Bringing The Space Station Perspective To Earth In VR!
Bringing The Space Station Perspective to Earth in VR!
Only a few humans ever get to experience the awe-inspiring vantage point provided by the space station, but a new virtual reality (VR) experience, Space Explorers: The ISS Experience (ISS Experience), attempts to bring this perspective back to Earth for the rest of us.

Partnering with the ISS National Lab and Time, a team from Felix and Paul Studios launched a high quality 360 degree camera to space to help tell the story of science and life aboard the orbiting laboratory.

The project, currently in the process of being filmed by the station astronauts themselves, serves as an outreach project as well a technology demonstration, testing the limits of filming in the harsh environment of space.

The camera flew to the station on 16th SpaceX commercial resupply services mission in December 2018 along with a number of other scientific experiments.

Since then, the team has recorded many moments, including the SPHERES robots flying around the station (see below) , the growing and harvesting of vegetables, jam session among the astronauts, crew meals and the arrival of new astronauts.

So far, the footage coming back seems to be achieving the goal of immersing audiences in science and life aboard the space station. NASA astronaut Sunita Williams got the chance to watch some of the initial footage and says it was like I was back on the station.

While most of the filming has been completed, the biggest technical challenge is yet to come: capturing a spacewalk in virtual reality. The team expects to launch a new camera for spacewalk filming and begin production of spacewalk filming in 2020.

Learn more about ISS Experience here.
For daily updates, follow @ISS_Research on Twitter, Space Station Research and Technology News or our Facebook. Follow the ISS National Lab for information on its sponsored investigations. For opportunities to see the space station pass over your town, check out Spot the Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Glacier Turns into a ‘Snow Swamp’
In just four days this summer, miles of snow melted from Lowell Glacier in Canada. Mauri Pelto, a glaciologist at Nichols College, called the area of water-saturated snow a “snow swamp.”

These false-color images show the rapid snow melt in Kluane National Park in the Yukon Territory. The first image was taken on July 22, 2018, by the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-2; the next image was acquired on July 26, 2018, by the Landsat 8 satellite.
Ice is shown as light blue, while meltwater is dark blue. On July 26, the slush covered more than 25 square miles (40 square km).
During those four days, daily temperatures 40 miles (60 km) northeast of the glacier reached 84 degrees Fahrenheit (29 degrees Celsius) — much higher than normal for the region in July.
Read more: https://go.nasa.gov/2Q9JSeO
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What is so special about the solar eclipse to you??
Huh, that’s a very good question and I probably answer it differently each time I get asked it. I love the fact that in totality you can see the solar atmosphere and get a chance to see the magnetic field structure of the Sun. This is something that you can’t normally do. I also love the idea that we’re going to be able to test a bunch of ionospheric models with the help of citizen scientist! This again is a very unique opportunity! But probably the thing that seems so special about this particular eclipse is seeing how excited everyone is about it! Most days I sit in my office working on my science (which I think is the best science and most interesting thing in the world- but I’m probably biased about that) and not too many other people in the world are all that excited about it. But with the eclipse, I get to share how cool this science is, and it’s amazing to see everyone get involved!
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
The solar system is vast, and exploring it requires not one expedition, but many. From the sun to the Earth to the depths of space beyond Pluto, an entire fleet of spacecraft is pushing back the frontiers of knowledge. Scientists and engineers around the world work together on dozens of missions, and the results of their work unfold on a daily basis. During any given week, astronauts and robotic spacecraft return thousands of pictures and other data from Earth orbit and from half a dozen other worlds.
The result? It’s nothing short of a visual and intellectual feast. For example, all of the following images were obtained over the course of one week during January this year.
The same missions that took these pictures are still at work – they may be photographing Saturn or transmitting a report from Mars as you read this.
1. The Sun

From its clear vantage point in Earth orbit, our Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) observes our nearby star almost continuously. This image shows activity on the sun’s surface on Jan. 18. You can also get similar pictures from SDO daily!
2. The Earth from Afar

The DSCOVR satellite orbits the Earth at a distance of nearly a million miles (1.5 million kilometers). It’s Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera (EPIC) keeps a steady watch on the home planet. This is how the world turned on Jan. 20. Get the latest daily images from EPIC HERE.
3. Mars from Above

The team that manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) recently celebrated a decade of observing the Red Planet. MRO took this detailed look at dunes and rocky buttes in Danielson Crater on Jan. 24. It was 3:06 p.m., local Mars time. On the right stide of the image, dust devils have left tracks in the sand.
4. Comet 67/P

The European Space Agency’s Rosetta probe caught this look at the surface of Comet 67/P from a distance of just 46 miles (75 kilometers) on Jan. 23.
5. Saturn

On the same day (Jan. 23), our Cassini spacecraft continued its odyssey of nearly two decades in space, bringing us this look at the sixth planet. See the latest images from Cassini HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up - July 2018
What's Up for July?
Mars is closest to Earth since 2003!

July’s night skies feature Mars opposition on the 27th, when Mars, Earth, and the Sun all line up, and Mars’ closest approach to Earth since 2003 on the 31st.

If you've been sky watching for 15 years or more, then you'll remember August 2003, when Mars approached closer to Earth than it had for thousands of years.

It was a very small percentage closer, but not so much that it was as big as the moon as some claimed.

Astronomy clubs everywhere had long lines of people looking through their telescopes at the red planet, and they will again this month!

If you are new to stargazing, this month and next will be a great time to check out Mars.

Through a telescope, you should be able to make out some of the light and dark features, and sometimes polar ice. Right now, though, a huge Martian dust storm is obscuring many features, and less planetary detail is visible.

July 27th is Mars opposition, when Mars, Earth, and the Sun all line up, with Earth directly in the middle.

A few days later on July 31st is Mars' closest approach. That's when Mars and Earth are nearest to each other in their orbits around the Sun. Although there will be a lot of news focusing on one or the other of these two dates, Mars will be visible for many months.

By the end of July, Mars will be visible at sunset.

But the best time to view it is several hours after sunset, when Mars will appear higher in the sky.

Mars will still be visible after July and August, but each month it will shrink in apparent size as it travels farther from Earth in its orbit around the Sun.

On July 27th a total lunar eclipse will be visible in Australia, Asia, Africa, Europe and South America.

For those viewers, Mars will be right next to the eclipsing moon!

Next month will feature August's summer Perseids. It's not too soon to plan a dark sky getaway for the most popular meteor shower of the year!
Watch the full What’s Up for July Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Say hello to spiral galaxy NGC 7331👋
Happy National Twin Day!
The majestic spiral galaxy NGC 7331 is almost like a long lost twin to our very own Milky Way. In this close-up, the galaxy’s magnificent spiral arms feature dark, obscuring dust lanes, bright bluish clusters of massive young stars and the telltale reddish glow of active star-forming regions. The yellowish central region harbors populations of older, cooler stars. Like in the Milky Way, a supermassive black hole lies at the galaxy’s core.
Our Hubble Space Telescope took this image while observing a supernova explosion — the fiery death of a massive star — within NGC 7331. Astronomers noted that the supernova, called SN 2014C, experienced a dramatic, hasty transformation that involved a significant upsurge in hydrogen content. This observation provided a rare chance to gain insight into the final stages of massive stars.
NGC 7331 was discovered in 1784 by famed astronomer William Herschel, who discovered the planet Uranus. It was originally classified as a nebula, which is an interstellar cloud of gas and dust, because no one knew that other galaxies existed until the 20th century. It turns out that NGC 7331 and the Milky Way are among billions and billions of galaxies in the universe!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
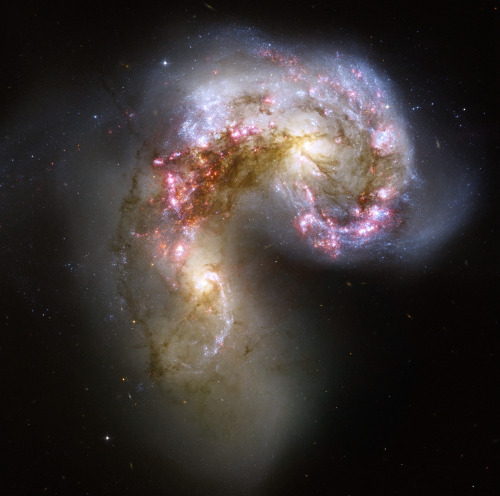

Say hello to the Antennae galaxies 👋
Two galaxies are locked in a deadly embrace in this Hubble Space Telescope image. Once normal, sedate spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, this galactic pair has spent the past few hundred million years sparring. The clash is so violent that stars have been ripped from their host galaxies to form a streaming arc between the two.
The far-flung stars and streamers of gas stretch out into space, creating long tidal tails reminiscent of antennae (not visible in this close-up Hubble view). Clouds of gas blossom out in bright pink and red, surrounding the bright flashes of blue star-forming regions — some of which are partially obscured by dark patches of dust.
Hubble’s observations have uncovered over 1,000 bright, young star clusters bursting to life as a result of the head-on wreck. The sweeping spiral-like patterns, traced by bright blue star clusters, shows the result of a firestorm of star-birth activity, which was triggered by the collision. The rate of star formation is so high that the Antennae galaxies are said to be in a state of starburst, a period in which all of the gas within the galaxies is being used to form stars. This cannot last forever, and neither can the separate galaxies; eventually the nuclei will coalesce and the galaxies will begin their retirement together as one large elliptical galaxy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
10 Things: Why Cassini Mattered
One year ago, on Sept. 15, 2017, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft ended its epic exploration of Saturn with a planned dive into the planet’s atmosphere--sending back new science to the last second. The spacecraft is gone, but the science continues. Here are 10 reasons why Cassini mattered...

1. Game Changers
Cassini and ESA (European Space Agency)’s Huygens probe expanded our understanding of the kinds of worlds where life might exist.

2. A (Little) Like Home
At Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, Cassini and Huygens showed us one of the most Earth-like worlds we’ve ever encountered, with weather, climate and geology that provide new ways to understand our home planet.

3. A Time Machine (In a Sense)
Cassini gave us a portal to see the physical processes that likely shaped the development of our solar system, as well as planetary systems around other stars.

4. The Long Run
The length of Cassini’s mission enabled us to observe weather and seasonal changes over nearly half of a Saturn year, improving our understanding of similar processes at Earth, and potentially those at planets around other stars.

5. Big Science in Small Places
Cassini revealed Saturn’s moons to be unique worlds with their own stories to tell.

6. Ringscape
Cassini showed us the complexity of Saturn’s rings and the dramatic processes operating within them.

7. Pure Exploration
Some of Cassini’s best discoveries were serendipitous. What Cassini found at Saturn prompted scientists to rethink their understanding of the solar system.

8. The Right Tools for the Job
Cassini represented a staggering achievement of human and technical complexity, finding innovative ways to use the spacecraft and its instruments, and paving the way for future missions to explore our solar system.

9. Jewel of the Solar System
Cassini revealed the beauty of Saturn, its rings and moons, inspiring our sense of wonder and enriching our sense of place in the cosmos.

10. Much Still to Teach Us
The data returned by Cassini during its 13 years at Saturn will continue to be studied for decades, and many new discoveries are undoubtedly waiting to be revealed. To keep pace with what’s to come, we’ve created a new home for the mission--and its spectacular images--at https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/cassini.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Four Cool Facts About Our New Rocket’s Booster Test Firing
The countdown to our last full-scale test firing of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) solid rocket boosters has begun (mark your calendars: June 28, 8:05 a.m. MDT [local time] 10:05 a.m. EDT). SLS is NASA’s new rocket that can go to deep space destinations, and this test is one more step on our Journey to Mars. This test will be broadcast live on NASA TV and our Facebook page. For those watching at home or work, here are four cool things that might not be so obvious on the screen.
1. So Hot, It Turns Sand Into Glass

With expanding gases and flames exiting the nozzle at speeds in excess of Mach 3 and temperatures reaching 3,700 degrees Fahrenheit, say goodbye to some of the sand at Orbital ATK’s test facility in the Utah desert because after the test, the sand at the aft, or rear, end of the booster motor will be glass.
2. This Motor’s Chill

This motor has been chilling — literally, down to 40 degrees — since the first week in May in Orbital ATK’s “booster house,” a special building on rails that moves to enclose the booster and rolls back so the motor can be test-fired. Even though SLS will launch from the normally balmy Kennedy Space Center in Florida, temperatures can vary there and engineers need to be sure the booster will perform as expected whether the propellant inside the motor is 40 degrees or 90 degrees (the temperature of the propellant during the first full-scale test, Qualification Motor 1 or QM-1).
3. This Booster’s on Lockdown

If you happen to be near Promontory, Utah, on June 28, you can view the test for yourself in the public viewing area off State Route 83. And don’t worry, this booster’s not going anywhere — engineers have it locked down. The motor is held securely in place by Orbital ATK’s T-97 test stand. During the test, the motor will push against a forward thrust block with more than three million pounds of force. Holding down the rocket motor is more than 13 million pounds of concrete — most of which is underground. The test stand contains a system of load cells that enable engineers to measure the thrust the motor produces and verify their predictions.
4. Next Time, It’s For Real

These solid rocket boosters are the largest and most powerful ever built for flight. They’ve been tested and retested in both full-scale and smaller subsystem-level tests, and vital parts like the nozzle, insulation and avionics control systems have been upgraded and revamped. Most of this work was necessary because, plainly put, SLS needs bigger boosters. Bigger boosters mean bolder missions – like around the moon during the first integrated mission of SLS and Orion. So the next time we see these solid rocket motors fire, they will be propelling SLS off the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center and on its first flight with NASA’s Orion spacecraft. For real.
We Like Big Rockets and We Cannot Lie: Saturn V vs. SLS
On this day 50 years ago, human beings embarked on a journey to set foot on another world for the very first time.

At 9:32 a.m. EDT, millions watched as Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins lifted off from Launch Pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, flying high on the most powerful rocket ever built: the mighty Saturn V.

As we prepare to return humans to the lunar surface with our Artemis program, we’re planning to make history again with a similarly unprecedented rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS will be our first exploration-class vehicle since the Saturn V took American astronauts to the Moon a decade ago. With its superior lift capability, the SLS will expand our reach into the solar system, allowing astronauts aboard our Orion spacecraft to explore multiple, deep-space destinations including near-Earth asteroids, the Moon and ultimately Mars.

So, how does the Saturn V measure up half a century later? Let’s take a look.
Mission Profiles: From Apollo to Artemis
Saturn V

Every human who has ever stepped foot on the Moon made it there on a Saturn V rocket. The Saturn rockets were the driving force behind our Apollo program that was designed to land humans on the Moon and return them safely back to Earth.

Developed at our Marshall Space Flight Center in the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket (V for the Roman numeral “5”) launched for the first time uncrewed during the Apollo 4 mission on November 9, 1967. One year later, it lifted off for its first crewed mission during Apollo 8. On this mission, astronauts orbited the Moon but did not land. Then, on July 16, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission was the first Saturn V flight to land astronauts on the Moon. In total, this powerful rocket completed 13 successful missions, landing humans on the lunar surface six times before lifting off for the last time in 1973.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Just as the Saturn V was the rocket of the Apollo generation, the Space Launch System will be the driving force behind a new era of spaceflight: the Artemis generation.

During our Artemis missions, SLS will take humanity farther than ever before. It is the vehicle that will return our astronauts to the Moon by 2024, transporting the first woman and the next man to a destination never before explored – the lunar South Pole. Over time, the rocket will evolve into increasingly more powerful configurations to provide the foundation for human exploration beyond Earth’s orbit to deep space destinations, including Mars.
SLS will take flight for the first time during Artemis 1 where it will travel 280,000 miles from Earth – farther into deep space than any spacecraft built for humans has ever ventured.
Size: From Big to BIGGER
Saturn V

The Saturn V was big.
In fact, the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume and was built specifically for assembling the massive rocket. At a height of 363 feet, the Saturn V rocket was about the size of a 36-story building and 60 feet taller than the Statue of Liberty!
Space Launch System (SLS)

Measured at just 41 feet shy of the Saturn V, the initial SLS rocket will stand at a height of 322 feet. Because this rocket will evolve into heavier lift capacities to facilitate crew and cargo missions beyond Earth’s orbit, its size will evolve as well. When the SLS reaches its maximum lift capability, it will stand at a height of 384 feet, making it the tallest rocket in the world.
Power: Turning Up the Heat
Saturn V
For the 1960s, the Saturn V rocket was a beast – to say the least.
Fully fueled for liftoff, the Saturn V weighed 6.2 million pounds and generated 7.6 million pounds of thrust at launch. That is more power than 85 Hoover Dams! This thrust came from five F-1 engines that made up the rocket’s first stage. With this lift capability, the Saturn V had the ability to send 130 tons (about 10 school buses) into low-Earth orbit and about 50 tons (about 4 school buses) to the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)

Photo of SLS rocket booster test
Unlike the Saturn V, our SLS rocket will evolve over time into increasingly more powerful versions of itself to accommodate missions to the Moon and then beyond to Mars.
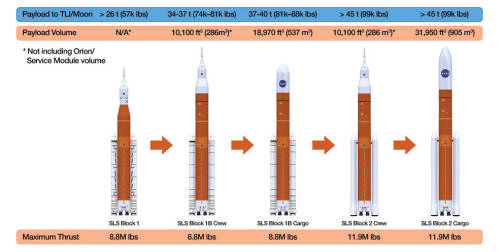
The first SLS vehicle, called Block 1, will weigh 5.75 million pounds and produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust at time of launch. That’s 15 percent more than the Saturn V produced during liftoff! It will also send more than 26 tons beyond the Moon. Powered by a pair of five-segment boosters and four RS-25 engines, the rocket will reach the period of greatest atmospheric force within 90 seconds!

Following Block 1, the SLS will evolve five more times to reach its final stage, Block 2 Cargo. At this stage, the rocket will provide 11.9 million pounds of thrust and will be the workhorse vehicle for sending cargo to the Moon, Mars and other deep space destinations. SLS Block 2 will be designed to lift more than 45 tons to deep space. With its unprecedented power and capabilities, SLS is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and large cargo to the Moon on a single mission.
Build: How the Rockets Stack Up
Saturn V

The Saturn V was designed as a multi-stage system rocket, with three core stages. When one system ran out of fuel, it separated from the spacecraft and the next stage took over. The first stage, which was the most powerful, lifted the rocket off of Earth’s surface to an altitude of 68 kilometers (42 miles). This took only 2 minutes and 47 seconds! The first stage separated, allowing the second stage to fire and carry the rest of the stack almost into orbit. The third stage placed the Apollo spacecraft and service module into Earth orbit and pushed it toward the Moon. After the first two stages separated, they fell into the ocean for recovery. The third stage either stayed in space or crashed into the Moon.
Space Launch System (SLS)
Much like the Saturn V, our Space Launch System is also a multi-stage rocket. Its three stages (the solid rocket boosters, core stage and upper stage) will each take turns thrusting the spacecraft on its trajectory and separating after each individual stage has exhausted its fuel. In later, more powerful versions of the SLS, the third stage will carry both the Orion crew module and a deep space habitat module.
A New Era of Space Exploration
Just as the Saturn V and Apollo era signified a new age of exploration and technological advancements, the Space Launch System and Artemis missions will bring the United States into a new age of space travel and scientific discovery.
Join us in celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing and hear about our future plans to go forward to the Moon and on to Mars by tuning in to a special two-hour live NASA Television broadcast at 1 p.m. ET on Friday, July 19. Watch the program at www.nasa.gov/live.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Spooky Sounds from Across the Solar System
Soaring to the depths of our universe, gallant spacecraft roam the cosmos, snapping images of celestial wonders. Some spacecraft have instruments capable of capturing radio emissions. When scientists convert these to sound waves, the results are eerie to hear.
In time for Halloween, we've put together a compilation of elusive "sounds" of howling planets and whistling helium that is sure to make your skin crawl.
Listen to a few here and visit our Soundcloud for more spooky sounds.
Cassini Ring Crossing
This eerie audio represents data collected by our Cassini spacecraft, as it crossed through the gap between Saturn and its rings on April 26, 2017, during the first dive of the mission's Grand Finale. The instrument is able to record ring particles striking the spacecraft in its data. In the data from this dive, there is virtually no detectable peak in pops and cracks that represent ring particles striking the spacecraft. The lack of discernible pops and cracks indicates the region is largely free of small particles.
Voyager Tsunami Waves in Interstellar Space
Listen to this howling audio from our Voyager 1 spacecraft. Voyager 1 has experienced three "tsunami waves" in interstellar space. This kind of wave occurs as a result of a coronal mass ejection erupting from the Sun. The most recent tsunami wave that Voyager experienced began in February 2014, and may still be going. Listen to how these waves cause surrounding ionized matter to ring like a bell.
Voyager Sounds of Interstellar Space
Our Voyager 1 spacecraft captured these high-pitched, spooky sounds of interstellar space from October to November 2012 and April to May 2013.
The soundtrack reproduces the amplitude and frequency of the plasma waves as "heard" by Voyager 1. The waves detected by the instrument antennas can be simply amplified and played through a speaker. These frequencies are within the range heard by human ears.
When scientists extrapolated this line even further back in time (not shown), they deduced that Voyager 1 first encountered interstellar plasma in August 2012.
Plasma Sounds at Jupiter
Ominous sounds of plasma! Our Juno spacecraft has observed plasma wave signals from Jupiter’s ionosphere. The results in this video show an increasing plasma density as Juno descended into Jupiter’s ionosphere during its close pass by Jupiter on February 2, 2017.
Roar of Jupiter
Juno's Waves instrument recorded this supernatural sounding encounter with the bow shock over the course of about two hours on June 24, 2016. "Bow shock" is where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by Jupiter's magnetosphere. It is analogous to a sonic boom on Earth. The next day, June 25, 2016, the Waves instrument witnessed the crossing of the magnetopause. "Trapped continuum radiation" refers to waves trapped in a low-density cavity in Jupiter's magnetosphere.
Visit the NASA Soundcloud for more spooky space sounds: https://soundcloud.com/nasa/sets/spookyspacesounds
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 kuevo7 reblogged this · 3 years ago
kuevo7 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nordgrenexperience liked this · 4 years ago
nordgrenexperience liked this · 4 years ago -
 ikonospacewebgalleries liked this · 4 years ago
ikonospacewebgalleries liked this · 4 years ago -
 uncanny-art liked this · 5 years ago
uncanny-art liked this · 5 years ago -
 supermassivespacebabe reblogged this · 5 years ago
supermassivespacebabe reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago
cherryobvious liked this · 5 years ago -
 xploseof reblogged this · 5 years ago
xploseof reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 valiantranchcreatorsuitcase liked this · 5 years ago
valiantranchcreatorsuitcase liked this · 5 years ago -
 nyctolemon liked this · 5 years ago
nyctolemon liked this · 5 years ago -
 crazykk777 reblogged this · 5 years ago
crazykk777 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 themostpowerfulmutant liked this · 5 years ago
themostpowerfulmutant liked this · 5 years ago -
 evolved-feral reblogged this · 5 years ago
evolved-feral reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mileysyrups liked this · 5 years ago
mileysyrups liked this · 5 years ago -
 theknightsystem liked this · 5 years ago
theknightsystem liked this · 5 years ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 mahadiahmed liked this · 5 years ago
mahadiahmed liked this · 5 years ago -
 neocortexsupernova reblogged this · 5 years ago
neocortexsupernova reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 neocortexsupernova liked this · 5 years ago
neocortexsupernova liked this · 5 years ago -
 kimbermcleod reblogged this · 5 years ago
kimbermcleod reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nervouspaintereggbailiff liked this · 5 years ago
nervouspaintereggbailiff liked this · 5 years ago -
 buz5 reblogged this · 5 years ago
buz5 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 buz5 liked this · 5 years ago
buz5 liked this · 5 years ago -
 luciferspoison liked this · 5 years ago
luciferspoison liked this · 5 years ago -
 alexanderreaderp liked this · 5 years ago
alexanderreaderp liked this · 5 years ago -
 ferociousqueak liked this · 5 years ago
ferociousqueak liked this · 5 years ago -
 shadesyste liked this · 5 years ago
shadesyste liked this · 5 years ago -
 iratelemming reblogged this · 5 years ago
iratelemming reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fourthage reblogged this · 5 years ago
fourthage reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 steadyfisheclipsepaper liked this · 5 years ago
steadyfisheclipsepaper liked this · 5 years ago -
 united-twosday reblogged this · 5 years ago
united-twosday reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 forevertheengineer reblogged this · 5 years ago
forevertheengineer reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 chickenscratch42 liked this · 5 years ago
chickenscratch42 liked this · 5 years ago -
 201006 liked this · 5 years ago
201006 liked this · 5 years ago -
 skcirthinq reblogged this · 5 years ago
skcirthinq reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 abbyyy264 liked this · 5 years ago
abbyyy264 liked this · 5 years ago -
 delightfulpaperpost liked this · 5 years ago
delightfulpaperpost liked this · 5 years ago -
 kneipho liked this · 5 years ago
kneipho liked this · 5 years ago -
 jolieward reblogged this · 5 years ago
jolieward reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 jolieward liked this · 5 years ago
jolieward liked this · 5 years ago -
 kimbermcleod liked this · 5 years ago
kimbermcleod liked this · 5 years ago -
 theulumuri liked this · 5 years ago
theulumuri liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts