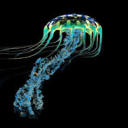
Marrus Orthocanna

Marrus orthocanna
Marrus orthocanna is a deep sea siphonophore found at depths between 400m to 2200m. It has a colony of gas-filled zooids on the top used for locomotion. It also has a long, bright orange tentacles on the bottom. Marrus orthocanna are viscous predators and consume small crustceans and copepods.
Photo credit: http://www.arcodiv.org/watercolumn/cnidarian/Marrus_orthocanna.html
More Posts from Bioluminescentoceangoddess and Others


Pacific Viperfish
Chauliodus macouni
The Pacific Viperfish looks intimidating with its sharp, pointy teeth and large jaws. However, its body is small and elongated. It can be found at depths ranging from 250m to 4390m. The Pacific Viperfish long teeth are an unique adaptation designed to keep prey trapped, but it is dangerously close to its eyes. There have been instances when they have caught prey that are too large to swallow and it dies along with its last meal. The Pacific Viper also has photophores along its body and a light organ near its dorsal fin. These organs exhibit bioluminescence and help with attracting pray: as well as, communicating with mates and confuse predators. It is one of the most ferocious predators of the deep ocean.
Photo credit: https://www.science-rumors.com/top-20-pacific-viperfish-facts-to-know-what-this-creature-is/
https://goldfisho.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-viperfish/

Glasshead Grenadier
Hymenocephalus italicus
The Glasshead Grenadier is a small deep sea fish named due to a transparent memberane that covers its head. It has fragile head bones, and it feeds on surface copepods and crustaceans. This fish is located between 100 m to 2000 m in the ocean.
Photo credit: https://www.fishbase.se/summary/1720
https://www.futura-sciences.com/planete/photos/oceanographie-abysses-ces-merveilles-profondeurs-40-photos-686/ocean-grenadier-vitrier-hymenocephalus-italicus-poisson-abysses-4541/


Blacksnout Seasnail
Paralipparis copei copei
The Blacksnout Seasnail may not look like a snail, but it does have a slimy, gelatinous substance that covers its body. It can be found at depths between 200 m to 1692 m, and adults grow up to be 17 cm in size (approximately 6.5 in). It also has an elongated body that resembles an eel. Furthermore, it can be seen rolling itself in a loop; this behavior is a defensive posture that makes it appear like a jelly. In the darkness, predators tend to avoid the Blacksnout Seasnail because its often mistaken as a hunter due to its appearance and behavior.
Sea sparkle is a common, bioluminescent plankton. Even though its not an animal, it is worth sharing.


Sea sparkle
Noctiluca scintillans
Sea sparkle is a bioluminescent dinoflagellate that blooms in many coastal waters. Sea sparkle feeds on plankton, diatoms, fish eggs, and other dinoflagellates. It also has a flagellum, or tiny tail, that helps it move around in the water. Even though sea sparkle is beautiful to witness at night, it is hazardous to other marine species and resembles a reddish-pink film during the day.
Photo credit:
https://alexandrathemb.tumblr.com/post/49814932878/noctilucas-scintillans-a-bioluminescent
https://thevelv.blogspot.com/2015/07/noctiluca-scintillans.html

Crystal Jellyfish
Aequorea victoria
The Crystal Jellyfish is a graceful, transparent jellyfish with long, thin tentacles. It has bioluminescent organs around it bell that produce a bright, green light. It tends to consume small copepods, but it has the ability to swallow other jellyfish half its size. Furthermore, this jelly is used in biological experiments to detect calcium.
Photo credit: https://www.montereybayaquarium.org/animals/animals-a-to-z/crystal-jelly
https://fineartamerica.com/featured/5-aequorea-crystal-jellyfish-with-amphipods-alexander-semenovscience-photo-library.html

Threadfin Snailfish
Careproctus longifilis
The Threadfin Snailfish resembles a prehistoric tadpole that is ghostly white. The holes in its face are large sensory pores that help them detect changes in the ocean. It is often found at depths between 1900 to 2997 meters.
Photo credit: https://www.timeout.com/singapore/museums/creatures-of-the-deep





Wake up babe new fish dropped


Sea elephant
Carinaria japonica
The Sea Elephant is a translucent sea snail that has a large muscular body and a tiny triangular shell. Its foot is used for crawling on the ground, and it can be transformed into a fin that is used for swimming. It is called the “sea elephant” because it has a small trunk in its mouth that is used to swallow prey. Furthermore, the Sea Elephant eats arrow worms and jellies.
Photo credit
https://bodegahead.blogspot.com/2014/12/carinaria-part-2.html
http://tolweb.org/Carinaria_japonica/28750



Black Dragonfish
Idiacanthus atlanticus
The Black Dragonfish are needle-like fish that migrate between 500m and 2000m in the deep ocean. Females are black with 6 stripes and lack a barbel, pelvic fins, and sharp teeth. Males, on the other hand, are dark brown and have a barbel, which is the light producing structure on its chin. Furthermore, it uses bioluminescence to detect prey instead of lure prey.
Photo credit: https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-learn-secrets-from-ultra-black-skin-that-allows-deep-sea-fish-to-lurk-unseen/
https://steemit.com/life/@munnashah/the-most-terrible-and-surprising-7-animals-of-the-sea
https://knowyourmeme.com/photos/995601-thalassophobia

Glass Octopus
Vitreledonella richardi
The Glass Octopus spend its entire life in the midwater section of the ocean and found at depths between 200m to 2000m. Even though it has no protection from predators, it achieves perfect transparency. The only part of the Glass Octopus that is visible is its digestive gland. However, the digestive gland is placed vertically to minimize detection. In addition, I find this octopus to be super cute!
Photo credit: https://www.mynumer.com/forums/topic/499/invisible-animals/view/post_id/859
-
 mycellpics liked this · 1 year ago
mycellpics liked this · 1 year ago -
 zenidogsworld liked this · 1 year ago
zenidogsworld liked this · 1 year ago -
 stardustandmoonflowers liked this · 1 year ago
stardustandmoonflowers liked this · 1 year ago -
 qta reblogged this · 2 years ago
qta reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 qta liked this · 2 years ago
qta liked this · 2 years ago -
 martian-marco reblogged this · 2 years ago
martian-marco reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 martian-marco liked this · 2 years ago
martian-marco liked this · 2 years ago -
 thirdtechnician liked this · 2 years ago
thirdtechnician liked this · 2 years ago -
 psulphuratus liked this · 2 years ago
psulphuratus liked this · 2 years ago -
 eggmixercortex reblogged this · 2 years ago
eggmixercortex reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 moondazie liked this · 2 years ago
moondazie liked this · 2 years ago -
 saltmatchescandlewax reblogged this · 2 years ago
saltmatchescandlewax reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 milliganopen liked this · 2 years ago
milliganopen liked this · 2 years ago -
 froakie7244 reblogged this · 2 years ago
froakie7244 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 froakie7244 liked this · 2 years ago
froakie7244 liked this · 2 years ago -
 graveyard-lagomorph liked this · 2 years ago
graveyard-lagomorph liked this · 2 years ago -
 booklover1323 reblogged this · 2 years ago
booklover1323 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 booklover1323 liked this · 2 years ago
booklover1323 liked this · 2 years ago -
 mysticalclamfishopera liked this · 2 years ago
mysticalclamfishopera liked this · 2 years ago -
 goth-slush reblogged this · 2 years ago
goth-slush reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 goth-slush liked this · 2 years ago
goth-slush liked this · 2 years ago -
 imjustvibingyaknow reblogged this · 2 years ago
imjustvibingyaknow reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 imjustvibingyaknow liked this · 2 years ago
imjustvibingyaknow liked this · 2 years ago -
 anemonether liked this · 2 years ago
anemonether liked this · 2 years ago -
 natanilik reblogged this · 2 years ago
natanilik reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 running-with-batfam liked this · 2 years ago
running-with-batfam liked this · 2 years ago -
 anony-mouse-writer reblogged this · 2 years ago
anony-mouse-writer reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 anony-mouse-writer liked this · 2 years ago
anony-mouse-writer liked this · 2 years ago -
 age-of-arcanum liked this · 2 years ago
age-of-arcanum liked this · 2 years ago -
 senshilegionnaire liked this · 2 years ago
senshilegionnaire liked this · 2 years ago -
 senshilegionnaire reblogged this · 2 years ago
senshilegionnaire reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 inanotherhappylifemaybe liked this · 3 years ago
inanotherhappylifemaybe liked this · 3 years ago -
 amethysthorizon reblogged this · 3 years ago
amethysthorizon reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 wayti-blog liked this · 3 years ago
wayti-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 redwolf1999 liked this · 3 years ago
redwolf1999 liked this · 3 years ago -
 aganatis liked this · 3 years ago
aganatis liked this · 3 years ago -
 battlemage94 liked this · 3 years ago
battlemage94 liked this · 3 years ago -
 chopped-peace-collection liked this · 3 years ago
chopped-peace-collection liked this · 3 years ago -
 sothatidostuff reblogged this · 3 years ago
sothatidostuff reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 algaejay liked this · 3 years ago
algaejay liked this · 3 years ago -
 cum--brulee liked this · 3 years ago
cum--brulee liked this · 3 years ago -
 snickeringdragon reblogged this · 3 years ago
snickeringdragon reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 snickeringdragon liked this · 3 years ago
snickeringdragon liked this · 3 years ago -
 ccprovolomies reblogged this · 3 years ago
ccprovolomies reblogged this · 3 years ago
Bioluminescence is a chemical reaction that produces light. Many deep sea animals use bioluminescence. This blog is dedicated to educating the public about the amazing creatures that thrive in the deep sea.
57 posts