@ladyknighttime: What's Your Favorite Activity To Do In Space That You Might Not Have Expected?
@ladyknighttime: What's your favorite activity to do in space that you might not have expected?
More Posts from Nasa and Others

The James Webb Space Telescope has just completed a successful first year of science. Let’s celebrate by seeing the birth of Sun-like stars in this brand-new image from the Webb telescope!
This is a small star-forming region in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. At 390 light-years away, it's the closest star-forming region to Earth. There are around 50 young stars here, all of them similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The darkest areas are the densest, where thick dust cocoons still-forming protostars. Huge red bipolar jets of molecular hydrogen dominate the image, appearing horizontally across the upper third and vertically on the right. These occur when a star first bursts through its natal envelope of cosmic dust, shooting out a pair of opposing jets into space like a newborn first stretching her arms out into the world. In contrast, the star S1 has carved out a glowing cave of dust in the lower half of the image. It is the only star in the image that is significantly more massive than the Sun.
Thanks to Webb’s sensitive instruments, we get to witness moments like this at the beginning of a star’s life. One year in, Webb’s science mission is only just getting started. The second year of observations has already been selected, with plans to build on an exciting first year that exceeded expectations. Here’s to many more years of scientific discovery with Webb.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI)

Marcos Berrios
Marcos Berrios is from Guaynabo, Puerto Rico, and received his Ph.D. in aeronautics and astronautics from Stanford. Berríos has logged over 1,400 hours of flight time in over 20 different aircraft. https://go.nasa.gov/49DEAAt
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
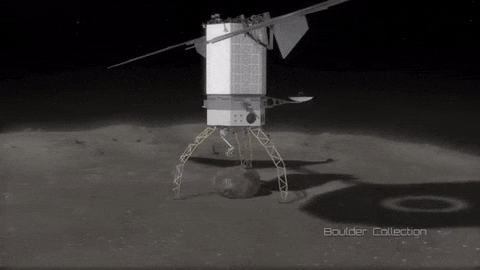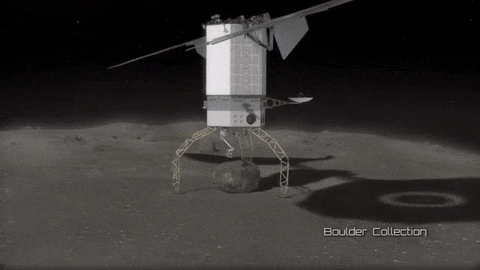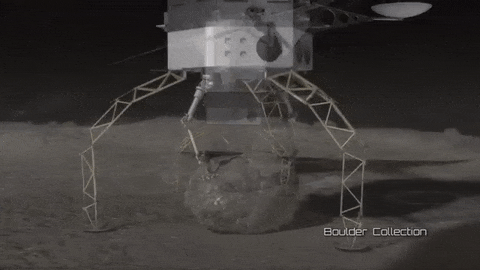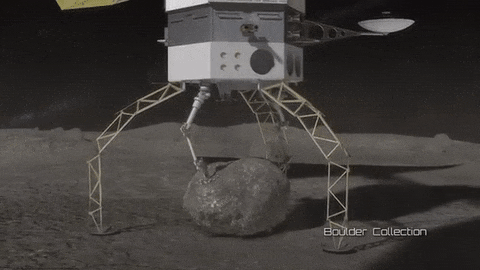
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
#YearInSpace Reddit AMA
NASA astronaut Scott Kelly and Russian cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko will return from a year-long mission to the International Space Station on Tuesday, March 1. Research conducted during this mission will help prepare us for future voyages beyond low-Earth orbit.

On Friday, March 4 at 11 a.m. EST, we will host a Reddit AMA with scientists and medical doctors from our Johnson Space Center. During the AMA, they will answer your questions about everything from how microgravity affects the human body to how astronauts’ food intake is closely monitored while on-orbit. Ask us anything about the science behind the One Year Mission!
Participants include:
Julie Robinson, Ph.D., NASA’s Chief Scientist for the International Space Station
John Charles, Ph.D., Associate Manager for International Science for NASA’s Human Research Program
Scott M. Smith, Ph.D., Nutritional Biochemistry Laboratory Manager for NASA’s Human Research Program
Dr. Shannan Moynihan, NASA Flight Surgeon
Bruce Nieschwitz, Strength and Conditioning Coach
Join us on Reddit here
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up For August 2018?
The summer Perseids are here!

The Perseid meteor shower is the best of the year! It peaks on a Moonless summer night from 4 p.m. EST on August 12 until 4 a.m. EST on August 13.

Because the new Moon falls near the peak night, the days before and after the peak will also provide nice, dark skies. Your best window of observation is from a few hours after twilight until dawn, on the days surrounding the peak.

Unlike most meteor showers, which have a short peak of high meteor rates, the Perseids have a very broad peak, as Earth takes more than three weeks to plow through the wide trail of cometary dust from comet Swift-Tuttle.

The Perseids appear to radiate from the constellation Perseus, visible in the northern sky soon after sunset this time of year. Observers in mid-northern latitudes will have the best views.

You should be able to see some meteors from July 17 to August 24, with the rates increasing during the weeks before August 12 and decreasing after August 13.

Observers should be able to see between 60 and 70 per hour at the peak. Remember, you don't have to look directly at the constellation to see them. You can look anywhere you want to-even directly overhead.

Meteor showers like the Perseids are caused by streams of meteoroids hitting Earth's atmosphere. The particles were once part of their parent comet-or, in some cases, from an asteroid.

The parade of planets Venus, Jupiter, Saturn and Mars--and the Milky Way continue to grace the evening sky, keeping you and the mosquitoes company while you hunt for meteors.

Watch the full What’s Up for August Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
It’s a Bird! It’s a Plane! It’s NASA’s Five Newest Airborne Campaigns!
We’re not just doing research in space! From the land, the sea and the sky, we study our planet up close. Right now, we’re gearing up for our newest round of Earth Expeditions, using planes, boats and instruments on the ground to study Earth and how it’s changing.

The newest round of campaigns takes place all across the United States – from Virginia to Louisiana to Kansas to California.

The five newest missions will combine measurements from the ground, the sea, air and space to investigate storms, sea level rise and processes in the atmosphere and ocean.
Let’s meet the newest Earth science missions:
1. IMPACTS
The Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Snowstorms will start from Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia to understand how bands of snow form during winter storms in the East Coast. This research will help us better forecast intense snowfall during extreme winter weather.

2. ACTIVATE
Flying out of Langley Research Center, the Aerosol Cloud Meteorology Interactions over the Western Atlantic Experiment is studying how specific types of clouds over oceans affect Earth’s energy balance and water cycle. The energy balance is the exchange of heat and light from the Sun entering Earth’s atmosphere vs. what escapes back into space.

3. Delta-X
Farther south, Delta-X is flying three planes around the Mississippi River Delta to study how land is deposited and maintained by natural processes. Studying these processes can help us understand what will happen as sea levels continue to rise.

4. DCOTSS
Heading out to the Midwest this summer, the Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere mission will study how thunderstorms can carry pollutants from high in the atmosphere deep into the lower stratosphere, where they can affect ozone levels.

5. S-MODE
About 200 miles off the coast of San Francisco, the Sub-Mesoscale Ocean Dynamics Experiment is using ships, planes and gliders to study the impact that ocean eddies have on how heat moves between the ocean and the atmosphere.

These missions are kicking off in January, so stay tuned for our updates from the field! You can follow along with NASA Expeditions on Twitter and Facebook.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Navigating Space by the Stars





A sextant is a tool for measuring the angular altitude of a star above the horizon and has helped guide sailors across oceans for centuries. It is now being tested aboard the International Space Station as a potential emergency navigation tool for guiding future spacecraft across the cosmos. The Sextant Navigation investigation will test the use of a hand-held sextant that utilizes star sighting in microgravity.
Read more about how we’re testing this tool in space!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What is Artemis I?

On November 14, NASA is set to launch the uncrewed Artemis I flight test to the Moon and back. Artemis I is the first integrated flight test of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the Orion spacecraft, and Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. These are the same systems that will bring future Artemis astronauts to the Moon.

Standing 322 feet (98 meters) tall, the SLS rocket comprises of a core stage, an upper stage, two solid boosters, and four RS-25 engines. The SLS rocket is the most powerful rocket in the world, able to carry 59,500 pounds (27 metric tons) of payloads to deep space — more than any other vehicle. With its unprecedented power, SLS is the only rocket that can send the Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and cargo directly to the Moon on a single mission.

Before launch, Artemis I has some big help: the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at KSC is the largest single-story building in the world. The VAB was constructed for the assembly of the Apollo/Saturn V Moon rocket, and this is where the SLS rocket is assembled, maintained, and integrated with the Orion spacecraft.

The mobile launcher is used to assemble, process, and launch the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft. The massive structure consists of a two-story base and a tower equipped with a number of connection lines to provide the rocket and spacecraft with power, communications, coolant, and fuel prior to launch.

Capable of carrying 18 million pounds (8.2 million kg) and the size of a baseball infield, crawler-transporter 2 will transport SLS and Orion the 4.2 miles (6.8 km) to Launch Pad 39B. This historic launch pad was where the Apollo 10 mission lifted off from on May 18, 1969, to rehearse the first Moon landing.

During the launch, SLS will generate around 8.8 million pounds (~4.0 million kg) of thrust, propelling the Orion spacecraft into Earth’s orbit. Then, Orion will perform a Trans Lunar Injection to begin the path to the Moon. The spacecraft will orbit the Moon, traveling 40,000 miles beyond the far side of the Moon — farther than any human-rated spacecraft has ever flown.

The Orion spacecraft is designed to carry astronauts on deep space missions farther than ever before. Orion contains the habitable volume of about two minivans, enough living space for four people for up to 21 days. Future astronauts will be able to prepare food, exercise, and yes, have a bathroom. Orion also has a launch abort system to keep astronauts safe if an emergency happens during launch, and a European-built service module that fuels and propels the spacecraft.

While the Artemis I flight test is uncrewed, the Orion spacecraft will not be empty: there will be three manikins aboard the vehicle. Commander Moonikin Campos will be sitting in the commander’s seat, collecting data on the vibrations and accelerations future astronauts will experience on the journey to the Moon. He is joined with two phantom torsos, Helga and Zohar, in a partnership with the German Aerospace Center and Israeli Space Agency to test a radiation protection vest.

A host of shoebox-sized satellites called CubeSats help enable science and technology experiments that could enhance our understanding of deep space travel and the Moon while providing critical information for future Artemis missions.

At the end of the four-week mission, the Orion spacecraft will return to Earth. Orion will travel at 25,000 mph (40,000 km per hour) before slowing down to 300 mph (480 km per hour) once it enters the Earth’s atmosphere. After the parachutes deploy, the spacecraft will glide in at approximately 20 mph (32 km per hour) before splashdown about 60 miles (100 km) off the coast of California. NASA’s recovery team and the U.S. Navy will retrieve the Orion spacecraft from the Pacific Ocean.

With the ultimate goal of establishing a long-term presence on the Moon, Artemis I is a critical step as NASA prepares to send humans to Mars and beyond.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Happy International Women’s Day!

Today we celebrate International Women’s Day, a day in which we honor and recognize the contributions of women…both on Earth and in space.

Since the beginning, women have been essential to the progression and success of America’s space program.

Throughout history, women have had to overcome struggles in the workplace. The victories for gender rights were not achieved easily or quickly, and our work is not done.

Today, we strive to make sure that our legacy of inclusion and excellence lives on.

We have a long-standing cultural commitment to excellence that is largely driven by data, including data about our people. And our data shows progress is driven by questioning our assumptions and cultural prejudices – by embracing and nurturing all talent we have available, regardless of gender, race or other protected status, to build a workforce as diverse as our mission. This is how we, as a nation, will take the next giant leap in exploration.

As a world leader in science, aeronautics, space exploration and technology, we have a diverse mission that demands talent from every corner of America, and every walk of life.

So, join us today, and every day, as we continue our legacy of inclusion and excellence.

Happy International Women’s Day!
Learn more about the inspiring woman at NASA here: https://women.nasa.gov/
How does the whole sleeping situation work with 0 gravity, or do sleep mid air?
-
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 3 years ago -
 bethelnie-blog liked this · 5 years ago
bethelnie-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 sahilshareef-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago
sahilshareef-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lucmarcou liked this · 5 years ago
lucmarcou liked this · 5 years ago -
 insertanonymousname liked this · 5 years ago
insertanonymousname liked this · 5 years ago -
 letsboldlygomotherfuckers liked this · 5 years ago
letsboldlygomotherfuckers liked this · 5 years ago -
 mandylee70 liked this · 5 years ago
mandylee70 liked this · 5 years ago -
 todisfake liked this · 5 years ago
todisfake liked this · 5 years ago -
 ashhcaughtem liked this · 5 years ago
ashhcaughtem liked this · 5 years ago -
 uss-protostar liked this · 5 years ago
uss-protostar liked this · 5 years ago -
 justarandombnhafan liked this · 5 years ago
justarandombnhafan liked this · 5 years ago -
 theyeetedsoul liked this · 5 years ago
theyeetedsoul liked this · 5 years ago -
 niceteethv liked this · 5 years ago
niceteethv liked this · 5 years ago -
 detective-kat liked this · 5 years ago
detective-kat liked this · 5 years ago -
 vivianit4 reblogged this · 6 years ago
vivianit4 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 lillianfrye liked this · 6 years ago
lillianfrye liked this · 6 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 09905785595 liked this · 6 years ago
09905785595 liked this · 6 years ago -
 soap-with-bite-marks liked this · 6 years ago
soap-with-bite-marks liked this · 6 years ago -
 goldenstripes001 liked this · 6 years ago
goldenstripes001 liked this · 6 years ago -
 jeanclaudevandammes liked this · 6 years ago
jeanclaudevandammes liked this · 6 years ago -
 fallen-angel-it-hurt reblogged this · 6 years ago
fallen-angel-it-hurt reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 joviere liked this · 6 years ago
joviere liked this · 6 years ago -
 elkvenison liked this · 6 years ago
elkvenison liked this · 6 years ago -
 eergene59 liked this · 6 years ago
eergene59 liked this · 6 years ago -
 acai-studies liked this · 6 years ago
acai-studies liked this · 6 years ago -
 stupendouspeanutpalacedrago-blog liked this · 6 years ago
stupendouspeanutpalacedrago-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 dontsmileattyler-blog liked this · 6 years ago
dontsmileattyler-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 whocareswhoami liked this · 6 years ago
whocareswhoami liked this · 6 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts