When Anne Carson Said “what Are We Made Of But Hunger And Rage?” And When Anne Carson Said “i
when anne carson said “what are we made of but hunger and rage?” and when anne carson said “i do not want to be a person. i want to be unbearable.” and when anne carson said “i am talking about evil. it blooms. it eats. it grins.” and when anne carson said “revenge is a form of desire.” and when anne carson said “to feel anything deranges you.” and when anne carson said “why does tragedy exist? because you are full of rage. why are you full of rage? because you are full of grief.” and when anne carson said
More Posts from Lrs35 and Others
The Two Types of Pacing
Pacing is a tricky, tricky thing. Hopefully, by breaking it down into two schools of thought, we can better our understanding of maintaining effective pacing.
as requested by @whisperinghallwaysofmirrors
First, Some Definitions
According to Writer’s Digest, narrative pacing is “a tool that controls the speed and rhythm at which a story is told… [H]ow fast or slow events in a piece unfold and how much time elapses in a scene or story.“
Pacing can be a lot of things. Slow, fast, suspenseful, meandering, boring, exciting, et cetera et cetera. While we don’t want meandering or boring, getting it to be the other things can be a feat.
As I go through all of this, I would like to say that the number one thing you should be keeping in mind with the pacing of your story is the purpose.
What is the purpose of this story, scene, dialogue, action, arc, plot point, chapter, et al? This and only this will keep you on track the whole way through.
Without further ado, here are the two types of pacing…
Micro Pacing
This, to me, is the harder of the two. Macro pacing usually comes naturally with our understanding of overall story structure that we see in books and movies. Micro is much more subjective and labor-intensive.
The first step of every scene you write is to identify what kind of pacing it needs to be effective. Is a slower pace going to nail in the emotional tone? Is a faster pace going to convey how urgent the scene is? Is choppy going to show how chaotic it is? How much attention to detail is needed? Et cetera. And even with the scene’s tone, there are also tones within with action, dialogue, and narrator perception.
There is no one-size-fits-all trick to mastering pacing. All you can do is try to keep it in mind as you draft. Don’t let it consume you, though. Just get it down. After drafting, look at the pacing with a critical eye. Do important scenes go too fast? Are unnecessary things being dragged out? Is this scene too detailed to be suspenseful?
A lot of errors in pacing are quick fixes. The adding or removal of details, shortening or lengthening of sentences, changing descriptions. However, these quick fixes do take a while when you have to look at every single scene in a story.
Macro Pacing
Rather than the contents of a scene, this deals with everything larger. Scenes, chapters, plot points, storylines, subplots, and arcs. This is taking a look at how they all work for each other when pieced together.
One of the biggest resources when it comes to analyzing macro pacing is story structure philosophy. The common examples are Freytag’s Pyramid, the 3-Act Structure, Hero’s Journey, and Blake Snyder’s 15 Beats. They follow the traditional story structure. Exposition, catalyst, rising action, climax, and resolution (albeit each in different terms and specificity). Though some see it as “cookie-cutter”, 99% of effective stories follow these formats at a considerable capacity. It’s not always about how the story is told, but rather who tells it. But I digress.
Looking at these structures, we can begin to see how the tried-and-true set-up is centered around effective pacing.
The beginning, where everything is set up, is slower but short and sweet. The catalyst happens early and our MC is sent out on a journey or quest whether they like it or not. The trek to a climax is a tricky stage for maintaining effective pacing. Good stories fluctuate between fast and slow. There is enough to keep it exciting, but we’re given breaks to stop and examine the finer details like theme, characterization, and arcs.
The edge before the climax is typically when the action keeps coming and we’re no longer given breaks. The suspense grabs us and doesn’t let go. This is the suspense that effectively amounts to the crescendo and leads to the emotional payoff and release that follows in the resolution. The resolution is nothing BUT a break, or a breather if you will. Though it is slower like the exposition, it is longer than that because this is where we wrap everything up for total closure. This is what the reader needs, rather than what they want. So you can take your time.
Not every story has to follow this recipe step-by-step. Critically acclaimed movies such as Pulp Fiction, Frances Ha, and Inside Llewyn Davis* break the traditional structure. However, they still keep certain ingredients in it. Whether it be the concept of a climax, the idea of a journey, or the overall balance of tension and release.
If you’re struggling with the macro side of your story’s pacing, I would try to identify what the weakest areas are and see if applying these story structure concepts and methodology strengthens it at all. If not, it may be that your story idea doesn’t fit the “substance” requirement of an 80k+ word novel. It may need more or fewer subplots or an increase of conflict or more things getting in the MC’s way. You could also see if adapting it to a shorter medium (novella, et al) or a longer medium (series, episodics, et al) would alleviate the pacing issues.
*sorry all my references are movies and not books, but I’ve seen more movies than I’ve read books
In Short–
Pacing, both macro and micro, are incredibly subjective concepts. The only way to really find out how effective your story’s pacing is, is to look at it through the lens of traditional structures and ask for feedback from beta readers. How a reader,who doesn’t know the whole story like you do feels about pacing is the best resource you could have.
How to learn a language when you don’t know where to start:
General Plan:
Weeks 1 and 2: Purpose:
Learn the fundamentals sentence construction
Learn how to spell and count
Start building a phrase stockpile with basic greetings
The Alphabet
Numbers 1 - 100
Subject Pronouns
Common Greetings
Conjugate the Two Most Important Verbs: to be and to have
Basic Definite and Indefinite Articles
Weeks 3 and 4: Purpose:
Learn essential vocabulary for the day-to-day
Start conjugating regular verbs
Days of the Week and Months of the Year
How to tell the time
How to talk about the weather
Family Vocabulary
Present Tense Conjugations Verbs
Weeks 5 and 6: Purpose:
Warm up with the last of the day-to-day vocabulary
Add more complex types of sentences to your grammar
Colours
House vocabulary
How to ask questions
Present Tense Conjugations Verbs
Forming negatives
Weeks 7 and 8: Purpose:
Learn how to navigate basic situations in a region of your target language country
Finish memorising regular conjugation rules
Food Vocabulary and Ordering at Restaurants
Money and Shopping Phrases
Present Tense Conjugations Verbs
Weeks 9 and 10: Purpose:
Start constructing descriptive and more complex sentences
Adjectives
Reflective verbs
Places vocabulary
Weeks 11 and 12: Purpose:
Add more complex descriptions to your sentences with adverbs
Wrap up vocabulary essentials
Adverbs
Parts of the body and medical vocabulary
Tips for Learning a Foreign Language:
Learning Vocabulary:
What vocabulary should I be learning?
There are hundreds of thousands of words in every language, and the large majority of them won’t be immediately relevant to you when you’re starting out.Typically, the most frequent 3000 words make up 90% of the language that a native speaker uses on any given day. Instead try to learn the most useful words in a language, and then expand outwards from there according to your needs and interests.
Choose the words you want/need to learn.
Relate them to what you already know.
Review them until they’ve reached your long-term memory.
Record them so learning is never lost.
Use them in meaningful human conversation and communication.
How should I record the vocabulary?
Learners need to see and/or hear a new word of phrase 6 to 17 times before they really know a piece of vocabulary.
Keep a careful record of new vocabulary.
Record the vocabulary in a way that is helpful to you and will ensure that you will practice the vocabulary, e.g. flashcards.
Vocabulary should be organised so that words are easier to find, e.g. alphabetically or according to topic.
Ideally when noting vocabulary you should write down not only the meaning, but the grammatical class, and example in a sentence, and where needed information about structure.
How should I practice using the vocabulary?
Look, Say, Cover, Write and Check - Use this method for learning and remembering vocabulary. This method is really good for learning spellings.
Make flashcards. Write the vocabulary on the front with the definition and examples on the back.
Draw mind maps or make visual representations of the new vocabulary groups.
Stick labels or post it notes on corresponding objects, e.g when learning kitchen vocabulary you could label items in your house.
How often should I be practising vocabulary?
A valuable technique is ‘the principle of expanding rehearsal’. This means reviewing vocabulary shortly after first learning them then at increasingly longer intervals.
Ideally, words should be reviewed:
5-10 minutes later
24 hours later
One week later
1-2 months later
6 months later
Knowing a vocabulary item well enough to use it productively means knowing:
Its written and spoken forms (spelling and pronunciation).
Its grammatical category and other grammatical information
Related words and word families, e.g. adjective, adverb, verb, noun.
Common collocations (Words that often come before or after it).
Receptive Skills: Listening and Reading
Reading is probably one of the most effective ways of building vocabulary knowledge.
Listening is also important because it occupies a big chunk of the time we spend communicating.
Tips for reading in a foreign language:
Start basic and small. Children’s books are great practice for beginners. Don’t try to dive into a novel or newspaper too early, since it can be discouraging and time consuming if you have to look up every other word.
Read things you’ve already read in your native language. The fact that you at least know the gist of the story will help you to pick up context clues, learn new vocabulary and grammatical constructions.
Read books with their accompanying audio books. Reading a book while listening to the accompanying audio will improve your “ear training”. It will also help you to learn the pronunciation of words.
Tips for listening in a foreign language:
Watch films in your target language.
Read a book while also listening along to the audio book version.
Listen to the radio in your target language.
Watch videos online in your target language.
Activities to do to show that you’ve understood what you’ve been listening to:
Try drawing a picture of what was said.
Ask yourself some questions about it and try to answer them.
Provide a summary of what was said.
Suggest what might come next in the “story.”
Translate what was said into another language.
“Talk back” to the speaker to engage in imaginary conversation.
Productive Skills: Speaking and Writing
Tips for speaking in a foreign language:
If you can, try to speak the language every day either out loud to yourself or chat to another native speaker whether it is a colleague, a friend, a tutor or a language exchange partner.
Write a list of topics and think about what you could say about each one. First you could write out your thoughts and then read them out loud. Look up the words you don’t know. You could also come up with questions at the end to ask someone else.
A really good way to improve your own speaking is to listen to how native speakers talk and imitate their accent, their rhythm of speech and tone of voice. Watch how their lips move and pay attention to the stressed sounds. You could watch interviews on YouTube or online news websites and pause every so often to copy what you have just heard. You could even sing along to songs sung in the target language.
Walk around the house and describe what you say. Say what you like or dislike about the room or the furniture or the decor. Talk about what you want to change.This gets you to practise every day vocabulary.
Tips for writing in a foreign language:
Practice writing in your target language. Keep it simple to start with. Beginner vocabulary and grammar concepts are generally very descriptive and concrete.
Practice writing by hand. Here are some things you can write out by hand:
Diary entries
Shopping lists
Reminders
What could I write about?
Write about your day, an interesting event, how you’re feeling, or what you’re thinking.
Make up a conversation between two people.
Write a letter to a friend, yourself, or a celebrity. You don’t need to send it; just writing it will be helpful.
Translate a text you’ve written in your native language into your foreign language.
Write a review or a book you’ve recently read or a film you’ve recently watched.
Write Facebook statuses, Tweets or Tumblr posts (whether you post them or not will be up to you).
Write a short story or poem.
Writing is one of the hardest things to do well as a non-native speaker of a language, because there’s no room to hide.
There are lots of ways to improve your writing ability, but they can be essentially boiled down to three key components:
Read a lot
Write a lot
Get your writing corrected





Animator Eric Larson uses two puppies as reference while he sketches scenes for Walt Disney's "One Hundred and One Dalmatians". 1960
ANATOMY STUDY GUIDE 101

So studying anatomy is nothing like any other topic, especially when you study it at uni level, where they expect you to know every single small component of the body! So this guide is going to be concerning the musculoskeletal system and the nerves (PNS) and arteries in the body.
I have mentioned some of these tips before but I will put them in here aswell and so this can work as sort of masterpost. This is like a more “overall” type of masterpost. So if you want to have topic specific posts for example for nerves and arteries then let me know.
1. Find a study partner. First and foremost anatomy is so much easier when you are two dealing with it. Me and my study partner used to do anatomy spots together and by doing it two people together you can discuss what it could possibly be. You get to hear their train of thoughts which sometimes can be better than yours. Also you will have someone to quiz you and correct you when you say something wrong.
2. Accept that it takes time. First step to learning anatomy is dedicating a lot of time. It is not easy, you are cramming so much information into your mind and for it to stay there you will have to go over the same topic again and again and again. And I know it is really frustrating and you are going to spent maybe 10 hours trying to figure out the muscles of the leg and then next week when you review it again it will feel like a whole new topic, but this is all a part of the proces, just keep revising again and again and again.
3. The Atlas is your best friend. Invest in a good atlas, they are a little expensive but they work wonders because first of all they give you an image of what you study. And usually the text book images are not enough. In an atlas you will have “isolated” images but you will also have images where relations are shown. HOWEVER if you dont want to buy an actual atlas then maybe buy Complete anatomy which is a computer program that I also reffered to in my “5 sites every med student should know about” post. Here you can play around with the structures, view it from different angles and add on to it with other nearby structures or remove structures.
4. Say it out loud. Pretty self explanatory.
5. Create an overview. Rather than focusing on the details try to focus on creating an overview. Anatomy is already so difficult so dont complicate things for yourself. And if you know the basics then learning the details will be so much easier.
6. Use a whiteboard. Speaking of creating an overview, try using a white board for this. It is such a good way for creating an overview. I think because deleting and writing is so easy it kinda makes it less stressful than writing in a note book where ofcourse you worry about the aesthetic. Also try to do this with your study partner. You can plan on studying a topic together so lets say for example the muscles of the leg, you both at home study it, try to memorize it, look at it in an atlas and then you two meet. Now when you meet you get infront of a white board and start talking and writing about what you guys think is important and when you guys cant go any further then grab your notes and then add more on to the board.
7. MAKE IT VISUAL!. This is the most important step! Use bones, pay attention in your dissection classes, if you have the upportunity to touch, feel and look at structures then DO IT! This is the best way to learn. Spot as often as you can.
8. Make up rules. you can find a lot of them online, or just make some up yourself, me and my study partner did, for example the muscles M. erector spinae: I (m. iliocostalis) Like (m. longissimus) Standing (m. spinalis). If you turn it into a “game” then remembering it will be much easier.
And most importantly dont stress your mind that much. Allow yourself to take breaks, because over feeding your mind with knowledge in a short period of time can also be very damaging since you will waste time and not remember most of what you studied.
Good luck, stay motivated and stay dedicated
Love
Dunia
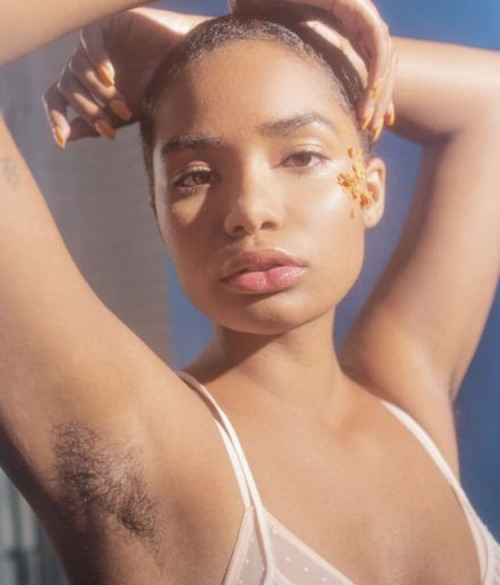
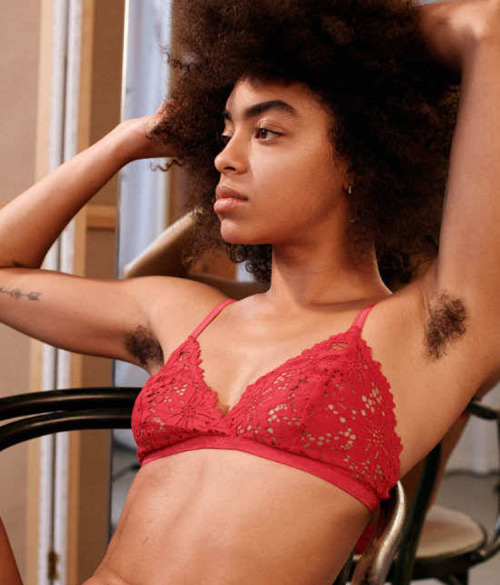
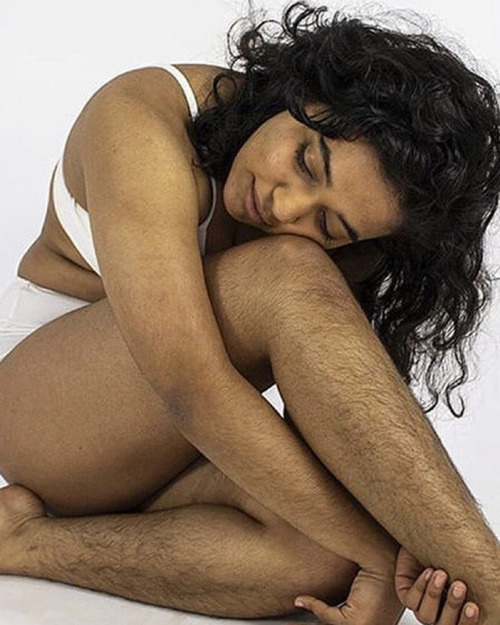
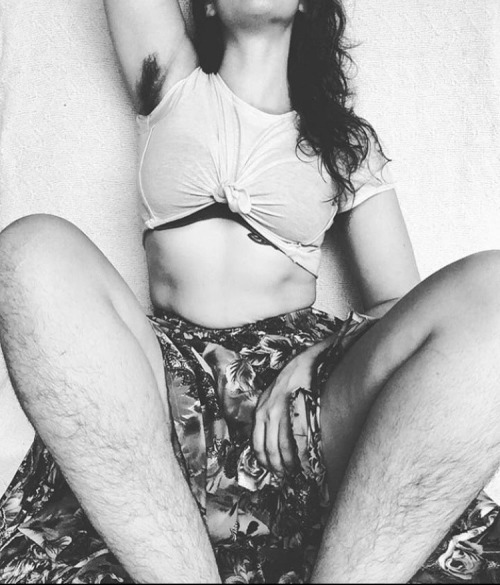
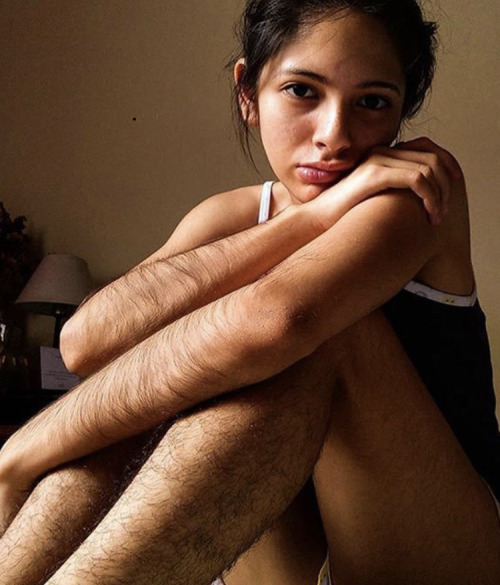
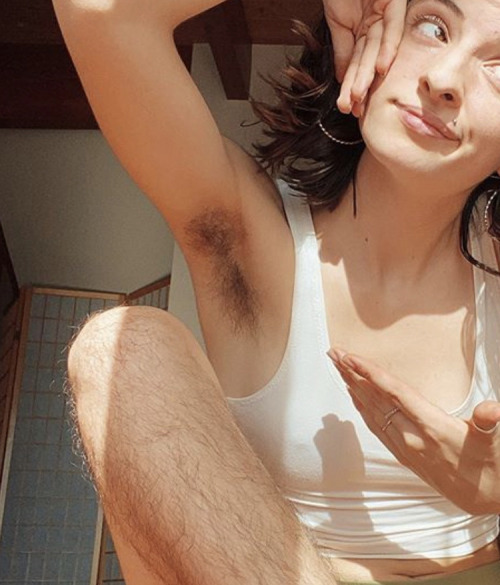
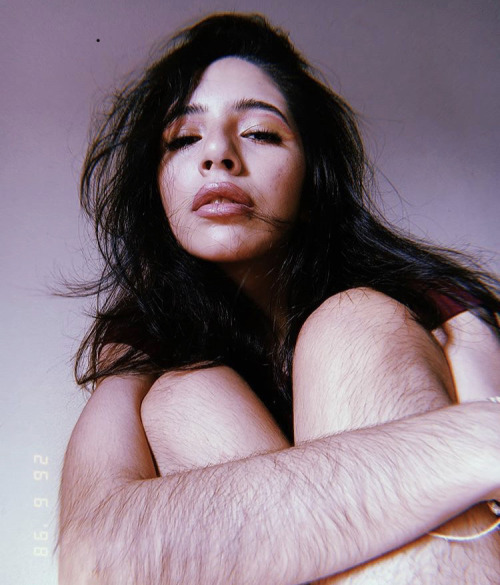
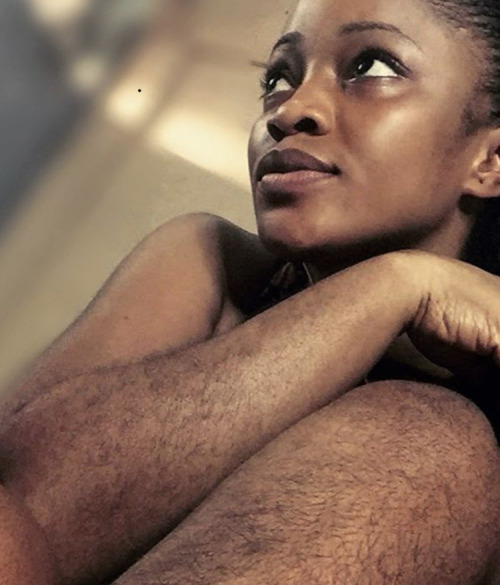


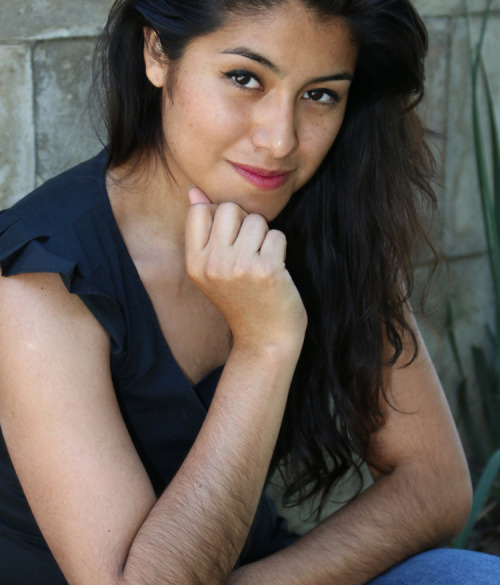






body hair appreciation post
poems about the moon 🌒
Worm Moon by Mary Oliver
Moon Song by Roy Ivan Johnson
To Catch the Moon by Chong Bum Kim
Morning Song by Sara Teasdale
Not The Moon by Margaret Atwood
Everyone Is Asleep by Enomoto Seifu-jo
The Sweetness of Dogs by Mary Oliver
The Moon Looked Into My Window by E. E. Cummings
Dear Moon by Warsan Shire
The Poet Of Ignorance by Anne Sexton
Owl and Pussycat, Some Years Later by Margaret Atwood
Will You Come? by Edward Thomas
If My Hands Could Peel by Federico García Lorca
Days Of Kindness by Leonard Cohen
The Moonlight by Noah Buchholz
The Moon was But a Chin of Gold by Emily Dickinson
What We Have by Warsan Shire
buy me a coffee





Caddo Lake, Texas by Fred R Cox

-
 hkhyuk liked this · 3 weeks ago
hkhyuk liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 patronsaintofvastnpreciouslosers liked this · 1 month ago
patronsaintofvastnpreciouslosers liked this · 1 month ago -
 lesbillusion reblogged this · 1 month ago
lesbillusion reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 voidlocket liked this · 2 months ago
voidlocket liked this · 2 months ago -
 xtrasluttyoliveoil reblogged this · 2 months ago
xtrasluttyoliveoil reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 dilvrgal liked this · 2 months ago
dilvrgal liked this · 2 months ago -
 bl1ssfulelleon liked this · 2 months ago
bl1ssfulelleon liked this · 2 months ago -
 dread-full reblogged this · 2 months ago
dread-full reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ghohl reblogged this · 3 months ago
ghohl reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ghohl liked this · 3 months ago
ghohl liked this · 3 months ago -
 lesyeuxdemeduse reblogged this · 3 months ago
lesyeuxdemeduse reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 fruitsenthusiast liked this · 3 months ago
fruitsenthusiast liked this · 3 months ago -
 revcntulet liked this · 4 months ago
revcntulet liked this · 4 months ago -
 sakurz reblogged this · 4 months ago
sakurz reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 hoods-in-the-wood reblogged this · 4 months ago
hoods-in-the-wood reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 sighing-is-a-song liked this · 5 months ago
sighing-is-a-song liked this · 5 months ago -
 fallintothestars reblogged this · 5 months ago
fallintothestars reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 asmolvaporeon liked this · 6 months ago
asmolvaporeon liked this · 6 months ago -
 libraryofrefshelp reblogged this · 6 months ago
libraryofrefshelp reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 skinnygirlzbleedflowers reblogged this · 6 months ago
skinnygirlzbleedflowers reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 gaymenschemistry reblogged this · 7 months ago
gaymenschemistry reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 keresthecursed liked this · 8 months ago
keresthecursed liked this · 8 months ago -
 snowberriesromanoff reblogged this · 8 months ago
snowberriesromanoff reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 chronologiesofwater reblogged this · 8 months ago
chronologiesofwater reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 cysm reblogged this · 8 months ago
cysm reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 hy2ka liked this · 8 months ago
hy2ka liked this · 8 months ago -
 pinkieroy reblogged this · 8 months ago
pinkieroy reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 pinkieroy liked this · 8 months ago
pinkieroy liked this · 8 months ago -
 raffaella-cerullo liked this · 8 months ago
raffaella-cerullo liked this · 8 months ago -
 veilguards reblogged this · 8 months ago
veilguards reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 livmondcole reblogged this · 8 months ago
livmondcole reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 veilguards liked this · 8 months ago
veilguards liked this · 8 months ago -
 redrosesandcharmingsouls reblogged this · 8 months ago
redrosesandcharmingsouls reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 redrosesandcharmingsouls liked this · 8 months ago
redrosesandcharmingsouls liked this · 8 months ago -
 coin-op-rusalka liked this · 8 months ago
coin-op-rusalka liked this · 8 months ago -
 applewoodvalley liked this · 9 months ago
applewoodvalley liked this · 9 months ago -
 idkmansmth liked this · 9 months ago
idkmansmth liked this · 9 months ago -
 bundledwaters reblogged this · 9 months ago
bundledwaters reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 shiv--roy reblogged this · 9 months ago
shiv--roy reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 bluestockingbaby liked this · 9 months ago
bluestockingbaby liked this · 9 months ago -
 orla-mccoolgirl reblogged this · 9 months ago
orla-mccoolgirl reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 teefsies reblogged this · 10 months ago
teefsies reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 fromirkwood liked this · 10 months ago
fromirkwood liked this · 10 months ago -
 klavieren reblogged this · 10 months ago
klavieren reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 wordsandliterature reblogged this · 10 months ago
wordsandliterature reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 reallifefandom reblogged this · 10 months ago
reallifefandom reblogged this · 10 months ago




