What’s The Best Piece Of Advice You Have Ever Received?
What’s the best piece of advice you have ever received?
More Posts from Nasa and Others
2017 Was One of Our Planet’s Hottest Years on Record

We just finished the second hottest year on Earth since global temperature estimates first became feasible in 1880. Although 2016 still holds the record for the warmest year, 2017 came in a close second, with average temperatures 1.6 degrees Fahrenheit higher than the mean.

2017’s temperature record is especially noteworthy, because we didn’t have an El Niño this year. Often, the two go hand-in-hand.
El Niño is a climate phenomenon that causes warming of the tropical Pacific Ocean waters, which affect wind and weather patterns around the world, usually resulting in warmer temperatures globally. 2017 was the warmest year on record without an El Niño.

We collect the temperature data from 6,300 weather stations and ship- and buoy-based observations around the world, and then analyze it on a monthly and yearly basis. Researchers at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) do a similar analysis; we’ve been working together on temperature analyses for more than 30 years. Their analysis of this year’s temperature data tracks closely with ours.

The 2017 temperature record is an average from around the globe, so different places on Earth experienced different amounts of warming. NOAA found that the United States, for instance, had its third hottest year on record, and many places still experienced cold winter weather.

Other parts of the world experienced abnormally high temperatures throughout the year. Earth’s Arctic regions are warming at roughly twice the rate of the rest of the planet, which brings consequences like melting polar ice and rising sea levels.

Increasing global temperatures are the result of human activity, specifically the release of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. The gases trap heat inside the atmosphere, raising temperatures around the globe.

We combine data from our fleet of spacecraft with measurements taken on the ground and in the air to continue to understand how our climate is changing. We share this important data with partners and institutions across the U.S. and around the world to prepare and protect our home planet.
Earth’s long-term warming trend can be seen in this visualization of NASA’s global temperature record, which shows how the planet’s temperatures are changing over time, compared to a baseline average from 1951 to 1980.
Learn more about the 2017 Global Temperature Report HERE.
Discover the ways that we are constantly monitoring our home planet HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn more about our Deep Space Network, where to watch the Ursid meteor shower, Cassini’s ring-grazing at Saturn and more.

1. A Deep Space Anniversary
On Dec. 24, 1963, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Deep Space Information Facility was renamed the Deep Space Network. And, it’s been humanity's ear to the skies ever since.
+ History of the Deep Space Network
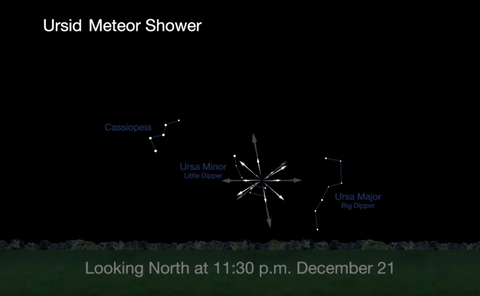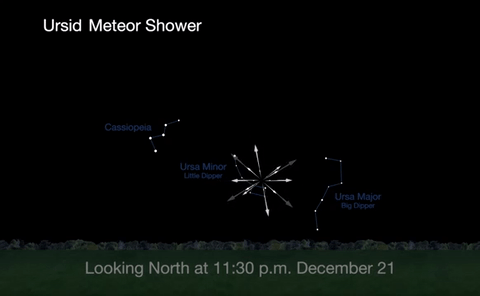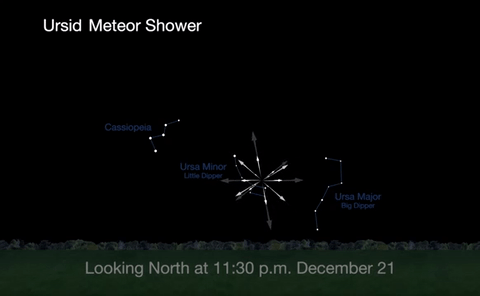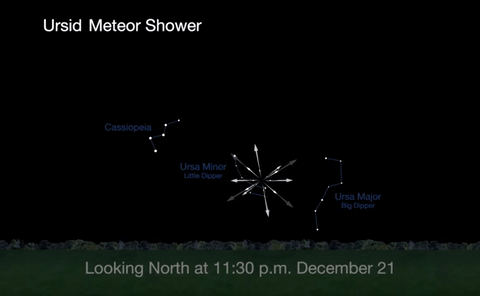
2. Ursid Meteor Shower
The best time to view the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, or the little Dipper, will be from midnight on December 21 until about 1a.m. on December 22, before the moon rises.

3. At Saturn, the Ring-Grazing Continues
Our Cassini spacecraft has completed several orbits that take it just outside Saturn’s famous rings. The first ring-grazing orbit began on November 30. The spacecraft will repeat this feat 20 times, with only about a week between each ring-plane crossing.
+ Learn more

4. Preparing for the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse
Next year North America will see one of the most rare and spectacular of all sky events. Learn how to prepare.
+ 2017 Solar Eclipse Toolkit

5. Searching for Rare Asteroids
Our first mission to return an asteroid sample to Earth will be multitasking during its two-year outbound cruise to the asteroid Bennu. On February 9-20, OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer) will activate its onboard camera suite and begin its search for elusive “Trojan,” asteroids, constant companions to planets in our solar system as they orbit the sun, remaining near a stable point 60 degrees in front of or behind the planet. Because they constantly lead or follow in the same orbit, they will never collide with their companion planet.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Will it take pictures of Pluto?
What did you major in? What was your college experience?
Everyone (Even You!) Can Use Satellite Data
At NASA we’re pretty great at putting satellites and science instruments into orbit around Earth. But it turns out we’re also pretty great at showing people how to get and use all that data.
One of the top ways you can learn how to use NASA data is our ARSET program. ARSET is our Applied Remote Sensing Training program and it helps people build skills that integrate all these Earth science data into their decision making.

ARSET will train you on how to use data from a variety of Earth-observing satellites and instruments aboard the International Space Station.
Once you take a training, you’ll be in GREAT company because thousands of people have taken an ARSET training.

We hold in person and online trainings to people around the world, showing them how to use NASA Earth science data. Trainings are offered in air quality, climate, disaster, health, land, water resources and wildfire management.
For example, if you’re trying to track how much fresh drinking water there is in your watershed, you can take an ARSET training and learn how to find satellite data on how much precipitation has fallen over a certain time period or even things like the ‘moistness’ of soil and the quality of the water.

Best yet, all NASA Earth observing data is open and freely available to the whole world! That’s likely one of the reasons we’ve had participants from 172 of the approximately 190 countries on Earth.

Since its beginning 10 years ago, ARSET has trained more than 30 thousand people all over the world. They’ve also worked with people from more than 7,500 different organizations and that includes government agencies, non-profit groups, advocacy organizations, private industry.
And even though 2019 is ARSET’s 10th birthday – we’ve only just begun. Every year about 60% of the organizations and agencies we train are new to the program. We’re training just about anyone who is anyone doing Earth science on Earth!
Join us, learn more about how we train people to use Earth observing data here, and heck, you can even take a training yourself: https://arset.gsfc.nasa.gov/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Hurricanes Have No Place to Hide, Thanks to Better Satellite Forecasts

If you’ve ever looked at a hurricane forecast, you’re probably familiar with “cones of uncertainty,” the funnel-shaped maps showing a hurricane’s predicted path. Thirty years ago, a hurricane forecast five days before it made landfall might have a cone of uncertainty covering most of the East Coast. The result? A great deal of uncertainty about who should evacuate, where it was safe to go, and where to station emergency responders and their equipment.

Over the years, hurricane forecasters have succeeded in shrinking the cone of uncertainty for hurricane tracks, with the help of data from satellites. Polar-orbiting satellites, which fly nearly directly above the North and South Poles, are especially important in helping cut down on forecast error.

The orbiting electronic eyeballs key to these improvements: the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) fleet. A collaborative effort between NOAA and NASA, the satellites circle Earth, taking crucial measurements that inform the global, regional and specialized forecast models that have been so critical to hurricane track forecasts.

The forecast successes keep rolling in. From Hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria in 2017 through Hurricanes Florence and Michael in 2018, improved forecasts helped manage coastlines, which translated into countless lives and property saved. In September 2018, with the help of this data, forecasters knew a week ahead of time where and when Hurricane Florence would hit. Early warnings were precise enough that emergency planners could order evacuations in time — with minimal road clogging. The evacuations that did not have to take place, where residents remained safe from the hurricane’s fury, were equally valuable.

The satellite benefits come even after the storms make landfall. Using satellite data, scientists and forecasters monitor flooding and even power outages. Satellite imagery helped track power outages in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria and in the Key West area after Hurricane Irma, which gave relief workers information about where the power grid was restored – and which regions still lacked electricity.

Flood maps showed the huge extent of flooding from Hurricane Harvey and were used for weeks after the storm to monitor changes and speed up recovery decisions and the deployment of aid and relief teams.

As the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season kicks off, the JPSS satellites, NOAA-20 and Suomi-NPP, are ready to track hurricanes and tropical cyclones as they form, intensify and travel across the ocean – our eyes in the sky for severe storms.
For more about JPSS, follow @JPSSProgram on Twitter and facebook.com/JPSS.Program, or @NOAASatellites on Twitter and facebook.com/NOAASatellites.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Happy International Women’s Day!

Today we celebrate International Women’s Day, a day in which we honor and recognize the contributions of women…both on Earth and in space.

Since the beginning, women have been essential to the progression and success of America’s space program.

Throughout history, women have had to overcome struggles in the workplace. The victories for gender rights were not achieved easily or quickly, and our work is not done.

Today, we strive to make sure that our legacy of inclusion and excellence lives on.

We have a long-standing cultural commitment to excellence that is largely driven by data, including data about our people. And our data shows progress is driven by questioning our assumptions and cultural prejudices – by embracing and nurturing all talent we have available, regardless of gender, race or other protected status, to build a workforce as diverse as our mission. This is how we, as a nation, will take the next giant leap in exploration.

As a world leader in science, aeronautics, space exploration and technology, we have a diverse mission that demands talent from every corner of America, and every walk of life.

So, join us today, and every day, as we continue our legacy of inclusion and excellence.

Happy International Women’s Day!
Learn more about the inspiring woman at NASA here: https://women.nasa.gov/
Hi, I'm a curious Malaysian 😁 can you explain to us about your career and how do one get to the point where you are now? Thanks! Oh, and could you comment on the recent climate crises like the Australian fires and Indonesia flooding? Thank you!
How to Do Business with NASA
It’s Small Business Week! To celebrate, we’re breaking down the process and explaining how YOUR small business can work with us. Here are 10 steps:

Prior to working with us, identify which of your products or services best fit within our industry. It’s also important to know the Federal Supply Class or Service Codes (FSC/SVC) for your products or services. Prepare a capability brief in both printed and electronic versions with an emphasis on Government work.

In order to register your business with us, there are three systems you’ll need to use. The Data Universal Numbering System (DUNS), the System for Award Management (SAM) and the NASA Vendor Data Base (NVDB). After you’ve survived all those acronyms, your business is registered!

Here at NASA we have centers around the country that each procure different types of business. Where does your product or service fit in? The best thing to do is visit THIS site and find out more about each center. You can also take a look at our Acquisition Forecast to find out about expected contract opportunities.

You can find current procurement opportunities in your product or service area by checking the Federal Business Opportunities website. This site also helps you identify our requirements and even send you e-mail notifications of released requirements.

Contracting procedures can be tedious, it’s always a good idea to familiarize yourself with the Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR), as well as our supplement to those regulations. Which can be found HERE.

Did you know that many of our purchases are orders on the Federal Supply Schedule contracts? They are, which means you can contact the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) for information on how to obtain a contract.

There are some very beneficial resources available to you throughout this process. You can request training and counseling on marketing, financial and contracting issues at minimal or no cost from Procurement Technical Assistance Centers (PTACs).
You also have the option to consult with the SBA’s Procurement Center Representatives (PCRs) and the SBA Business Development Centers. The SBA provides each of our centers with a liaison.
There is also an option to get free and confidential mentoring by former CEOs through SCORE.

Direct contracting is not the only route for small businesses. Consider subcontracting opportunities, and get information through the SBA’s SUB-Net or Subcontracting Opportunities Directory. Solicitations or notices are posted by prime contractors. Our list of prime vendors is located on our Marshall Space Flight Center’s website.

Explore other small business programs, such as our Mentor-Protégé Program, the Small Business Innovation Research Program and the Historically Black Colleges and Universities and Minority-Serving Institutions Program. Information on these and other programs is available on our Office of Small Business Programs website.

After you have identified your customers, researched their requirements and familiarized yourself with our procurement regulations and strategies, it’s time to market your product or service. Present your capabilities directly to the NASA Centers that buy your products or services. Realize that, as with yours, their time is valuable. If the match is a good one, you can provide them with a cost-effective, quality solution to their requirements. Good luck!
Here are a Few Small Businesses We’re Already Working With…

Dynetics Technical Services, Inc., of Huntsville, AL works with us on enterprise information technology services so that we have the right tools to reach for new heights. This company was also named Agency Small Business Prime Contractor of the Year.

Arcata Associates, Inc., of Las Vegas, NV manages operations and maintenance for our Dryden Aeronautical Test Range in Edwards, CA. Their work ensures that we can continue our critical work in aviation research and development. This company was even named Agency Small Business Subcontractor of the Year.
Want to learn more about our Office of Small Business Programs? Visit their site HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 queer-omens-in-the-archives liked this · 5 years ago
queer-omens-in-the-archives liked this · 5 years ago -
 jr-doctor liked this · 5 years ago
jr-doctor liked this · 5 years ago -
 cbacl liked this · 5 years ago
cbacl liked this · 5 years ago -
 shes-beauty-shes-ace reblogged this · 5 years ago
shes-beauty-shes-ace reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mttbellamy liked this · 5 years ago
mttbellamy liked this · 5 years ago -
 letswishuponastar liked this · 5 years ago
letswishuponastar liked this · 5 years ago -
 bellegerant reblogged this · 5 years ago
bellegerant reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 piinek liked this · 5 years ago
piinek liked this · 5 years ago -
 1989nihil reblogged this · 5 years ago
1989nihil reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 insertanonymousname liked this · 5 years ago
insertanonymousname liked this · 5 years ago -
 nasatranscription reblogged this · 5 years ago
nasatranscription reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 qweenofghosts liked this · 5 years ago
qweenofghosts liked this · 5 years ago -
 lennoxs liked this · 5 years ago
lennoxs liked this · 5 years ago -
 nicoleiswayhaught liked this · 5 years ago
nicoleiswayhaught liked this · 5 years ago -
 lucmarcou liked this · 5 years ago
lucmarcou liked this · 5 years ago -
 windyleaf reblogged this · 5 years ago
windyleaf reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 barcerona liked this · 5 years ago
barcerona liked this · 5 years ago -
 gnotee liked this · 5 years ago
gnotee liked this · 5 years ago -
 bi-streetcat reblogged this · 5 years ago
bi-streetcat reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 bi-streetcat liked this · 5 years ago
bi-streetcat liked this · 5 years ago -
 passionatedisdain liked this · 5 years ago
passionatedisdain liked this · 5 years ago -
 fellowitch liked this · 5 years ago
fellowitch liked this · 5 years ago -
 fuzzy-socks-in-winter liked this · 5 years ago
fuzzy-socks-in-winter liked this · 5 years ago -
 delicatemusictale liked this · 5 years ago
delicatemusictale liked this · 5 years ago -
 malecus liked this · 5 years ago
malecus liked this · 5 years ago -
 ritzbot liked this · 5 years ago
ritzbot liked this · 5 years ago -
 gautrau liked this · 5 years ago
gautrau liked this · 5 years ago -
 finniccc liked this · 5 years ago
finniccc liked this · 5 years ago -
 chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 5 years ago
chocolateismynemesis reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 rosaliachristian liked this · 5 years ago
rosaliachristian liked this · 5 years ago -
 roadtripjb406 liked this · 5 years ago
roadtripjb406 liked this · 5 years ago -
 marsbartobobbity liked this · 5 years ago
marsbartobobbity liked this · 5 years ago -
 moonyshiro liked this · 5 years ago
moonyshiro liked this · 5 years ago -
 itarilde-elentari reblogged this · 5 years ago
itarilde-elentari reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 itarilde-elentari liked this · 5 years ago
itarilde-elentari liked this · 5 years ago -
 awkwardranga liked this · 5 years ago
awkwardranga liked this · 5 years ago -
 bruinhilda liked this · 5 years ago
bruinhilda liked this · 5 years ago -
 lesbiangummybearmafia liked this · 5 years ago
lesbiangummybearmafia liked this · 5 years ago -
 realspaceships liked this · 5 years ago
realspaceships liked this · 5 years ago -
 moonr1ce liked this · 5 years ago
moonr1ce liked this · 5 years ago -
 madokaoyabin reblogged this · 5 years ago
madokaoyabin reblogged this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts