Coffee In Space: Keeping Crew Members Grounded In Flight
Coffee in Space: Keeping Crew Members Grounded in Flight
Happy National Coffee Day, coffee lovers!
On Earth, a double shot mocha latte with soymilk, low-fat whip and a caramel drizzle is just about as complicated as a cup of coffee gets. Aboard the International Space Station, however, even just a simple cup of black coffee presents obstacles for crew members.

Understanding how fluids behave in microgravity is crucial to bringing the joys of the coffee bean to the orbiting laboratory. Astronaut Don Pettit crafted a DIY space cup using a folded piece of overhead transparency film. Surface tension keeps the scalding liquid inside the cup, and the shape wicks the liquid up the sides of the device into the drinker’s mouth.

The Capillary Beverage investigation explored the process of drinking from specially designed containers that use fluid dynamics to mimic the effect of gravity. While fun, this study could provide information useful to engineers who design fuel tanks for commercial satellites!

The capillary beverage cup allows astronauts to drink much like they would on Earth. Rather than drinking from a shiny bag and straw, the cup allows the crew member to enjoy the aroma of the beverage they’re consuming.

On Earth, liquid is held in the cup by gravity. In microgravity, surface tension keeps the liquid stable in the container.

The ISSpresso machine brought the comforts of freshly-brewed coffees and teas to the space station. European astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti enjoyed the first cup of espresso brewed using the ISSpresso machine during Expedition 43.


Now, during Expedition 53, European astronaut Paolo Nespoli enjoys the same comforts.

Astronaut Kjell Lindgren celebrated National Coffee Day during Expedition 45 by brewing the first cup of hand brewed coffee in space.

We have a latte going on over on our Snapchat account, so give us a follow to stay up to date! Also be sure to follow @ISS_Research on Twitter for your daily dose of space station science.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
NASA’s View of COVID-19
#COVID19 led to changes in human activities around the globe. We can see some of these changes from space. Some bodies of water have run clearer, emissions of pollutants have temporarily declined, and transportation and shipment of goods have decreased.

Along with our partner agencies – ESA and JAXA – we’re making satellite data available on the COVID-19 Earth Observation Dashboard, where you can explore some of the changes we can see from space.

But it’s not just what we can see. When the pandemic began, NASA engineers sprang into action to build ventilators, oxygen hoods and more to help save lives.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are five things you need to know this week:
1. The Lure of the Rings

Scientists and stargazers alike can’t resist the call of Saturn’s rings, or of its moon Titan. Both have been under close scrutiny by the Cassini spacecraft lately, and there are striking new pictures to prove it. Check out the latest images HERE.
2. A New Moon Rises

The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter has captured dramatic landscapes on the moon for more than six years. “A New Moon Rises,” now on display at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC, showcases those images ranging from Apollo landing sites to mountains that rise out of the darkness of the lunar poles. See an online version of the exhibit HERE.
3. Around the (Giant) World in (Just Under) 88 Days

The Juno mission is closing in on Jupiter. On July 4, the spacecraft enters orbit around the king of planets. Learn more about Juno HERE.
4. Spiders and Volcanoes and Glaciers, Oh My

The more data that New Horizons spacecraft sends down about Pluto and its moons, the more there is to fascinate explorers, from spider-shaped canyons to signs of glacial flow. Take a peek at the new finds on Pluto HERE.
5. World of Wonders

Hexagonal craters, mysterious mountains, eye-catching bright patches — the dwarf planet Ceres is proving to be an intriguing place. The Dawn mission is looking for clues to how it works. See the latest from Ceres HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Don’t Say “Bye, Bye, Bye” To Your Vision: Solar Eclipse Safety Tips
On Oct. 14, 2023, many people across North, Central, and South America will have an opportunity to view a “ring of fire” eclipse – an annular solar eclipse – when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun! During an annular eclipse, it is never safe to look directly at the Sun without specialized eye protection designed for solar viewing. To spread the word, *NSYNC's Lance Bass stopped by to share some tips on how to stay safe while viewing a solar eclipse.
Check out these detailed viewing maps to see if you will be able to see the entire or partial solar eclipse. If you are, make sure your solar viewing glasses have the ISO certification 12312-2. You can also check with local libraries or science museums to see if they have safe solar viewing glasses to hand out. You can also make a simple pinhole camera at home with some paper and aluminum foil: go.nasa.gov/pinholeprojector
Everyone online can watch the eclipse with NASA. Set a reminder to watch live: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LlY79zjud-Q
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Black Marble: NASA View Illuminates Earth at Night
When the sun goes down, the lights on Earth shine bright. A new look using our satellite data captures the lights coming from our neighborhoods, vehicles, buildings, factories, fishing vessels and other human activity brightening the night.

Our scientists have just released the first new global map of Earth at night since 2012. This nighttime view of our home planet, dubbed the Black Marble, provides researchers with a unique perspective of human activities around the globe.
By studying Earth at night, researchers can investigate how and why cities expand, monitor light intensity to estimate energy use and economic activity, and aid in disaster response in near-real time.

The data on Earth at night comes from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument on the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite, jointly managed by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
VIIRS captures visible and infrared light, allowing researchers to glimpse the Earth as it looks to astronauts peering out of the International Space Station. The new map is a composite of data collected in 2016, and it took several months of processing to filter out clouds, moonlight, airglow, and other interfering features to create the global image. In the coming months our scientists will release daily nighttime lights data at even finer resolutions for the first time.

The East Coast sparkles with population hubs, suburbs circling cities and major roadways. The I-95 corridor includes the most densely populated region of the United States – the stretch from Washington, DC to Boston.
To get images like these from the satellite data, our scientists had to filter out moonlight, aerosols and other sources of extraneous light – the goal is to eventually be able to detect the lights from a single building or fishing boat.

Daytime satellite images, like this one from Landsat 8, can show us the forests, deserts, mountains, waterways and built-up cities. Add a nighttime view, and scientists can study when and how people are using these limited resources – like the lights tracing the Nile River leading to the metropolis of Cairo, Egypt.

Lights aren’t confined to land. With the global nighttime view, the ocean is dotted with fishing fleets, including boats that try to attract their catch with bright lights.

What lights illuminate your neighborhood? Download a high-resolution version of the Black Marble HERE, and find out more about our new night lights data HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
15 Years of Station Told in 15 Gifs
1. International Space Station Assembly Animation

From 1998 to 2011, five different space agencies representing 15 countries assembled the International Space Station, the largest structure ever built in space. Today humans are still living and work in the orbital laboratory. November 2, 2015 marks the 15th anniversary of continuous human presence onboard.
2. Entry of Expedition 1

Expedition 1 crew members including, Commander William Shepherd and Cosmonauts Sergei Krikalev and Yuri Gidzenko arrive to the International Space Station for the first time on November 2, 2000.
3. September 11, 2001

Expedition 3 Commander Frank Culbertson was the only American living off the planet on September 11, 2001. He captured his view of the fateful day from the space station.
4. Kibo

The Japanese Experiment Module, or Kibo, is installed to the space station on June 3, 2008. Kibo means “hope” in Japanese, and it is the largest single space station module.
5. First 6-person Crew

The first 6 person crew on the space station gathers for a press conference in May 29, 2009. Because it was comprised of astronauts from NASA, CSA, ESA, JAXA, and Russia, this was the first and only time all international partners were represented on the space station at the same time.
6. SpaceX Dragon

The space station’s robotic arm captures the SpaceX Dragon during its demonstration flight on May 25, 2012, making it the first commercial vehicle ever to dock with the space station.
7. Olympic Torch

Russian Cosmonauts Sergey Ryanzanskiy and Oleg Kotov bring the Olympic torch outside the space station during a spacewalk on November 9, 2013. The torch traveled to the station as part of the Olympic torch relay ahead of the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia.
8. Testing Fire in Space

Astronaut Reid Weisman captured a floating sphere of fire observed during the Flex-2 experiment on space station on July 18, 2014. The findings may lead to better engines here on Earth.
9. Aurora

Astronaut Reid Weisman’s timelapse of a flickering aurora seen from space station on August 28, 2014.
10. Sunrise

Astronaut Reid Weisman’s timelapse of what a sunrise looks like from the space station on September 23, 2014.
11. Water Bubbles

Astronaut Reid Weisman experiments with water bubbles in space on November 8, 2014.
12. GoPro

Astronauts Terry Virts and Barry “Butch” Wilmore capture the first GoPro footage of a spacewalk on February 25, 2015.
13. Lightning

Astronaut Terry Virts filmed a massive lightning storm over India from the space station on May 9, 2015.
14. Milky Way

Astronaut Terry Virts captured a stunning view of the Milky Way from space station on May 15, 2015.
15. Veggie

Astronauts Scott Kelly, Kjell Lindgren, and Kimiya Yui taste lettuce that had been grown and harvested in space for the very first time on August 10, 2015.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com
If I am in the path of totality (Hopkinsville, KY) when can I take off my glasses to view the eclipse? Can I keep them off for the entire 2 minutes and 40 seconds?
If you are viewing the partial eclipse or lead up to totality, once you no longer can see any light through your eclipse glasses, then you can take them off. As long as the moon is fully covering the Sun you are safe. I would err on the side of caution and look away from the Sun a few moments before it’s over. This is also a great time to see what is happening around you! The animals should be responding differently than normal and this would be a great time to see that.
7 Things You Didn’t Know Came from NASA Technology
Every year, we publish a round-up of 50 or so NASA innovations that can also be found in our daily lives here on Earth.
We call them spinoffs — technologies spun off from America’s space program — and this week the 2017 edition was published. Here are some of our favorite things we bet you didn’t know use space technology.

1.Crash Test Cameras
Parachutes are a key part of the landing system for many of our spacecraft, but before we send them into orbit — or beyond — we have to make sure that they’re going to work as designed. One important component of testing is a video that captures every millisecond as the chute opens, to see if it’s working and if not, what went wrong.
Integrated Design Tools built a camera for us that could do just that: rugged and compact, it can film up to 1,000 frames per second and back up all that data almost as fast. Now that same technology is being used to record crash tests, helping ensure that we’re all safer on the roads.

2.Archaeology
We often use laser-imaging technology, or lidar, on missions in outer space. Thanks to lidar, snow was discovered on Mars, and the technology will soon help us collect a sample from an asteroid to bring home to Earth.
To do all that, we’ve helped make smaller, more rugged, and more powerful lidar devices, which have proven useful here on Earth in a lot of ways, including for archaeologists. Lidar scans can strip away the trees and bushes to show the bare earth—offering clues to help find bones, fossils, and human artifacts hidden beneath the surface.

3.Golf Clubs
A screw is a screw, right? Or is it?
When we were building the Space Shuttle, we needed a screw that wouldn’t loosen during the intense vibrations of launch. An advanced screw threading called Spiralock, invented by the Holmes Tool Company and extensively tested at Goddard Space Flight Center, was the answer.
Now it’s being used in golf clubs, too. Cobra Puma Golf built a new driver with a spaceport door (designed to model the International Space Station observatory) that allows the final weight to be precisely calibrated by inserting a tungsten weight before the door is screwed on.
And to ensure that spaceport door doesn’t pop off, Cobra Puma Golf turned to the high-tech threading that had served the Space Shuttle so well.

4.Brain Surgery
Neurosurgery tools need to be as precise as possible.
One important tool, bipolar forceps, uses electricity to cut and cauterize tissue. But electricity produces waste heat, and to avoid singeing healthy brain tissue, Thermacore Inc. used a technology we’ve been relying on since the early days of spaceflight: heat pipes. The company, which built its expertise in part through work it has done for us over more than 30 years, created a mini heat pipe for bipolar forceps.
The result means surgery is done more quickly, precisely — and most importantly, more safely.

5.Earthquake Protection
The Ares 1 rocket, originally designed to launch crewed missions to the moon and ultimately Mars, had a dangerous vibration problem, and the usual solutions were way too bulky to work on a launch vehicle.
Our engineers came up with a brand new technology that used the liquid fuel already in the rocket to get rid of the vibrations. And, it turns out, it works just as well with any liquid—and not just on rockets.
An adapted version is already installed on a building in Brooklyn and could soon be keeping skyscrapers and bridges from being destroyed during earthquakes.

6.Fertilizer
When excess fertilizer washes away into ground water it’s called nutrient runoff, and it’s a big problem for the environment. It’s also a problem for farmers, who are paying for fertilizer the plant never uses.
Ed Rosenthal, founder of a fertilizer company called Florikan, had an idea to fix both problems at once: coating the fertilizer in special polymers to control how quickly the nutrient dissolves in water, so the plant gets just the right amount at just the right time.
Our researchers helped him perfect the formula, and the award-winning fertilizer is now used around the world — and in space.

7. Cell Phone Cameras
The sensor that records your selfies was originally designed for something very different: space photography.
Eric Fossum, an engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, invented it in the 1990s, using technology called complementary metal-oxide semiconductors, or CMOS. The technology had been used for decades in computers, but Fossum was the first person to successfully adapt it for taking pictures.
As a bonus, he was able to integrate all the other electronics a camera needs onto the same computer chip, resulting in an ultra-compact, energy-efficient, and very reliable imager. Perfect for sending to Mars or, you know, snapping a pic of your meal.
To learn about NASA spinoffs, visit: https://spinoff.nasa.gov/index.html
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
The solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are the top 10 things you should know this week:
1. Big “Wows” from Small Worlds

Our robotic explorers continue to send truly spectacular pictures and data from deep space. Our New Horizons mission to Pluto and Dawn mission to dwarf planet Ceres are revealing never-before-seen landscapes on a regular basis. If you missed it, check out the most recent images from Pluto and Ceres.
2. Deep Waters

Saturn’s moon Enceladus has intrigued many with its geysers that erupt continuously in spectacular plumes. Our Cassini spacecraft has provided scientists with data that is allowing them to determine the source of those plumes. New evidence points to a global ocean of liquid water hidden beneath the moon’s icy shell!
3. A Super Eclipse

This weekend a “supermoon” lunar eclipse will be visible in the night sky. Supermoons occur when the moon is at its closest point to the Earth in its orbit, making it appear slightly larger. This one is extra special because it will also undergo a lunar eclipse! Beginning at 9:07 p.m. EDT on Sept. 27, make sure you get outside and look up! For more information visit: What’s Up for September.
4. All Things Equal

Sept. 23 marks the autumnal equinox, which is the official beginning of the Fall season in the northern hemisphere. The word “equinox” comes from the Latin for “equal night,” meaning day and night will be of equal length on that day.
5. Explore Goddard Space Flight Center

This weekend, Goddard Space Flight Center will be offering tours, presentations and other activities for children and adults. The theme this year is “Celebrating Hubble and the Spirit of Exploration”. This event is free and open to the public, and will be held on Saturday, Sept. 26 from 11 a.m. to 5 p.m. Join in HERE.
6. Titan’s Haze

This week, our Cassini spacecraft will observe Saturn’s hazy, planet-sized moon Titan. Scientists will use these images to look for clouds across Titan’s exotic regions. Explore HERE.
7. New Horizons Team on Pluto

Ever wondered what it was like to be part of the team that explored Pluto for the first time? If you’ll be near the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC on Sept. 22 you’re invited to a free lecture and Q&A to find out! Get the details HERE.
8. Martian Weather Report

Every day, our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter delivers a global view of the planet and its atmospheric activity. The most recent report included lots of water-ice clouds in the afternoon, with dust storms developing along the south polar region. Get the latest HERE.
9. Imagine: The View from Pluto

If you’ve ever wondered what it would look like to stand on the icy terrain of Pluto, you’re not alone. Artist Karl Kofoed created a series of digital paintings that render scenes from the dwarf planet based on data from the New Horizons July 14 Pluto flyby. View them HERE.
10. What’s the Big Idea?

We’re giving university students a chance to help us come up with solutions for our journey to Mars. This Breakthrough, Innovative, and Game-changing (BIG) Idea Challenge will look for creative solutions for generating lift using inflatable spacecraft heat shields on Mars. Enter your BIG Idea.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space:http://nasa.tumblr.com
Watch a Launch From Your Own Backyard
On Monday, Oct. 17, we’re launching cargo to the International Space Station, and if you live on the east coast, there’s a chance you can catch a glimpse!

The above map shows the areas on the east coast where launch may be visible, depending on cloud conditions.
Liftoff is currently scheduled for 7:40 p.m. EDT from our Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
The launch of Orbital ATK’s Cygnus spacecraft will carry around 5,100 pounds of supplies and research materials to the crew on the space station.
Not in the launch viewing area? No worries! Full launch coverage will be available starting at 6:45 p.m. EDT HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
You Are Made of Stardust
Though the billions of people on Earth may come from different areas, we share a common heritage: we are all made of stardust! From the carbon in our DNA to the calcium in our bones, nearly all of the elements in our bodies were forged in the fiery hearts and death throes of stars.

The building blocks for humans, and even our planet, wouldn’t exist if it weren’t for stars. If we could rewind the universe back almost to the very beginning, we would just see a sea of hydrogen, helium, and a tiny bit of lithium.
The first generation of stars formed from this material. There’s so much heat and pressure in a star’s core that they can fuse atoms together, forming new elements. Our DNA is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. All those elements (except hydrogen, which has existed since shortly after the big bang) are made by stars and released into the cosmos when the stars die.

Each star comes with a limited fuel supply. When a medium-mass star runs out of fuel, it will swell up and shrug off its outer layers. Only a small, hot core called a white dwarf is left behind. The star’s cast-off debris includes elements like carbon and nitrogen. It expands out into the cosmos, possibly destined to be recycled into later generations of stars and planets. New life may be born from the ashes of stars.

Massive stars are doomed to a more violent fate. For most of their lives, stars are balanced between the outward pressure created by nuclear fusion and the inward pull of gravity. When a massive star runs out of fuel and its nuclear processes die down, it completely throws the star out of balance. The result? An explosion!
Supernova explosions create such intense conditions that even more elements can form. The oxygen we breathe and essential minerals like magnesium and potassium are flung into space by these supernovas.
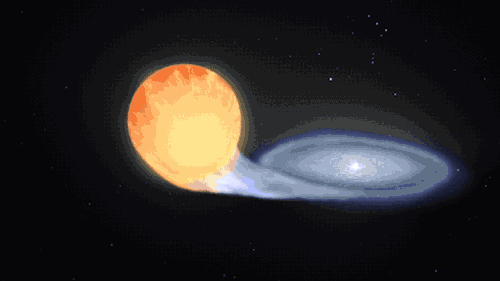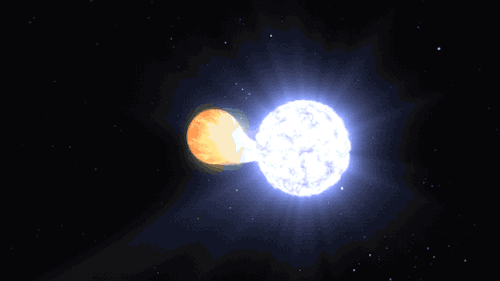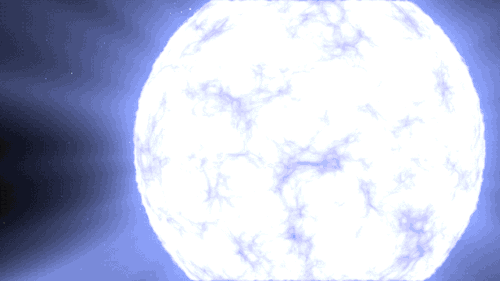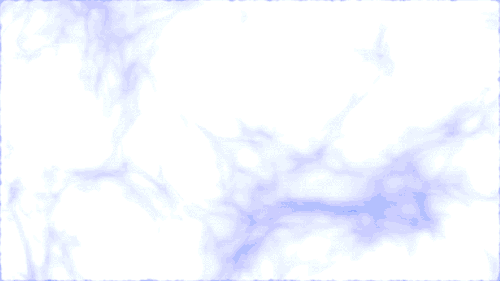
Supernovas can also occur another way in binary, or double-star, systems. When a white dwarf steals material from its companion, it can throw everything off balance too and lead to another kind of cataclysmic supernova. Our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will study these stellar explosions to figure out what’s speeding up the universe’s expansion.
This kind of explosion creates calcium – the mineral we need most in our bodies – and trace minerals that we only need a little of, like zinc and manganese. It also produces iron, which is found in our blood and also makes up the bulk of our planet’s mass!

A supernova will either leave behind a black hole or a neutron star – the superdense core of an exploded star. When two neutron stars collide, it showers the cosmos in elements like silver, gold, iodine, uranium, and plutonium.

Some elements only come from stars indirectly. Cosmic rays are nuclei (the central parts of atoms) that have been boosted to high speed by the most energetic events in the universe. When they collide with atoms, the impact can break them apart, forming simpler elements. That’s how we get boron and beryllium – from breaking star-made atoms into smaller ones.
Half a dozen other elements are created by radioactive decay. Some elements are radioactive, which means their nuclei are unstable. They naturally break down to form simpler elements by emitting radiation and particles. That’s how we get elements like radium. The rest are made by humans in labs by slamming atoms of lighter elements together at super high speeds to form heavier ones. We can fuse together elements made by stars to create exotic, short-lived elements like seaborgium and einsteinium.
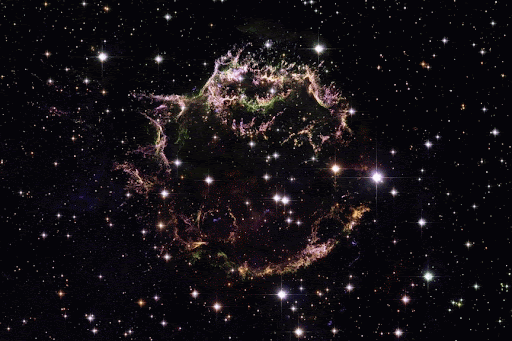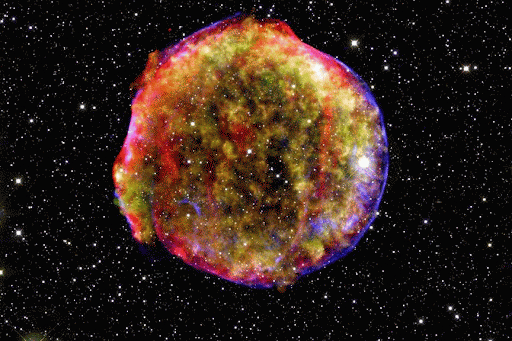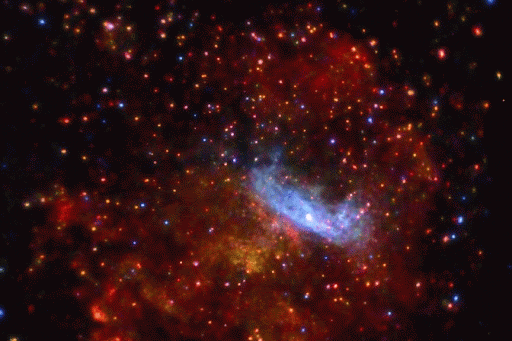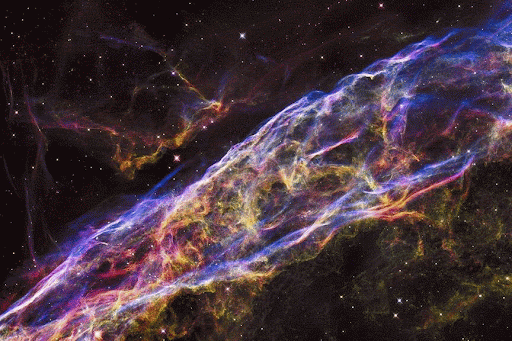
From some of the most cataclysmic events in the cosmos comes all of the beauty we see here on Earth. Life, and even our planet, wouldn’t have formed without them! But we still have lots of questions about these stellar factories.
In 2006, our Stardust spacecraft returned to Earth containing tiny particles of interstellar dust that originated in distant stars, light-years away – the first star dust to ever be collected from space and returned for study. You can help us identify and study the composition of these tiny, elusive particles through our Stardust@Home Citizen Science project.
Our upcoming Roman Space Telescope will help us learn more about how elements were created and distributed throughout galaxies, all while exploring many other cosmic questions. Learn more about the exciting science this mission will investigate on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
-
 mushroomsinthemaking liked this · 7 months ago
mushroomsinthemaking liked this · 7 months ago -
 nunyo-bizznez liked this · 1 year ago
nunyo-bizznez liked this · 1 year ago -
 t-wav liked this · 4 years ago
t-wav liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts