Five Times Astronaut Peggy Whitson Made History
Five Times Astronaut Peggy Whitson Made History
On April 24, 2017, NASA Astronaut Peggy Whitson established the new record for the most time spent in space by an American astronaut. She’s spent more than 76 weeks of her life floating in microgravity! It’s not the first time in her career at NASA that Whitson has established new milestones: here are just a few.

First NASA Science Officer
Peggy Whitson was the named the first NASA Science Officer aboard the space station in 2002. The position was created to work with the United States research community to understand and meet the requirements and objectives of each space station experiment.

First Female to Command the Space Station… Twice
Whitson became the first female to command the space station during Expedition 16 in 2008. Then Whitson became the first female to command the station twice during her current mission on April 9, 2017.

First Female Chief of the Astronaut Office
In 2009, Whitson became the first female and first non-pilot to achieve the most senior position for active astronauts, Chief of the Astronaut Office.

Most Spacewalks for a Female
On March 30, 2017, Peggy Whitson broke the record for most spacewalks and most time spent spacewalking for female astronauts. Suni Williams had previously held the record at 7 spacewalks.

Most Time In Space By A NASA Astronaut
At 1:27 a.m. ET on April 24, Peggy Whitson set the new record for cumulative time spent in space by an American astronaut. Jeff Williams previously set the record in 2016.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
10 Questions for Our Chief Scientist
NASA Chief Scientist…pretty cool title, right? The office represents all the scientific endeavors at NASA, ensuring they’re aligned with and fulfilling the administration’s science goals.

After more than three years as Chief Scientist, Ellen Stofan is departing for new adventures. We caught up with her to ask 10 questions about her role and what she will miss most after she leaves the agency. Take a look…

1) What were some of your expectations coming in as NASA’s chief scientist?
When I started as Chief Scientist, all I knew is that I would be science advisor to the Administrator, Charlie Bolden, overseeing the agency’s science portfolio. What I did not realize at the time was the degree that I would be impressed by him.

Charlie is an amazing leader who deeply cares about each and every person at this agency. He makes everyone feel valued. That is why NASA has just been voted by our employees for the fifth straight year as the Best Place to Work in the federal government!
2) What do you think it the next big thing for NASA science?
Looking across our science portfolio, I think the most exciting area, which actually connects everything we do, is the search for life beyond Earth. People have long wondered if we are alone, and we are now actually going to answer that question in the next few decades. We are exploring Mars, where it is very likely that life evolved at around the same time life evolved here on Earth. Conditions on Mars deteriorated after about a billion years, so life either went underground, or became extinct. It will likely take future Mars astronauts to find the best evidence of Mars life.

We also are planning to explore the ocean worlds of the outer solar system, like Europa, where we might find life in subsurface oceans. Beyond our solar system, the thousands of planets discovered by the Kepler Space Telescope have made me very optimistic that we are close to finding an Earth 2.0—though that will take us a little longer.
3) NASA science rewrites textbooks all the time. What is something you've seen here that has the potential to occur in the future that will change the textbooks for kids of tomorrow?
For kids 16 and under today, for every day of their life, we have been living and working in space on board the International Space Station. Now we are ready to take that next step in the coming decade, to move humans beyond low-Earth orbit where we have been for such a long time, out to the vicinity of the moon and then on to Mars.

These kids are the “Mars generation,” and the exploration of Mars will change our outlook in profound ways, from looking back at Earth -- that will just look like another star -- to finding evidence of life beyond Earth. So it will not just change science textbooks, it will change how we look at ourselves when we become a multi-planetary species.
4) Behind every pretty space image is a team of scientists who analyze all the data to make the discovery happen. What do you wish the public knew about the people and work that goes into each of those pretty pictures?
It really does take a team. When I go out and talk to school kids, I tell them learning how to be a good member of a team is so important in life. You need to learn to be a leader and a follower, and above all a listener. Our teams at NASA are becoming more and more diverse, which is incredibly important. If everyone looks the same and comes from the same background, they are likely to approach problems the same way. And when you are trying to do tough things -- from addressing climate change to sending humans to Mars -- you need the best team, which means a diverse team.

5) We have a lot of opportunities for citizen science. What’s one opportunity you wish everyone knew about that they could get involved with at NASA?
Go to www.nasa.gov/solve where you can find all kinds of great opportunities to join us at NASA in searching for planets around other stars, exploring Mars, helping us gather data about this planet, and tackling technology challenges. We really are stronger together, and getting the public involved in what we do is helping us get more good science every day. Even more importantly, it lets people know that science is fun!

6) What changes did you make at the agency while you were there?
As Chief Scientist, I got to work on a lot of fun challenges, from our strategy on how to get humans to Mars, to learning about and promoting the research we do every day on the International Space Station. But one of the things that I am most proud of is that, working with my team, NASA now collects voluntary demographic data on all of our grant proposals. Implicit or unconscious bias is all around us; we may act on deep-seated biases that we don’t even know we have. The first step in dealing with bias is seeing if you have a problem, and that is what the data collection will tell us.
7) You worked a lot with kids as the agency’s Chief Scientist. How important do you feel STEM education is for NASA?
We need the next generation of scientists, doctors, computer programmers, technologists and engineers, and NASA provides the inspiration and hands-on activities that help get kids interested in science. Because of climate change, we are facing rising sea levels, changing patterns of agriculture, and changing weather. We need good engineers and scientists to help us mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce carbon emissions.

On top of that, we live in a society that is dependent on technology; I don’t think most of us can go very long without checking our smartphones. But as technology becomes more complex, we need everyone in society to have at least a basic understanding of it, and that’s where the importance of STEM education comes in. We are ALL consumers of science and technology. We all need to be informed consumers.
8) What solar system destination are you still most excited/eager for NASA to still go explore?
As a planetary geologist, I am most excited by one of the ocean worlds of the outer solar system. Titan, one of Saturn’s moons, is an amazing little world where it rains, and the liquid forms rivers, lakes and seas. But this liquid is actually liquid methane and ethane --basically gasoline, rather than water -- due to the extremely cold temperatures out by Saturn.

Titan is an excellent place to explore to help us better understand how oceans and atmospheres interact, and maybe even understand more about the limits of life. We think water is critical to the evolution of life, but Titan may tell us that having a liquid is the most important factor.
9) What will you miss most?
It’s the people of NASA whom I will miss the most. Everyone I work with is so committed to the mission of this agency—pushing back the frontiers of science and technology to accomplish great things for the nation. NASA represents the best of this country. We demonstrate that with hard work and determination, we can explore the universe, our galaxy, our solar system and our home planet.

Our partnerships with other space agencies from around the world and with the private sector here have shown me that great teams accomplish great things. I like to say that NASA is the keeper of the future—we don’t just wait for the future to happen. We work to create it every day.
10) In your opinion, after seeing everything you've seen here, why should people care about the science at NASA?
At NASA, we gather the data to help answer the most fundamental and profound questions: Where did we come from? How does our planet and our universe work? What is the fate of our planet? It is only by exploring, by making measurements, by answering scientific questions that we can move forward as a society. And in doing so, we push technology and engineering in ways that benefit us every day right here on Earth.

NASA makes measurements that show how the sea level is rising, how Arctic ice is melting, and how weather patterns are changing. We also gather data to help farmers grow more crops using less water, help understand our water resources, and do the research to improve forecasting. These data keep us secure and improve the quality of life on Earth every day.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
You’ve seen things floating in space, but why does that happen and how does it affect science being conducted aboard the International Space Station?
Sure, floating looks like fun, but it could also unlock new scientific discoveries!
Microgravity makes the International Space Station the perfect place to perform research that is changing the lives of people on Earth, and preparing us to go deeper into space. This season on our series NASA Explorers, we are following science into low-Earth orbit and seeing what it takes to do research aboard the space station.
Follow NASA Explorers on Facebook to catch new episodes of season 4 every Wednesday. https://www.facebook.com/NASAExplorersSeries/
More than Just Dust in the Wind

From space, we can see a swirling brown mass making its way across the Atlantic – dust from the Sahara Desert – the largest hot desert in the world. It’s a normal phenomenon. Every year, winds carry millions of tons of dust from North Africa, usually during spring and summer in the Northern Hemisphere.

June 2020 has seen a massive plume of dust crossing the ocean. It’s so large it’s visible from one million miles away in space.

Dust clouds this large can affect air quality in regions where the dust arrives. The particles can also scatter the Sun’s light, making sunrises and sunsets more vibrant.

Dust particles in the air are also known as aerosols. We can measure aerosols, including dust, sea salt and smoke, from satellites and also use computer models to study how they move with the wind.

Following the transport of dust from space shows us how one of the driest places on Earth plays a role in fertilizing the Amazon rainforest. There are minerals in Saharan dust, like phosphorous, that exist in commercial fertilizers, helping seed the rainforest.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Infrared is Beautiful
Why was James Webb Space Telescope designed to observe infrared light? How can its images hope to compare to those taken by the (primarily) visible-light Hubble Space Telescope? The short answer is that Webb will absolutely capture beautiful images of the universe, even if it won’t see exactly what Hubble sees. (Spoiler: It will see a lot of things even better.)

The James Webb Space Telescope, or Webb, is our upcoming infrared space observatory, which will launch in 2019. It will spy the first luminous objects that formed in the universe and shed light on how galaxies evolve, how stars and planetary systems are born, and how life could form on other planets.
What is infrared light?
This may surprise you, but your remote control uses light waves just beyond the visible spectrum of light—infrared light waves—to change channels on your TV.
Infrared light shows us how hot things are. It can also show us how cold things are. But it all has to do with heat. Since the primary source of infrared radiation is heat or thermal radiation, any object that has a temperature radiates in the infrared. Even objects that we think of as being very cold, such as an ice cube, emit infrared.
There are legitimate scientific reasons for Webb to be an infrared telescope. There are things we want to know more about, and we need an infrared telescope to learn about them. Things like: stars and planets being born inside clouds of dust and gas; the very first stars and galaxies, which are so far away the light they emit has been stretched into the infrared; and the chemical fingerprints of elements and molecules in the atmospheres of exoplanets, some of which are only seen in the infrared.
In a star-forming region of space called the 'Pillars of Creation,' this is what we see with visible light:

And this is what we see with infrared light:

Infrared light can pierce through obscuring dust and gas and unveil a more unfamiliar view.
Webb will see some visible light: red and orange. But the truth is that even though Webb sees mostly infrared light, it will still take beautiful images. The beauty and quality of an astronomical image depends on two things: the sharpness of the image and the number of pixels in the camera. On both of these counts, Webb is very similar to, and in many ways better than, Hubble. Webb will take much sharper images than Hubble at infrared wavelengths, and Hubble has comparable resolution at the visible wavelengths that Webb can see.

Webb’s infrared data can be translated by computer into something our eyes can appreciate – in fact, this is what we do with Hubble data. The gorgeous images we see from Hubble don’t pop out of the telescope looking fully formed. To maximize the resolution of the images, Hubble takes multiple exposures through different color filters on its cameras.
The separate exposures, which look black and white, are assembled into a true color picture via image processing. Full color is important to image analysis of celestial objects. It can be used to highlight the glow of various elements in a nebula, or different stellar populations in a galaxy. It can also highlight interesting features of the object that might be overlooked in a black and white exposure, and so the images not only look beautiful but also contain a lot of useful scientific information about the structure, temperatures, and chemical makeup of a celestial object.
This image shows the sequences in the production of a Hubble image of nebula Messier 17:

Here’s another compelling argument for having telescopes that view the universe outside the spectrum of visible light – not everything in the universe emits visible light. There are many phenomena which can only be seen at certain wavelengths of light, for example, in the X-ray part of the spectrum, or in the ultraviolet. When we combine images taken at different wavelengths of light, we can get a better understanding of an object, because each wavelength can show us a different feature or facet of it.
Just like infrared data can be made into something meaningful to human eyes, so can each of the other wavelengths of light, even X-rays and gamma-rays.
Below is an image of the M82 galaxy created using X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory, infrared data from the Spitzer Space Telescope, and visible light data from Hubble. Also note how aesthetically pleasing the image is despite it not being just optical light:

Though Hubble sees primarily visible light, it can see some infrared. And despite not being optimized for it, and being much less powerful than Webb, it still produced this stunning image of the Horsehead Nebula.

It’s a big universe out there – more than our eyes can see. But with all the telescopes now at our disposal (as well as the new ones that will be coming online in the future), we are slowly building a more accurate picture. And it’s definitely a beautiful one. Just take a look...
…At this Spitzer infrared image of a shock wave in dust around the star Zeta Ophiuchi.

…this Spitzer image of the Helix Nebula, created using infrared data from the telescope and ultraviolet data from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer.

…this image of the “wing” of the Small Magellanic Cloud, created with infrared data from Spitzer and X-ray data from Chandra.

...the below image of the Milky Way’s galactic center, taken with our flying SOFIA telescope. It flies at more than 40,000 feet, putting it above 99% of the water vapor in Earth's atmosphere-- critical for observing infrared because water vapor blocks infrared light from reaching the ground. This infrared view reveals the ring of gas and dust around a supermassive black hole that can't be seen with visible light.

…and this Hubble image of the Mystic Mountains in the Carina Nebula.

Learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope HERE, or follow the mission on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Image Credits Eagle Nebula: NASA, ESA/Hubble and the Hubble Heritage Team Hubble Image Processing - Messier 17: NASA/STScI Galaxy M82 Composite Image: NASA, CXC, JHU, D.Strickland, JPL-Caltech, C. Engelbracht (University of Arizona), ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Horsehead Nebula: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Zeta Ophiuchi: NASA/JPL-Caltech Helix Nebula: NASA/JPL-Caltech Wing of the Small Magellanic Cloud X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ.Potsdam/L.Oskinova et al; Optical: NASA/STScI; Infrared: NASA/JPL-Caltech Milky Way Circumnuclear Ring: NASA/DLR/USRA/DSI/FORCAST Team/ Lau et al. 2013 Mystic Mountains in the Carina Nebula: NASA/ESA/M. Livio & Hubble 20th Anniversary Team (STScI)
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Space Lettuce in the White House Kitchen Garden
While most people plant gardens on Earth, we’re working to cultivate one in space!

On April 5, the First Lady welcomed students from across the country as well as NASA Deputy Administrator Dava Newman and NASA astronaut Cady Coleman to the White House Kitchen Garden.

While there, they planted various produce, including the same variety of lettuce that will be sent to the International Space Station on the April 8 SpaceX cargo launch.

These seeds were prepared and packaged for both the First Lady’s garden, as well as the batch headed up to space station. “Outredgeous” Red Romaine Lettuce and “Tokyo bekana” Chinese Cabbage will soon be growing in both gardens!
Why do we grow plants in space?

Our Veggie plant growth system on the space station provides lighting and nutrient supply for a space garden. It supports a variety of plant species that can be cultivated for educational outreach, fresh food and even recreation for crew members on long-duration missions.
When crews travel farther into space, they will need a self-sustaining life support system, and that means growing their own food.
How do we grow plants in space? Here’s a resource for “Space Gardening 101”.
Want to see the space station seeds launch? You can watch Friday’s SpaceX cargo launch live online starting at 3:30 p.m. EDT, with launch scheduled for 4:43 p.m.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Tornado Recovery Underway at Michoud Assembly Facility
Teams at our Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans worked overnight and are continuing Wednesday with assessment and recovery efforts following a tornado strike at the facility Tuesday at 11:25 a.m. CST. All 3,500 employees at the facility have been accounted for, with five sustaining minor injuries.
Teams worked through the night on temporary repairs to secure the perimeter fencing and provide access for the essential personnel through the main gate. Approximately 40 to 50 percent of the buildings at Michoud have some kind of damage; about five buildings have some form of severe damage.

Approximately 200 parked cars were damaged, and there was damage to roads and other areas near Michoud.

“The entire NASA family pulls together during good times and bad, and the teams at the Michoud Assembly Facility are working diligently to recover from the severe weather that swept through New Orleans Tuesday and damaged the facility,” said acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. “We are thankful for the safety of all the NASA employees and workers of onsite tenant organizations, and we are inspired by the resilience of Michoud as we continue to assess the facility’s status.”

Teams will reassess the condition of the Vertical Assembly Center (VAC), as the initial examination revealed some electrical damage to its substation. The VAC is used to weld all major pieces of hardware for the core stage of the Space Launch System. The most recently welded part was removed from the facility last week.

The team has prioritized completing the assessment at the site’s main manufacturing building for the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft flight hardware so power can be restored in phases and temporary protection put in place to shield hardware from any further inclement weather.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
7 Sports Astronauts Love Without Gravity (Including Football)
Astronauts onboard the International Space Station spend most of their time doing science, exercising and maintaining the station. But they still have time to shoot hoops and toss around a football.
From chess to soccer, there’s a zero-gravity spin to everything.
1. Baseball



Baseball: America’s favorite pastime. JAXA astronaut, Satoshi Furukawa shows us how microgravity makes it possible to be a one-man team. It would be a lot harder to hit home runs if the players could jump that high to catch the ball.
2. Chess

Yes, it’s a sport, and one time NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff (right) played Earth on a Velcro chess board. An elementary school chess team would pick moves that everyone could vote for online. The winning move would be Earth’s play, and then Chamitoff would respond. About every two days, a move would be made. But who won the historic Earth vs. Space match? Earth! Chamitoff resigned after Earth turned its pawn into a queen, but it was game well played.
3. Soccer


NASA astronaut Steve Swanson put a new spin on soccer by juggling the ball upside down. However, he might not have considered himself upside down. On the space station, up and down are relative.
4. Gymnastics
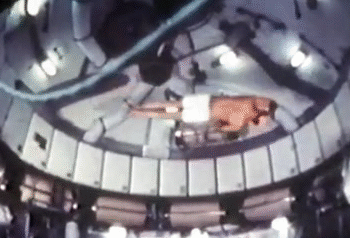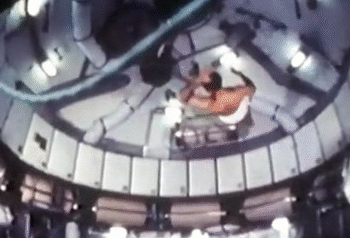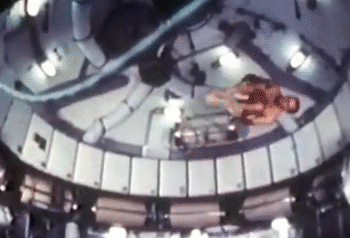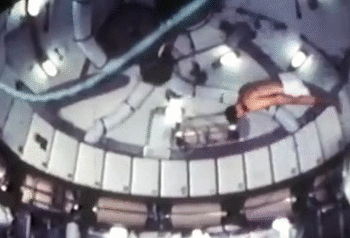
NASA astronauts usually sign off their videos with a zero-gravity somersault (either forwards or backwards). But astronauts are also proficient in handstands, flips and twists. The predecessor to the International Space Station, the Skylab, had the best space for the moves. The current space station is a bit tight in comparison.
5. Basketball

Objects that aren’t heavy don’t move very well on the space station. They kind of just float. It’s like Earth, but exaggerated. For example, on Earth a beach ball wouldn’t go as far as a basketball. The same is true in space, which is why playing with a basketball in space is more fun than playing with a beach ball.
6. Golf

People talk about hitting golf balls off skyscrapers, but what about off the International Space Station? While golf isn’t a normal occurrence on the station, it’s been there. One golf company even sent an experiment to the station to find out how to make better golf clubs.
7. Football

Zero gravity doesn’t make everything easier. Astronauts need to relearn how to throw things because their brains need to relearn how to interpret sensory information. A bowling ball on the space station no longer feels as heavy as a bowling ball on Earth. When astronauts first throw things on the space station, everything keeps going too high. That would put a wrench in your spiral for a couple of months. But once you adjust, the perfect spiral will just keep spiraling!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
@manishkumarmishra: How does all this work benefit us back here on Earth?
Meet America’s #NewAstronauts
We’re so excited to introduce America’s new astronauts! After evaluating a record number of applications, we’re proud to present our 2017 astronaut class!

These 12 new astronaut candidates were chosen from more than 18,300 people who submitted applications from December 2015 to February 2016. This was more than double the previous record of 8,000 set in 1978.

Meet them…
Kayla Barron

This Washington native graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy with a Bachelor’s degree in Systems Engineering. A Gates Cambridge Scholar, Barron earned a Master’s degree in Nuclear Engineering from the University of Cambridge.
She enjoys hiking, backpacking, running and reading.
Zena Cardman

Zena is a native of Virginia and completed a Bachelor of Science degree in Biology and Master of Science degree in Marine Sciences at The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Her research has focused on microorganisms in subsurface environments, ranging from caves to deep sea sediments.
In her free time, she enjoys canoeing, caving, raising backyard chickens and glider flying.
Raja Chari

Raja is an Iowa native and graduated from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1999 with Bachelor’s degrees in Astronautical Engineering and Engineering Science. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology and graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has accumulated more than 2,000 hours of flight time in the F-35, F-15, F-16 and F-18 including F-15E combat missions in Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Matthew Dominick

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from the University of San Diego and a Master of Science degree in Systems Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School. He graduated from U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has more than 1,600 hours of flight time in 28 aircraft, 400 carrier-arrested landigns and 61 combat missions.
Bob Hines

Bob is a Pennsylvania native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from Boston University. He is a graduate of the U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School, where he earned a Master’s degree in Flight Test Engineering. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Alabama.
During the last five years, he has served as a research pilot at NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
Warren Hoburg

Nicknamed “Woody”, this Pennsylvania native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and a Doctorate in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from the University of California, Berkley.
He is an avid rock climber, moutaineer and pilot.
Jonny Kim

This California native trained and operated as a Navy SEAL, completing more than 100 combat operations and earning a Silver Star and Bronze Star with Combat “V”. Afterward, he went on to complete a degree in Mathematics at the University of San Diego and a Doctorate of Medicine at Harvard Medical School.
His interests include spending time with his family, volunteering with non-profit vertern organizations, academic mentoring, working out and learning new skills.
Robb Kulin

Robb is an Alaska native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Denver, before going on to complete a Master’s degree in Materials Science and a Doctorate in Engineering at the University of California, San Diego.
He is a private pilot and also enjoys playing piano, photography, packrafting, running, cycling, backcountry skiing and SCUBA diving.
Jasmin Moghbeli

This New York native earned a Bachlor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering with Information Technology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, followed by a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School.
She is also a distinguished graduate of the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School and has accumulated mofre than 1,600 hours of flight time and 150 combat missions.
Loral O’Hara

This Texas native earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering at the University of Kansas and a Master of Science degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Purdue University.
In her free time, she enjoys working in the garage, traveling, surfing, diving, flying, sailing, skiing, hiking/orienteering, caving, reading and painting.
Frank Rubio

Frank is a Florida native and graduated from the U.S. Military Academy and earned a Doctorate of Medicine from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences.
He is a board certified family physician and flight surgeon. At the time of his selection, he was serving in the 10th Special Forces Group (Airborne).
Jessica Watkins

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Geological and Environmental Sciences at Stanford University, and a Doctorate in Geology from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
She enjoys soccer, rock climbing, skiing and creative writing.

After completing two years of training, the new astronaut candidates could be assigned to missions performing research on the International Space Station, launching from American soil on spacecraft built by commercial companies, and launching on deep space missions on our new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Do you guys (everyone at mission control) have inside jokes?
What is the best about being mission control?
As someone who's about to go to college to hopefully be astronaut if everything goes to plan. What is some good advice you wish someone told you?
-
 dflogerzi liked this · 1 month ago
dflogerzi liked this · 1 month ago -
 monpanache reblogged this · 1 month ago
monpanache reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 monpanache liked this · 1 month ago
monpanache liked this · 1 month ago -
 67-rats-in-a-trenchcoat reblogged this · 1 month ago
67-rats-in-a-trenchcoat reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 67-rats-in-a-trenchcoat liked this · 1 month ago
67-rats-in-a-trenchcoat liked this · 1 month ago -
 justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 7 months ago
justanoldfashiontumblog liked this · 7 months ago -
 seo-jo-eun liked this · 1 year ago
seo-jo-eun liked this · 1 year ago -
 iwantedamogusasmyblogname liked this · 2 years ago
iwantedamogusasmyblogname liked this · 2 years ago -
 forestchild04 liked this · 3 years ago
forestchild04 liked this · 3 years ago -
 selkierosemary liked this · 3 years ago
selkierosemary liked this · 3 years ago -
 naturegirlsbeauty liked this · 4 years ago
naturegirlsbeauty liked this · 4 years ago -
 lemonysnicket liked this · 4 years ago
lemonysnicket liked this · 4 years ago -
 adultdaughter-deactivated liked this · 4 years ago
adultdaughter-deactivated liked this · 4 years ago -
 welt-verbessererin liked this · 4 years ago
welt-verbessererin liked this · 4 years ago -
 orangecanary18 reblogged this · 4 years ago
orangecanary18 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 orangecanary18 liked this · 4 years ago
orangecanary18 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sokkalogic liked this · 4 years ago
sokkalogic liked this · 4 years ago -
 everythingman liked this · 4 years ago
everythingman liked this · 4 years ago -
 the-golden-yet-weird-girl liked this · 4 years ago
the-golden-yet-weird-girl liked this · 4 years ago -
 molly-loves-tay13 liked this · 4 years ago
molly-loves-tay13 liked this · 4 years ago -
 allthingsaestetic liked this · 4 years ago
allthingsaestetic liked this · 4 years ago -
 theartisticscientistsworld liked this · 4 years ago
theartisticscientistsworld liked this · 4 years ago -
 marsalka liked this · 4 years ago
marsalka liked this · 4 years ago -
 shallowexcerpt3rg liked this · 5 years ago
shallowexcerpt3rg liked this · 5 years ago -
 sheppardbv liked this · 5 years ago
sheppardbv liked this · 5 years ago -
 flippantalbum23fe liked this · 5 years ago
flippantalbum23fe liked this · 5 years ago -
 glossyzeal62lq liked this · 5 years ago
glossyzeal62lq liked this · 5 years ago -
 willieqg reblogged this · 5 years ago
willieqg reblogged this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts