanets. The cameras would cover about 90 percent of the sky by the end of the mission. This makes TESS an ideal follow-up to the Kepler mission, which searches for exoplanets in a fixed area of the sky. Because the TESS mission surveys the entire sky, TESS is expected to find exoplanets much closer to Earth, making them easier for further study.
Stay updated on this planet-hunting mission HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for March 2016?
In March, Jupiter, it’s moons and moon shadows will all be visible in the sky. Find out when and where to look up:

Jupiter dominates the evening sky this month, rising at sunset and setting at dawn. On March 8, Jupiter reaches what is called “opposition”. Imagine that Jupiter and the sun are at opposite ends of a straight line, with the Earth in between. This brings Jupiter its closest to Earth, so it shines brighter and appears larger in telescopes.

On the nights of March 14 – 15, March 21 – 22 and March 29, two of Jupiter’s moons will cross the planet’s disk.

When the planet is at opposition and the sun shines on Jupiter’s moons, we can see the moon’s shadow crossing the planet. There are actually 11 of these double shadow transits in March!

The next six months will be awesome times for you to image Jupiter when it’s highest in the sky; near midnight now, and a little earlier each night through the late summer.
Even through the smallest telescopes or binoculars, you should be able to see the two prominent belts on each side of Jupiter’s equator made up of the four Galilean moons: Io, Europa Ganymede and Calisto. If you have a good enough view, you may even see Jupiter’s Red Spot!

Our Juno spacecraft will arrive at Jupiter on July 4th of this year and will go into orbit around the giant planet. Right now, the Juno mission science team is actively seeking amateur and professional images of the planet. These images are uploaded to a Juno website, and the public is invited to discuss points of interest in Jupiter’s atmosphere.

Locations will later be voted on and the favorites will be targets for JunoCam, the spacecraft’s imaging camera. Once JunoCam has taken the images, they’ll be posted online. Imaging participants can then process these raw mission images and re-upload them for others to view.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
House of Horrors: Exoplanet Edition
Astronomers may be closer than ever to discovering a planet that’s habitable like our own, but along the way they’ve discovered some very scary exoplanets – places where conditions are far too harsh for life as we know it to exist.
Okay, but what IS an exoplanet???

We’ve rounded up some of the most frightening, deadly exoplanets, places that make even the scariest haunted house on Earth pale in comparison. Check them out...
Radiation Bath, Anyone?
The exoplanets PSR B1257+12 B, C & D were among the first discovered, and also happened to be three of the weirdest! The entire system is a graveyard, remnants of what used to be a normal, functional solar system before the star blew apart in a giant explosion known as a supernova.

The massive shockwave from the supernova stripped away any atmosphere or living creatures that might have once lived on these planets, leaving behind ghostly, rocky shells, dead planets orbiting the corpse of an extinct star.
Except that the system isn’t completely dead…the remaining core from the old star has become a zombie star called a pulsar. Literally spinning in its grave, it makes a full rotation every 6.22 milliseconds and emits an intense beam of radiation that can be detected from Earth. The star’s unfortunate planets are thus bathed in deadly radiation on a regular basis, making sure that this system remains a cosmic no-man’s land.
A Mighty Wind
The sound of howling wind is a must for any Earth-based haunted house, but weather conditions on HD 189733 b make it a very dangerous place to go trick-or-treating.
At first glance, this exoplanet looks like the typical “hot Jupiter” — a huge gas planet perched dangerously to a burning-hot star, with daytime temperatures around a balmy 1,770 degrees Fahrenheit. This exoplanet is also “tidally locked” in its orbit, which means that the same side of the planet always faces its star.

But when scientists measured the planet’s nighttime temperature, they were shocked to find that it was only 500 degrees cooler. How does the back side of the planet stay so warm?
The answer is wind! Insanely fast, dangerous wind that whisks heat from day-side to night-side at a speed of 4,500 mph, nearly six times the speed of sound! In fact, astronomers estimate that wind speeds might top out at 5,400 mph, conditions that make hurricanes on Earth look like a breezy day at the beach.
Newborn Exoplanet Around Scorching Star
This exoplanet, named K2-33b, is the youngest fully formed exoplanet ever detected. This planet is a bit larger than Neptune and whips tightly around its star every five days. Since this planet sits nearly 10 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our sun, it’s HOT!

No matter how cute you think infants are, this is one baby you’d want to stay away from.
Boil, Boil, Toil and Trouble
The planet HD 209458 b (aka. Osiris - the god of death) has a few things in common with Earth: water vapor, methane and carbon dioxide in its atmosphere, key ingredients for life on our planet. Don’t be fooled, though, because this planet is a rolling cauldron of almost unimaginable heat.

Even the hottest summer days on Earth don’t get as dangerous as the conditions here. A planet that orbits so close to its host star that its atmosphere is literally boiling off, ripped away from the planet as it whips around on its breakneck 3.5-day orbit.
All Alone and Very, Very Cold
While most of the exoplanets found so far are hellishly hot, OGLE-2005-BLG-390L b has the distinction of being extremely cold.
The planet takes about 10 Earth years to orbit its tiny dwarf star, and it’s a chilly trip; the average temperature on this exoplanet is 50 Kelvin, or minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit! A good costume for trick-or-treating on this frigid planet would be a toasty self-heating spacesuit, an oxygen supply, ice skates and plenty of hot cocoa.

Of course, don’t expect to find many houses with candy here, because despite the fact that it’s just a few times bigger than Earth, this exoplanet is an uninhabitable ice ball stuck in a perpetual winter freeze.
A Scorched World
Kepler-10b is a scorched world, orbiting at a distance that’s more than 20 times closer to its star than Mercury is to our own sun. The daytime temperatures are expected to be more than 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit, hotter than lava flows here on Earth.

Intense radiation from the star has kept the planet from holding onto an atmosphere, but flecks of silicates and iron that have boiled off a molten surface are swept away by the stellar radiation.
Learn more about worlds beyond our solar system at: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 claired3lune reblogged this · 1 month ago
claired3lune reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 retroowl liked this · 2 months ago
retroowl liked this · 2 months ago -
 eriadu-in-the-wildwood reblogged this · 5 months ago
eriadu-in-the-wildwood reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 timetravelbypen reblogged this · 5 months ago
timetravelbypen reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 that-transformers-fan liked this · 5 months ago
that-transformers-fan liked this · 5 months ago -
 m4yara-th3-d0g liked this · 7 months ago
m4yara-th3-d0g liked this · 7 months ago -
 stigmaticfag liked this · 8 months ago
stigmaticfag liked this · 8 months ago -
 embroideryinspoooooo reblogged this · 8 months ago
embroideryinspoooooo reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 stitchlingbelle reblogged this · 10 months ago
stitchlingbelle reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 lunar-wanderer liked this · 10 months ago
lunar-wanderer liked this · 10 months ago -
 ella-elei liked this · 11 months ago
ella-elei liked this · 11 months ago -
 lifenolonger liked this · 11 months ago
lifenolonger liked this · 11 months ago -
 fuckin-gender-disaster liked this · 1 year ago
fuckin-gender-disaster liked this · 1 year ago -
 jfoejfpsjeo liked this · 1 year ago
jfoejfpsjeo liked this · 1 year ago -
 foggywinnerwerewolf liked this · 1 year ago
foggywinnerwerewolf liked this · 1 year ago -
 darkbouquetpoet liked this · 1 year ago
darkbouquetpoet liked this · 1 year ago -
 leg-gayblonde reblogged this · 1 year ago
leg-gayblonde reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 chickenbyday liked this · 1 year ago
chickenbyday liked this · 1 year ago -
 slightlytiredbutstilltrying liked this · 1 year ago
slightlytiredbutstilltrying liked this · 1 year ago -
 notsureaboutthishug liked this · 1 year ago
notsureaboutthishug liked this · 1 year ago -
 andineverwill liked this · 1 year ago
andineverwill liked this · 1 year ago -
 eli-thinks liked this · 1 year ago
eli-thinks liked this · 1 year ago -
 slimeshifter reblogged this · 1 year ago
slimeshifter reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 slimeshifter liked this · 1 year ago
slimeshifter liked this · 1 year ago -
 bildadtheshuhitestudies liked this · 1 year ago
bildadtheshuhitestudies liked this · 1 year ago -
 smiley-aea reblogged this · 1 year ago
smiley-aea reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 smiley-aea liked this · 1 year ago
smiley-aea liked this · 1 year ago -
 horsesmaybe liked this · 1 year ago
horsesmaybe liked this · 1 year ago -
 kinna-bari liked this · 1 year ago
kinna-bari liked this · 1 year ago -
 flintandpyrite reblogged this · 1 year ago
flintandpyrite reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 justonebigbee liked this · 1 year ago
justonebigbee liked this · 1 year ago -
 avidfireflycatcher liked this · 1 year ago
avidfireflycatcher liked this · 1 year ago -
 throwinghalos liked this · 1 year ago
throwinghalos liked this · 1 year ago -
 ace-of-pans liked this · 1 year ago
ace-of-pans liked this · 1 year ago -
 ss--aa--mm liked this · 1 year ago
ss--aa--mm liked this · 1 year ago -
 itrvahn liked this · 1 year ago
itrvahn liked this · 1 year ago -
 eduardopepe liked this · 1 year ago
eduardopepe liked this · 1 year ago -
 mano8 liked this · 1 year ago
mano8 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ironsoul69 liked this · 1 year ago
ironsoul69 liked this · 1 year ago -
 chubby-aphrodite reblogged this · 1 year ago
chubby-aphrodite reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 imrryr liked this · 1 year ago
imrryr liked this · 1 year ago -
 deepestanimeartmuffin reblogged this · 1 year ago
deepestanimeartmuffin reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rede3pl liked this · 1 year ago
rede3pl liked this · 1 year ago -
 jay-dozed-off liked this · 1 year ago
jay-dozed-off liked this · 1 year ago -
 hiro-sedgefield liked this · 1 year ago
hiro-sedgefield liked this · 1 year ago -
 insert-math-username reblogged this · 1 year ago
insert-math-username reblogged this · 1 year ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts