Solar System: Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Almost every day, we receive a message from a spacecraft more than 10.6 billion miles (about 17 billion km) away.
At that unimaginable distance, it takes the radio signal almost 16 hours to arrive. The spacecraft is Voyager 2, which launched 40 years ago this month. It’s still operating, sending back dispatches from the dark reaches well beyond the orbit of Pluto. Even now, scientists are still actively exploring the outer boundaries of the solar system using Voyager 2, decades after its “Grand Tour” of the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune revealed their splendors like never before. This week, we recall 10 highlights from one of the most epic voyages in human history.
1. A Journey of 10 Billion Miles Begins With the First Step

Voyager 2 set out from Earth on Aug. 20, 1977. Even though it launched before its twin spacecraft, Voyager 1, it carried the ‘2’ moniker because mission planners knew its trajectory would bring it to Jupiter after Voyager 1’s arrival there.
2. The Grand Tour
Voyager 2’s trajectory was special because it took advantage of a rare orbital alignment to fly by all four gas giant planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. It was the first, and so far the only, spacecraft to carry out a close-up reconnaissance of Uranus and Neptune.
3. Not-So-Gentle Giant
Voyager 2 flew by Jupiter in April 1979, capturing striking images of the planet’s volcanic moon Io and its violent storms larger than the entire Earth.
4. Saturn’s Not the Only One

Jupiter has its own ring system, and Voyager 2 provided the first pictures.
5. An Ocean Under Ice
During its Jupiter encounter, Voyager 2 obtained close-up looks at Jupiter’s moon Europa, including linear cracks and other features which first led scientists to realize Europa probably hides a vast sea of liquid water beneath an icy shell, the first known world outside Earth that could have an ocean.
6. Ringworld, the Prequel
Voyager 2 zoomed through the Saturn system in August 1981. It saw hints of mysterious features that the Cassini mission would later reveal in stunning detail, including Enceladus, with its bright surface that suggested geologic activity, and Saturn’s intriguing hexagonal jet stream.
7. Swiftly by a Tilted Planet
In January 1984, Voyager offered humanity its first detailed look at the seventh planet, Uranus, the only one tilted on its side relative to the Sun. Voyager images revealed 11 new moons, including Juliet, Puck, Cressida, Rosalind and Ophelia. The moon Miranda presented a bizarre landscape that left scientists debating its origins for years. Voyager also captured views of the planet’s lacy rings, and found that it is the coldest in the solar system, at minus 353 degrees Fahrenheit (59 Kelvin).
8. In Neptune’s Blue Realm

After picking up a gravitational speed boost at each previous planetary encounter, by the time Voyager reached Neptune it shot through the entire system of Neptunian rings and moons in a matter of hours. Voyager saw a titanic storm in Neptune’s windy atmosphere, discovered new moons, and revealed active geysers erupting on Triton’s frigid surface.
9. Postcards From the Edge
Although their cameras are no longer functioning, other key scientific instruments on board both Voyager spacecraft are still collecting data. Voyager 1 is exploring the boundary between the Sun’s realm and interstellar space. Voyager 2 hasn’t traveled quite as far. In September 2007, it crossed the termination shock (where the speed of the solar wind of charged particles drops below the speed of sound) at a point about 84 Astronomical Units from the Sun (more than twice the distance to Pluto). See https://go.nasa.gov/2uwrndb
10. Ride Along
Voyager’s mission is far from over. Engineers estimate the spacecraft will have enough power to operate into the mid-2020s. You can ride along at www.jpl.nasa.gov/voyager, or by following @NASAVoyager on Twitter and by downloading our free 3-D space simulation software, Eyes on the Solar System at eyes.nasa.gov.

One more thing: Inspired by the messages of goodwill carried on Voyager’s Golden Record, you’re invited to send a short, uplifting message to Voyager and all that lies beyond it via social media. With input from the Voyager team and a public vote, one of these messages will be selected for us to beam into interstellar space on Sept. 5, 2017—the 40th anniversary of Voyager 1’s launch. Post your message on social media with the tag #MessageToVoyager by Aug 15. Details: www.jpl.nasa.gov/voyager/message/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Maevetheeuropan and Others
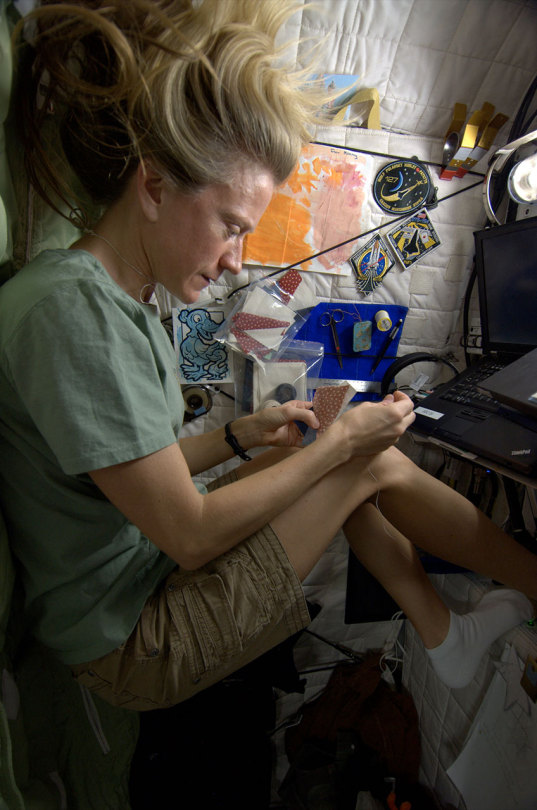


NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg is a self proclaimed crafter. A week ago she made a stuffed dinosaur from scraps on the space station. The little T-rex is made form the lining of Russian food containers and the toy is stuffed with scraps from an old T-shirt. While many toys have flown into space, this is the first produced in space.
Photos: Karen Nyberg, via CollectSpace









this is a massive step forward for renewable energy (x) | follow @the-future-now

What’s hard about Mars?
Mars, unlike the Moon, is far away. It also has an atmosphere - but not a useful one. Atmospheric density, wind, dust storms… all of these things contribute to a larger list of circumstances that any given mission needs to be ready for.
All those circumstances contribute heavily to the cost, time and hard resources needed to be poured into the mission preparation. In addition, the vast distance to Mars means the cost of carrying all this prepared hardware must be covered.
The atmosphere of Mars is such that if you’re going too fast during entry, you’ll burn up. It’s such a low density however that parachutes aren’t tremendously useful.
During the Curiosity rover’s landing it needed a heat shield, a supersonic parachute, rocket boosters to slow it down, a sky-crane to allow Curiosity to drop to the surface like an interplanetary spider and then explosive propulsion to send the platform it dropped from a safe distance away to crash into the surface.
During this landing, the rover experienced a force of about 15 g’s. That force would make a 200 lb man weigh 3000 lbs. Without proper precautions it would make the average head snap down at about 150 to 165 lbs.
NASA’s developing a new type of parachute and it’s being attached to a flying saucer-like spacecraft known as the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator. This is currently hoped to provide NASA with a stable go-to architecture for future Mars missions.
The red planet’s killed most missions sent there. Power for solar-panels on rovers get covered during planet-wide dust storms. Some missions smashed into its moons. Some have smashed into its surface. Others have simply missions the planet entirely only to drift away as Mars dances around the Sun.
The world is an untamed place and has sought to buck all attempts to temper its mysteries.
(Image credit: ESA / DLR / FU Berlin (G. Neukum) / animation by Emily Lakdawalla)
GUYS https://twitter.com/AltNatParkSer/status/824054953404669953 http://www.scientistsmarchonwashington.com/ THE NATIONAL PARK SERVICE IS IN OPEN REBELLION


Spacewalk Friday: Installing a New "Parking Spot" on Station
This Friday, Aug. 19, two U.S. astronauts will install a new gateway for American commercial crew spacecraft at the International Space Station.

Commercial crew flights from Florida’s Space Coast to the International Space Station will restore America’s human spaceflight launch capability and increase the time U.S. crews can dedicate to scientific research.

The adapter being installed (imaged below) was launched on a SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft and arrived on orbit July 20. NASA astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will perform the spacewalk to install the equipment this Friday, Aug. 19. This will be the fourth spacewalk in Williams’ career and the first for Rubins.

Four previous spacewalks…like the one below…helped set the stage for installation of this docking adapter. During those previous spacewalks, other crew members laid hundreds of feet of power and data cables outside the space station.

On Wednesday, the robotics team using the Canadarm2 and its attached “Dextre” manipulator, will reach into the SpaceX Dragon trunk and pull out the docking adapter and position it for Friday’s spacewalk activities.

The morning of the spacewalk, while the astronauts are getting suited up, the robotic arm will position the docking adaptor near the port so that it will be ready for installation.

The two astronauts will venture outside the space station to install the first International Docking Adapter (IDA). This new adapter port will provide a parking space for U.S. Commercial Crew vehicles.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Friday, Aug. 19; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Reaching out into space yields benefits on Earth. Many of these have practical applications — but there’s something more than that. Call it inspiration, perhaps, what photographer Ansel Adams referred to as nature’s “endless prospect of magic and wonder."
Our ongoing exploration of the solar system has yielded more than a few magical images. Why not keep some of them close by to inspire your own explorations? This week, we offer 10 planetary photos suitable for wallpapers on your desktop or phone. Find many more in our galleries. These images were the result of audacious expeditions into deep space; as author Edward Abbey said, "May your trails be crooked, winding, lonesome, dangerous, leading to the most amazing view.”

1. Martian Selfie
This self-portrait of NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover shows the robotic geologist in the “Murray Buttes” area on lower Mount Sharp. Key features on the skyline of this panorama are the dark mesa called “M12” to the left of the rover’s mast and pale, upper Mount Sharp to the right of the mast. The top of M12 stands about 23 feet (7 meters) above the base of the sloping piles of rocks just behind Curiosity. The scene combines approximately 60 images taken by the Mars Hand Lens Imager, or MAHLI, camera at the end of the rover’s robotic arm. Most of the component images were taken on September 17, 2016.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

2. The Colors of Pluto
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft captured this high-resolution, enhanced color view of Pluto on July 14, 2015. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Pluto’s surface sports a remarkable range of subtle colors, enhanced in this view to a rainbow of pale blues, yellows, oranges, and deep reds. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story that scientists have only just begun to decode.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

3. The Day the Earth Smiled
On July 19, 2013, in an event celebrated the world over, our Cassini spacecraft slipped into Saturn’s shadow and turned to image the planet, seven of its moons, its inner rings — and, in the background, our home planet, Earth. This mosaic is special as it marks the third time our home planet was imaged from the outer solar system; the second time it was imaged by Cassini from Saturn’s orbit, the first time ever that inhabitants of Earth were made aware in advance that their photo would be taken from such a great distance.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

4. Looking Back
Before leaving the Pluto system forever, New Horizons turned back to see Pluto backlit by the sun. The small world’s haze layer shows its blue color in this picture. The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn’s moon Titan. The source of both hazes likely involves sunlight-initiated chemical reactions of nitrogen and methane, leading to relatively small, soot-like particles called tholins. This image was generated by combining information from blue, red and near-infrared images to closely replicate the color a human eye would perceive.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

5. Catching Its Own Tail
A huge storm churning through the atmosphere in Saturn’s northern hemisphere overtakes itself as it encircles the planet in this true-color view from Cassini. This picture, captured on February 25, 2011, was taken about 12 weeks after the storm began, and the clouds by this time had formed a tail that wrapped around the planet. The storm is a prodigious source of radio noise, which comes from lightning deep within the planet’s atmosphere.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

6. The Great Red Spot
Another massive storm, this time on Jupiter, as seen in this dramatic close-up by Voyager 1 in 1979. The Great Red Spot is much larger than the entire Earth.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

7. More Stormy Weather
Jupiter is still just as stormy today, as seen in this recent view from NASA’s Juno spacecraft, when it soared directly over Jupiter’s south pole on February 2, 2017, from an altitude of about 62,800 miles (101,000 kilometers) above the cloud tops. From this unique vantage point we see the terminator (where day meets night) cutting across the Jovian south polar region’s restless, marbled atmosphere with the south pole itself approximately in the center of that border. This image was processed by citizen scientist John Landino. This enhanced color version highlights the bright high clouds and numerous meandering oval storms.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

8. X-Ray Vision
X-rays stream off the sun in this image showing observations from by our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, overlaid on a picture taken by our Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The NuSTAR data, seen in green and blue, reveal solar high-energy emission. The high-energy X-rays come from gas heated to above 3 million degrees. The red channel represents ultraviolet light captured by SDO, and shows the presence of lower-temperature material in the solar atmosphere at 1 million degrees.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

9. One Space Robot Photographs Another
This image from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows Victoria crater, near the equator of Mars. The crater is approximately half a mile (800 meters) in diameter. It has a distinctive scalloped shape to its rim, caused by erosion and downhill movement of crater wall material. Since January 2004, the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity has been operating in the region where Victoria crater is found. Five days before this image was taken in October 2006, Opportunity arrived at the rim of the crater after a drive of more than over 5 miles (9 kilometers). The rover can be seen in this image, as a dot at roughly the “ten o'clock” position along the rim of the crater. (You can zoom in on the full-resolution version here.)
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

10. Night Lights
Last, but far from least, is this remarkable new view of our home planet. Last week, we released new global maps of Earth at night, providing the clearest yet composite view of the patterns of human settlement across our planet. This composite image, one of three new full-hemisphere views, provides a view of the Americas at night from the NASA-NOAA Suomi-NPP satellite. The clouds and sun glint — added here for aesthetic effect — are derived from MODIS instrument land surface and cloud cover products.
Full Earth at night map
Americas at night
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Ice is no match for CSU-developed coating
Anyone who’s ever chipped ice off a windshield or nervously watched a plane get de-iced, take note: Colorado State University researchers have invented an ice-repellent coating that out-performs today’s best de-icing products.
Researchers led by Arun Kota, assistant professor of mechanical engineering and biomedical engineering, have created an environmentally friendly, inexpensive, long-lasting coating that could keep everything from cars and ships to planes and power lines ice-free.
Their innovation, described in the Journal of Materials Chemistry, is a gel-based, soft coating made out of PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane), a silicone polymer gel with already widespread industrial use. Their experiments were supported by careful analysis of ice adhesion mechanics.
The performance measure of de-icing coatings is called ice adhesion strength - the shear stress necessary to remove ice from a surface - and is measured in kilopascals (kPa). Kota’s group demonstrated ice adhesion strength for their coating of about 5 kPa. By contrast, soft coatings available on the market have ice adhesion strength of about 40 kPa (lower is better). Other types of de-icing coatings made of rigid materials like Teflon typically perform at around 100 kPa.
Read more.
-
 smallbluelight liked this · 5 years ago
smallbluelight liked this · 5 years ago -
 fairystars liked this · 5 years ago
fairystars liked this · 5 years ago -
 reincarnated2a3cycle liked this · 6 years ago
reincarnated2a3cycle liked this · 6 years ago -
 palesoulvoidathlete-blog liked this · 6 years ago
palesoulvoidathlete-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 oroichonno liked this · 6 years ago
oroichonno liked this · 6 years ago -
 nuckton liked this · 7 years ago
nuckton liked this · 7 years ago -
 fammivolareancora-blog liked this · 7 years ago
fammivolareancora-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 cara-linea reblogged this · 7 years ago
cara-linea reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 reve-noire liked this · 7 years ago
reve-noire liked this · 7 years ago -
 casualwanderess liked this · 7 years ago
casualwanderess liked this · 7 years ago -
 ferociousqueak liked this · 7 years ago
ferociousqueak liked this · 7 years ago -
 october-faye liked this · 7 years ago
october-faye liked this · 7 years ago -
 fourthage reblogged this · 7 years ago
fourthage reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 anmin-mesimu-blog liked this · 7 years ago
anmin-mesimu-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 xd-1691-blog liked this · 7 years ago
xd-1691-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 bymulaer liked this · 7 years ago
bymulaer liked this · 7 years ago -
 aaronstjames liked this · 7 years ago
aaronstjames liked this · 7 years ago -
 afrodita-niculescu-blog liked this · 7 years ago
afrodita-niculescu-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 alone-in-my-little-infinity liked this · 7 years ago
alone-in-my-little-infinity liked this · 7 years ago -
 sylvermyth reblogged this · 7 years ago
sylvermyth reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 streamsofsound liked this · 7 years ago
streamsofsound liked this · 7 years ago -
 lxlteo liked this · 7 years ago
lxlteo liked this · 7 years ago -
 levitatingcoffin liked this · 7 years ago
levitatingcoffin liked this · 7 years ago

