Solar System: Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

For the first time in almost a decade, we're going back to Jupiter. Our Juno spacecraft arrives at the king of planets on the fourth of July. From a unique polar orbit, Juno will repeatedly dive between the planet and its intense belts of charged particle radiation. Juno's primary goal is to improve our understanding of Jupiter's formation and evolution, which will help us understand the history of our own solar system and provide new insight into how other planetary systems form.
In anticipation, here are a few things you need to know about the Juno mission and the mysterious world it will explore:
1. This is the Big One

The most massive planet in our solar system, with dozens of moons and an enormous magnetic field, Jupiter rules over a kind of miniature solar system.
2. Origin Story

Why study Jupiter in the first place? How does the planet fit into the solar system as a whole? What is it hiding? How will Juno unlock its secrets? A series of brief videos tells the stories of Jupiter and Juno. Watch them HERE.
3. Eyes on Juno
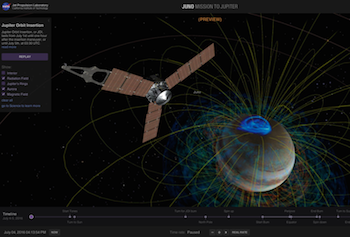
If you really want a hands-on understanding of Juno's flight through the Jupiter system, there's no better tool than the "Eyes on Juno" online simulation. It uses data from the mission to let you realistically see and interact with the spacecraft and its trajectory—in 3D and across both time and space.
4. You’re on JunoCam!

Did you know that you don't have to work for NASA to contribute to the Juno mission? Amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts everywhere are invited to help with JunoCam, the mission's color camera. You can upload your own images of Jupiter, comment on others' images, and vote on which pictures JunoCam will take when it reaches the Jovian system.
5. Ride Along
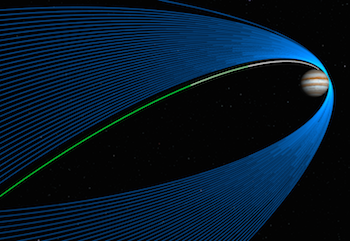
It's easy to follow events from the Juno mission as they unfold. Here are several ways to follow along online:
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
How to Do Business with NASA
It’s Small Business Week! To celebrate, we’re breaking down the process and explaining how YOUR small business can work with us. Here are 10 steps:

Prior to working with us, identify which of your products or services best fit within our industry. It’s also important to know the Federal Supply Class or Service Codes (FSC/SVC) for your products or services. Prepare a capability brief in both printed and electronic versions with an emphasis on Government work.

In order to register your business with us, there are three systems you’ll need to use. The Data Universal Numbering System (DUNS), the System for Award Management (SAM) and the NASA Vendor Data Base (NVDB). After you’ve survived all those acronyms, your business is registered!

Here at NASA we have centers around the country that each procure different types of business. Where does your product or service fit in? The best thing to do is visit THIS site and find out more about each center. You can also take a look at our Acquisition Forecast to find out about expected contract opportunities.

You can find current procurement opportunities in your product or service area by checking the Federal Business Opportunities website. This site also helps you identify our requirements and even send you e-mail notifications of released requirements.

Contracting procedures can be tedious, it’s always a good idea to familiarize yourself with the Federal Acquisition Regulations (FAR), as well as our supplement to those regulations. Which can be found HERE.

Did you know that many of our purchases are orders on the Federal Supply Schedule contracts? They are, which means you can contact the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) for information on how to obtain a contract.

There are some very beneficial resources available to you throughout this process. You can request training and counseling on marketing, financial and contracting issues at minimal or no cost from Procurement Technical Assistance Centers (PTACs).
You also have the option to consult with the SBA’s Procurement Center Representatives (PCRs) and the SBA Business Development Centers. The SBA provides each of our centers with a liaison.
There is also an option to get free and confidential mentoring by former CEOs through SCORE.

Direct contracting is not the only route for small businesses. Consider subcontracting opportunities, and get information through the SBA’s SUB-Net or Subcontracting Opportunities Directory. Solicitations or notices are posted by prime contractors. Our list of prime vendors is located on our Marshall Space Flight Center’s website.

Explore other small business programs, such as our Mentor-Protégé Program, the Small Business Innovation Research Program and the Historically Black Colleges and Universities and Minority-Serving Institutions Program. Information on these and other programs is available on our Office of Small Business Programs website.

After you have identified your customers, researched their requirements and familiarized yourself with our procurement regulations and strategies, it’s time to market your product or service. Present your capabilities directly to the NASA Centers that buy your products or services. Realize that, as with yours, their time is valuable. If the match is a good one, you can provide them with a cost-effective, quality solution to their requirements. Good luck!
Here are a Few Small Businesses We’re Already Working With…

Dynetics Technical Services, Inc., of Huntsville, AL works with us on enterprise information technology services so that we have the right tools to reach for new heights. This company was also named Agency Small Business Prime Contractor of the Year.

Arcata Associates, Inc., of Las Vegas, NV manages operations and maintenance for our Dryden Aeronautical Test Range in Edwards, CA. Their work ensures that we can continue our critical work in aviation research and development. This company was even named Agency Small Business Subcontractor of the Year.
Want to learn more about our Office of Small Business Programs? Visit their site HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

From the vantage point of the International Space Station, astronaut Shane Kimbrough (@astro_kimbrough) captured this image over the Earth, writing “Looking west over the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia and Egypt. #EarthArt from the amazing space station.”
The space station serves as the world's laboratory for conducting cutting-edge microgravity research, and is the primary platform for technology development and testing in space to enable human and robotic exploration of destinations beyond low-Earth orbit, including asteroids and Mars.

Hello! Jeanette Epps here ready to take your @nasa questions!
Taking the Vital Signs of Mars
Does Mars have quakes? What is the temperature of the Red Planet? How did Mars even form? What can it tell us about how other rocky planets formed?
The Mars InSight lander is scheduled to launch in May 2018 to search for the answers to those questions.

InSight (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) will conduct the first thorough “check-up” of Mars in more than 4.5 billion years, measuring its “pulse”, or seismic activity; its temperature; and its “reflexes” (the way the planet wobbles when it is pulled by the Sun and its moons).
How and Why?

By using sophisticated instruments – tools that can measure the vital signs of a planet – InSight will delve deep beneath the surface of Mars, detecting the clues left by the earliest stages of planetary formation.

Previous Mars missions have explored the surface history of the Red Planet. Mars has been less geologically active than Earth, so it retains a more complete record of its history in its core, mantle and crust. InSight will study the sizes, densities and overall structure of the Red Planet’s core, mantle and crust.

The lander will also measure the rate at which heat escapes from the planet’s interior, and provide glimpses into the evolutionary processes of all the rocky planets in our solar system, including Earth, and even those circling other stars!

Send Your Name to Mars!

You can send your name to Mars onboard the InSight lander! The deadline to get your Martian boarding pass is Nov. 1. To submit your name, visit: mars.nasa.gov/syn/insight
Learn more about Mars InSight HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Photos of the eclipse are okay and just as neat to look at? Will NASA post to twitter. Will the Space station take photos also?
Yes, we will be posting a ton of photos and you can add to them as well! https://www.flickr.com/groups/nasa-eclipse2017/ I agree, the photos are incredibly cool!
13 Reasons to Have an Out-of-This-World Friday (the 13th)
1. Not all of humanity is bound to the ground

Since 2000, the International Space Station has been continuously occupied by humans. There, crew members live and work while conducting important research that benefits life on Earth and will even help us eventually travel to deep space destinations, like Mars.
2. We’re working to develop quieter supersonic aircraft that would allow you to travel from New York to Los Angeles in 2 hours

We are working hard to make flight greener, safer and quieter – all while developing aircraft that travel faster, and building an aviation system that operates more efficiently. Seventy years after Chuck Yeager broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1 aircraft, we’re continuing that supersonic X-plane legacy by working to create a quieter supersonic jet with an aim toward passenger flight.
3. The spacecraft, rockets and systems developed to send astronauts to low-Earth orbit as part of our Commercial Crew Program is also helping us get to Mars
Changes to the human body during long-duration spaceflight are significant challenges to solve ahead of a mission to Mars and back. The space station allows us to perform long duration missions without leaving Earth’s orbit.

Although they are orbiting Earth, space station astronauts spend months at a time in near-zero gravity, which allows scientists to study several physiological changes and test potential solutions. The more time they spend in space, the more helpful the station crew members can be to those on Earth assembling the plans to go to Mars.
4. We’re launching a spacecraft in 2018 that will go “touch the Sun”

In the summer of 2018, we’re launching Parker Solar Probe, a spacecraft that will get closer to the Sun than any other in human history. Parker Solar Probe will fly directly through the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona. Getting better measurements of this region is key to understanding our Sun.
For instance, the Sun releases a constant outflow of solar material, called the solar wind. We think the corona is where this solar wind is accelerated out into the solar system, and Parker Solar Probe’s measurements should help us pinpoint how that happens.
5. You can digitally fly along with spacecraft…that are actually in space…in real-time!

NASA’s Eyes are immersive, 3D simulations of real events, spacecraft locations and trajectories. Through this interactive app, you can experience Earth and our solar system, the universe and the spacecraft exploring them. Want to watch as our Juno spacecraft makes its next orbit around Juno? You can! Or relive all of the Voyager mission highlights in real-time? You can do that too! Download the free app HERE to start exploring.
6. When you feel far away from home, you can think of the New Horizons spacecraft as it heads toward the Kuiper Belt, and the Voyager spacecraft are beyond the influence of our sun…billions of miles away

Our New Horizons spacecraft completed its Pluto flyby in July 2015 and has continued on its way toward the Kuiper Belt. The spacecraft continues to send back important data as it travels toward deeper space at more than 32,000 miles per hour, and is ~3.2 billion miles from Earth.

In addition to New Horizons, our twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-37-year journey since their 1977 launches, they are each much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between the stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago.
7. There are humans brave enough to not only travel in space, but venture outside space station to perform important repairs and updates during spacewalks

Just this month (October 2017) we’ve already had two spacewalks on the International Space Station...with another scheduled on Oct. 20.
Spacewalks are important events where crew members repair, maintain and upgrade parts of the International Space Station. These activities can also be referred to as EVAs – Extravehicular Activities. Not only do spacewalks require an enormous amount of work to prepare for, but they are physically demanding on the astronauts. They are working in the vacuum of space in only their spacewalking suit.
8. Smart people are up all night working in control rooms all over NASA to ensure that data keeps flowing from our satellites and spacecraft

Our satellites and spacecraft help scientists study Earth and space. Missions looking toward Earth provide information about clouds, oceans, land and ice. They also measure gases in the atmosphere, such as ozone and carbon dioxide and the amount of energy that Earth absorbs and emits. And satellites monitor wildfires, volcanoes and their smoke.
9. A lot of NASA-developed tech has been transferred for use to the public
Our Technology Transfer Program highlights technologies that were originally designed for our mission needs, but have since been introduced to the public market. HERE are a few spinoff technologies that you might not know about.
10. We have a spacecraft currently traveling to an asteroid to collect a sample and bring it back to Earth

OSIRIS-REx is our first-ever mission that will travel to an asteroid and bring a sample of it back to Earth. Currently, the spacecraft is on its way to asteroid Bennu where it will survey and map the object before it “high-fives” the asteroid with its robotic arm to collect a sample, which it will send to Earth.
If everything goes according to plan, on Sept. 24, 2023, the capsule containing the asteroid sample will make a soft landing in the Utah desert.
11. There are Earth-sized planets outside our solar system that may be habitable
To date, we have confirmed 3,000+ exoplanets, which are planets outside our solar system that orbit a Sun-like star. Of these 3,000, some are in the habitable zone – where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on the surface.

Recently, our Spitzer Space Telescope revealed the first known system of SEVEN Earth-size planets around a single star. Three of these plants are firmly in the habitable zone, and could have liquid water on the surface, which is key to life as we know it.
12. Earth looks like art from space

In 1960, the United States put its first Earth-observing environmental satellite into orbit around the planet. Over the decades, these satellites have provided invaluable information, and the vantage point of space has provided new perspectives on Earth.

The beauty of Earth is clear, and the artistry ranges from the surreal to the sublime.
13. We’re building a telescope that will be able to see the first stars ever formed in the universe

Wouldn’t it be neat to see a period of the universe’s history that we’ve never seen before? That’s exactly what the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will be able to do…plus more!
Specifically, Webb will see the first objects that formed as the universe cooled down after the Big Bang. We don’t know exactly when the universe made the first stars and galaxies – or how for that matter. That is what we are building Webb to help answer.
Happy Friday the 13th! We hope it’s out-of-this-world!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
10 Ways to Celebrate Halloween with NASA
There’s a whole universe of mysteries out there to put some fun—and maybe a touch of fright—into your All Hallows Eve festivities. Here are a few:
1. Universe of Monsters
Mythical monsters of Earth have a tough time of it. Vampires don’t do sunlight. Werewolves must wait for a full Moon to howl. Now, thanks to powerful space telescopes, some careful looking and a lot of whimsy, NASA scientists have found suitable homes for the most terrifying Halloween monsters.

2. Be a Spacecraft
No costume. No problem. NASA Blueshift offers some handy tips on transforming yourself into a powerful space telescope before hitting the sidewalk to trick-or-treat.

3. Robot Pumpkins
At Halloween, engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory craft dramatic creations that have as much in common with standard jack-o'-lanterns as paper airplanes do with NASA spacecraft. The unofficial pumpkin carving contest gives engineers a chance to flex their creative muscles and bond as a team. The rules are simple: no planning, carving or competing during work hours.
The results? See for yourself!
Can’t wait to see this year’s creations? Do it yourself!



4. Skull Comet
Scientists think a large space rock that zipped past Earth on Halloween in 2015 was most likely a dead comet or an asteroid that, fittingly, bore an eerie resemblance to a skull.
"The object might be a dead comet, but in the (radar) images it appears to have donned a skull costume for its Halloween flyby," said NASA scientist Kelly Fast,
As with a lot of spooky things, the asteroid looked a lot less scary upon closer inspection.

5. Spooky Sun
Not to be outdone, the Sun—our star—has been known to put on a scary face.
In this October 2014 Solar Dynamic Observatory image, active regions on the Sun combined to look something like a jack-o-lantern’s face.
The active regions appear brighter because those are areas that emit more light and energy—markers of an intense and complex set of magnetic fields hovering in the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona. This image blends together two sets of wavelengths at 171 and 193 angstroms, typically colorized in gold and yellow, to create a particularly Halloween-like appearance.

6. Halloween on a Mission
Halloween held a special significance for NASA’s Cassini mission, which launched in October 1997. The team held its own elaborate pumpkin carving competitions for many years. The mission also shared whimsical Halloween greetingswith its home planet.
Cassini ended its extended mission at Saturn in 2017.

7. The Ghost of Cassiopeia
The brightest stars embedded in nebulae throughout our galaxy pour out a torrent of radiation that eats into vast clouds of hydrogen gas – the raw material for building new stars. This etching process sculpts a fantasy landscape where human imagination can see all kinds of shapes and figures. This nebula in the constellation of Cassiopeia has flowing veils of gas and dust that have earned it the nickname "Ghost Nebula."

8. They’re Everywhere
Turns out the human mind—including space scientists and engineers among us—find spooky shapes in many places.
This infrared view of the Helix Nebula reminded astronomers of a zombie eyeball.

9. What Do You See?
The Oct. 26 Earth Observatory’s Puzzler feature offers a spooky shape for your consideration. What is it and what does it look like? You tell us.

10. Space Candy
The trick-or-treat tradition is still—so far—pretty much confined to Earth. But thanks to the men and women who have been living aboard the International Space Station for more than 17 years, we have a preview of what a future space-based trick-or-treater’s Halloween candy haul would look like in microgravity.

Bonus: 11. Want More?
Our education team offers a bunch more Halloween activities, including space-themed pumpkin stencils, costume tips and even some mysteries to solve like a scientist or engineer.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Photograph of the Apollo 13 Spacecraft Being Returned to the Prime Recovery Ship, USS Iwo Jima, 4/17/1970
Series: Color Photograph Files, 1965 - 2002. Record Group 255: Records of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 1903 - 2006.
Apollo 13 was intended to be the third Apollo mission to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Florida on April 11, 1970. Two days into the flight, damaged wire insulation inside the oxygen tank in the service module ignited, causing an explosion which vented the oxygen tank into space. Without oxygen, the service module became inoperable and the lunar mission quickly turned into a mission to safely return the crew to Earth. The astronauts worked with Mission Control to shut down the command module in order to conserve the remaining oxygen, forcing all three astronauts into the lunar module. The astronauts continued to work with Mission Control to combat one technical failure after another until, on April 17, 1970, the crew landed safely in the South Pacific Ocean.
source: phillyarchives.tumblr.com
who was your biggest inspiration, if any, and what events led you to follow this career choice?
Swift: Our Sleuth for the Universe’s Gamma-ray Bursts
The universe is full of mysteries, and we continue to search for answers. How can we study matter and energy that we can’t see directly? What’s it like inside the crushed core of a massive dead star? And how do some of the most powerful explosions in the universe evolve and interact with their surrounding environment?
Luckily for us, NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory is watching the skies and helping astronomers answer that last question and more! As we celebrate its 15-year anniversary, let’s get you up to speed about Swift.

What are gamma-ray bursts and why are they interesting?
Gamma-ray bursts are the most powerful explosions in the universe. When they occur, they are about a million trillion times as bright as the Sun. But these bursts don’t last long — from a few milliseconds (we call those short duration bursts) to a few minutes (long duration). In the 1960s, spacecraft were watching for gamma rays from Earth — a sign of nuclear testing. What scientists discovered, however, were bursts of gamma rays coming from space!
Gamma-ray bursts eventually became one of the biggest mysteries in science. Scientists wanted to know: What events sparked these fleeting but powerful occurrences?
So how do gamma-ray bursts and Swift connect?
When it roared into space on a rocket, Swift’s main goals included understanding the origin of gamma-ray bursts, discovering if there were additional classes of bursts (besides the short and long ones), and figuring out what these events could tell us about the early universe.

With Swift as our eyes on the sky, we now know that gamma-ray bursts can be some of the farthest objects we’ve ever detected and lie in faraway galaxies. In fact, the closest known gamma-ray burst occurred more than 100 million light-years from us. We also know that these explosions are associated with some of the most dramatic events in our universe, like the collapse of a massive star or the merger of two neutron stars — the dense cores of collapsed stars.

Swift is still a powerful multiwavelength observatory and continues to help us solve mysteries about the universe. In 2018 it located a burst of light that was at least 10 times brighter than a typical supernova. Last year Swift, along with NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, announced the discovery of a pair of distant explosions which produced the highest-energy light yet seen from gamma-ray bursts.
Swift can even study much, much closer objects like comets and asteroids!

Why is Swift unique?
How do we study events that happen so fast? Swift is first on the scene because of its ability to automatically and quickly turn to investigate sudden and fascinating events in the cosmos. These qualities are particularly helpful in pinpointing and studying short-lived events.

The Burst Alert Telescope, which is one of Swift’s three instruments, leads the hunt for these explosions. It can see one-sixth of the entire sky at one time. Within 20 to 75 seconds of detecting a gamma-ray burst, Swift automatically rotates so that its X-ray and ultraviolet telescopes can view the burst.

Because of the “swiftness” of the satellite, it can look at a lot in 24 hours — between 50 and 100 targets each day! Swift has new “targets-of-opportunity” to look at every day and can also look at objects for follow up observations. By doing so, it can see how events in our cosmos change over time.
How did Swift get its name?
You may have noticed that lots of spacecraft have long names that we shorten to acronyms. However, this isn’t the case for Swift. It’s named after the bird of the same name, and because of the satellite’s ability to move quickly and re-point its science instruments.
When it launched, Swift was called NASA’s Swift Observatory. But in January 2018, Swift was renamed the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory in memory of the mission’s original principal investigator, Neil Gehrels.

Follow along with Swift to see a typical day in the life of the satellite:
-
 mercedesalma liked this · 1 year ago
mercedesalma liked this · 1 year ago -
 lumibean liked this · 5 years ago
lumibean liked this · 5 years ago -
 auntiedonna101 liked this · 5 years ago
auntiedonna101 liked this · 5 years ago -
 analog-machine liked this · 6 years ago
analog-machine liked this · 6 years ago -
 bibliophilea liked this · 6 years ago
bibliophilea liked this · 6 years ago -
 melisa-may-taylor72 liked this · 6 years ago
melisa-may-taylor72 liked this · 6 years ago -
 unirazzi liked this · 6 years ago
unirazzi liked this · 6 years ago -
 somethingsquishdraws-blog liked this · 6 years ago
somethingsquishdraws-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 coldbloodedgoat-blog liked this · 6 years ago
coldbloodedgoat-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 nickisgirl reblogged this · 6 years ago
nickisgirl reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 nickisgirl liked this · 6 years ago
nickisgirl liked this · 6 years ago -
 awesome-casuallyfamouscollector liked this · 6 years ago
awesome-casuallyfamouscollector liked this · 6 years ago -
 ishillreadlater reblogged this · 6 years ago
ishillreadlater reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 sonicsoundscapes liked this · 6 years ago
sonicsoundscapes liked this · 6 years ago -
 dont-box-me-in liked this · 7 years ago
dont-box-me-in liked this · 7 years ago -
 oniromante liked this · 7 years ago
oniromante liked this · 7 years ago -
 timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago
timallenphoto liked this · 7 years ago -
 which-wiitch liked this · 8 years ago
which-wiitch liked this · 8 years ago -
 gotink56 liked this · 8 years ago
gotink56 liked this · 8 years ago -
 indycoveryourheart reblogged this · 8 years ago
indycoveryourheart reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 redamnesiac liked this · 8 years ago
redamnesiac liked this · 8 years ago -
 tsarchaic reblogged this · 8 years ago
tsarchaic reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astcoscsmr liked this · 8 years ago
astcoscsmr liked this · 8 years ago -
 kkiiss-mmeetmrw-blog liked this · 8 years ago
kkiiss-mmeetmrw-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 views100 liked this · 8 years ago
views100 liked this · 8 years ago -
 ohyeaman liked this · 8 years ago
ohyeaman liked this · 8 years ago -
 vinobaroad liked this · 8 years ago
vinobaroad liked this · 8 years ago -
 theperon1709 liked this · 8 years ago
theperon1709 liked this · 8 years ago -
 luckyivleafclover reblogged this · 8 years ago
luckyivleafclover reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 luckyivleafclover liked this · 8 years ago
luckyivleafclover liked this · 8 years ago -
 rgloom liked this · 8 years ago
rgloom liked this · 8 years ago -
 saleih liked this · 8 years ago
saleih liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts